
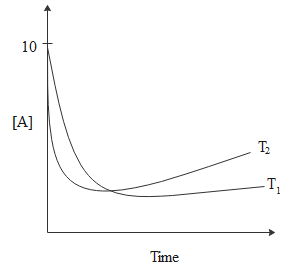
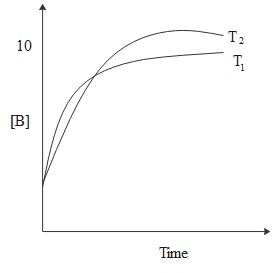
For a reaction, $A \rightleftharpoons P$, the plots of $\left[ A \right]$ and $\left[ P \right]$ with time at temperature ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$ are given below. If ${T_2} > {T_1}$, the correct statement(s) is/are:
(Assume $\Delta {H^\theta }$ and $\Delta {S^\theta }$ are independent of temperature and ratio of $\ln K$ at ${T_1}$ and $\ln K$ at ${T_2}$ is greater than $\dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$. Here, $H,S,G$ and $K$ are enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs energy and equilibrium constant, respectively.)
A.$\Delta {H^\theta } < 0,\Delta {S^\theta } < 0$
B.$\Delta {H^\theta } > 0,\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$
C.$\Delta {S^\theta } < 0,\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$
D.$\Delta {S^\theta } > 0,\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$


Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, you must recall the relation between the Gibbs free energy and equilibrium constant of a reaction. Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that is used to calculate the maximum work that can be performed by a system at a constant pressure and temperature.
Formula used:
$\Delta {G^\theta } = - RT\ln {K_{eq}}$
Where, $\Delta {G^\theta }$ is the change in free energy of reaction, ${K_{eq}}$ is the equilibrium constant of the reaction, $R$ is the gas constant and $T$ is the temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction,$A \rightleftharpoons P$
From the graph, we can see that at equilibrium $\left[ A \right] < 5$ and $\left[ P \right] > 5$.
Thus, we can write the equilibrium constant as, ${K_{eq}} = \dfrac{{\left[ A \right]}}{{\left[ P \right]}} > 1$.
Since $\Delta {G^\theta } = - RT\ln {K_{eq}}$, we can say that,$\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$.
We are given in the question that ${T_2} > {T_1}$.
From this we can infer, that,$\dfrac{{\ln {K_{{T_1}}}}}{{\ln {K_{{T_2}}}}} > \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}} > 1$
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{K_{{T_1}}}}}{{{K_{{T_2}}}}} > 1 \\
\Rightarrow {K_{{T_2}}} < {K_{{T_1}}} \\
$
This implies that the given reaction is exothermic which means that the change in enthalpy of the reaction will be zero.
$\Delta {H^\theta } < 0$
Also, we know that,
$
\Delta {G^\theta } = \Delta {H^\theta } - T\Delta {S^\theta } \\
\Rightarrow \Delta {S^\theta } = \dfrac{{\Delta {H^\theta } - \Delta {G^\theta }}}{T} \\
$
Since $\Delta {H^\theta } < 0$ and $\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$, it is necessary for the change in entropy to be negative; $\Delta {S^\theta } < 0$.
Therefore, the correct options are A and C.
Note:
The importance of the Gibbs function is that it is the single master variable that can determine whether a certain chemical change is thermodynamically possible. If the free energy of the reactants is greater than that of the products the reaction takes place spontaneously. $\Delta {G^\theta }$ is a key quantity in determining whether a reaction will take place in a given direction or not. For most reactions taking place in solutions or gaseous mixtures, the value of $\Delta {G^\theta }$ depends on the proportions of the various reaction components in the mixture; it is not a simple sum of the "products minus reactants" type, as is the case with $\Delta {H^\theta }$.
Formula used:
$\Delta {G^\theta } = - RT\ln {K_{eq}}$
Where, $\Delta {G^\theta }$ is the change in free energy of reaction, ${K_{eq}}$ is the equilibrium constant of the reaction, $R$ is the gas constant and $T$ is the temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction,$A \rightleftharpoons P$
From the graph, we can see that at equilibrium $\left[ A \right] < 5$ and $\left[ P \right] > 5$.
Thus, we can write the equilibrium constant as, ${K_{eq}} = \dfrac{{\left[ A \right]}}{{\left[ P \right]}} > 1$.
Since $\Delta {G^\theta } = - RT\ln {K_{eq}}$, we can say that,$\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$.
We are given in the question that ${T_2} > {T_1}$.
From this we can infer, that,$\dfrac{{\ln {K_{{T_1}}}}}{{\ln {K_{{T_2}}}}} > \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}} > 1$
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{K_{{T_1}}}}}{{{K_{{T_2}}}}} > 1 \\
\Rightarrow {K_{{T_2}}} < {K_{{T_1}}} \\
$
This implies that the given reaction is exothermic which means that the change in enthalpy of the reaction will be zero.
$\Delta {H^\theta } < 0$
Also, we know that,
$
\Delta {G^\theta } = \Delta {H^\theta } - T\Delta {S^\theta } \\
\Rightarrow \Delta {S^\theta } = \dfrac{{\Delta {H^\theta } - \Delta {G^\theta }}}{T} \\
$
Since $\Delta {H^\theta } < 0$ and $\Delta {G^\theta } < 0$, it is necessary for the change in entropy to be negative; $\Delta {S^\theta } < 0$.
Therefore, the correct options are A and C.
Note:
The importance of the Gibbs function is that it is the single master variable that can determine whether a certain chemical change is thermodynamically possible. If the free energy of the reactants is greater than that of the products the reaction takes place spontaneously. $\Delta {G^\theta }$ is a key quantity in determining whether a reaction will take place in a given direction or not. For most reactions taking place in solutions or gaseous mixtures, the value of $\Delta {G^\theta }$ depends on the proportions of the various reaction components in the mixture; it is not a simple sum of the "products minus reactants" type, as is the case with $\Delta {H^\theta }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




