
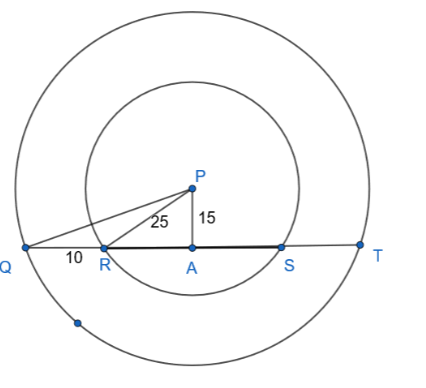
For a lezim kawayat the girls of standard IX are arranged in two circular concentric rings as shown in the figure. If PA=15m, PR=25m, QR=10m then find the measures of RS, PQ, and QT.
(a) \[40m,15\sqrt 5 m,and60m,\]
(b) \[20m,30\sqrt 5 m,and60m,\]
(c) \[40m,15\sqrt 5 m,and30m,\]
(d) \[10m,30\sqrt 5 m,and60m,\]

Answer
615.9k+ views
Hint:We can use the Pythagoras theorem, which states the relation between base, perpendicular, and hypotenuse.
\[{{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
We can see in the figure that triangle ARP is right-angled at A. So, we can apply Pythagoras Theorem here to find out the value of AR.
\[{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 25 \right)}^{2}}\]
Now, we will simplify the above equation to find the value of AR.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( AR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 25 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( AR \right)}^{2}}=625-225=400\]
\[\Rightarrow AR=20\]
So, we have now found the value of the length of line segment AR.
Also, we also know that perpendicular from the center to a chord bisects the chord.
So, we can find out the length of the line segment RS.
\[RS=2\left( AR \right)=40m..................(i)\]
Since we are already provided with the length of line segment QR, we can find out the length of the line segment AQ.
AQ=AR+QR
\[\Rightarrow AQ=20+10=30m..................(ii)\]
Now, we can see that the triangle PAQ is also right-angled at A.
\[{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AQ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}+{{30}^{2}}=900+225=1125\]
\[\Rightarrow PQ=15\sqrt{5}m....................(iii)\]
Again, we are left only with QT to be found. We can see that AP is bisecting the line segment QT. So, we can find the length of the line segment QT by doubling the QA.
QT=2(QA)
\[\Rightarrow QT=2(30)=60m......................(iv)\]
So, we have found out the value of RS, PQ, QT.
RS=40m
\[PQ=15\sqrt{5}m\]
QT=60m
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Note: We have to be aware of identifying the hypotenuse. One common mistake is that while writing the Pythagoras Theorem, one needs to identify the right angle and write the hypotenuse. A common method to memorize is that the side opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse.
\[{{\left( base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
We can see in the figure that triangle ARP is right-angled at A. So, we can apply Pythagoras Theorem here to find out the value of AR.
\[{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 25 \right)}^{2}}\]
Now, we will simplify the above equation to find the value of AR.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( AR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 25 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( AR \right)}^{2}}=625-225=400\]
\[\Rightarrow AR=20\]
So, we have now found the value of the length of line segment AR.
Also, we also know that perpendicular from the center to a chord bisects the chord.
So, we can find out the length of the line segment RS.
\[RS=2\left( AR \right)=40m..................(i)\]
Since we are already provided with the length of line segment QR, we can find out the length of the line segment AQ.
AQ=AR+QR
\[\Rightarrow AQ=20+10=30m..................(ii)\]
Now, we can see that the triangle PAQ is also right-angled at A.
\[{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AQ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}+{{30}^{2}}=900+225=1125\]
\[\Rightarrow PQ=15\sqrt{5}m....................(iii)\]
Again, we are left only with QT to be found. We can see that AP is bisecting the line segment QT. So, we can find the length of the line segment QT by doubling the QA.
QT=2(QA)
\[\Rightarrow QT=2(30)=60m......................(iv)\]
So, we have found out the value of RS, PQ, QT.
RS=40m
\[PQ=15\sqrt{5}m\]
QT=60m
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Note: We have to be aware of identifying the hypotenuse. One common mistake is that while writing the Pythagoras Theorem, one needs to identify the right angle and write the hypotenuse. A common method to memorize is that the side opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




