
For a first order reaction $A(g)\to 2B(g)+C(g)$at constant volume and 300 K, the total pressure at the beginning (t=0) and at time are ${{P}_{0}}$ and ${{P}_{t}}$ respectively. Initially, only A is present with concentration${{[A]}_{0}}$, and ${{t}_{1/3}}$is the time required for the partial pressure of A to reach $1/{{3}^{rd}}$of its initial value. The correct option(s) is/are:
(Assume that all these gases behave as ideal gases).
A.

B.

C.
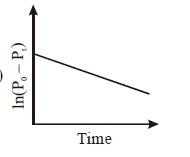
D.
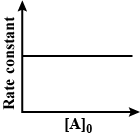




Answer
537k+ views
Hint: Chemical reactions are those reactions in which reactants get converted into products under some conditions like at fixed temperature and pressure and some reactions proceed with the help of catalysts which increase their rate of reaction.
Complete answer:
There is a special branch of chemistry which deals with the rate of reaction and the order of reaction can be defined as the power which depends on the rate of concentration of all reactants. The rate of a first-order reaction is dependent only on the concentration of one species in the reaction.
Now the question can be solved by considering the given equation
$A(g)\to 2B(g)+C(g)$
${{t}_{1/3}}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}/3}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln 3$$\therefore {{P}_{0}}+2P={{P}_{t}}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{t}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}-P}$
Now put the value of P in the above equation
$K=\dfrac{1}{t}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}-(\dfrac{{{P}_{t}}-{{P}_{0}}}{2})}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{t}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{3{{P}_{0}}-{{P}_{t}}}$
$-Kt+\ln 2{{P}_{0}}=\ln (3{{P}_{0}}-{{P}_{t}})$
And ${{t}_{1/3}}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}/3}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln 3$this would be equal to constant. Then the correct options for this term will be A and D, as rate constants do not depend on concentration.
Note:
A first-order reaction can also be defined as a chemical reaction for which the reaction rate is purely dependent on the concentration of only one reactant and in these reactions if the concentration of the first order reactant is doubled then the rate of reaction is also doubled.
Complete answer:
There is a special branch of chemistry which deals with the rate of reaction and the order of reaction can be defined as the power which depends on the rate of concentration of all reactants. The rate of a first-order reaction is dependent only on the concentration of one species in the reaction.
Now the question can be solved by considering the given equation
$A(g)\to 2B(g)+C(g)$
| T = 0 | ${{P}_{0}}$ | - | - |
| T = t | ${{P}_{0}}-P$ | 2P | P |
${{t}_{1/3}}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}/3}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln 3$$\therefore {{P}_{0}}+2P={{P}_{t}}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{t}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}-P}$
Now put the value of P in the above equation
$K=\dfrac{1}{t}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}-(\dfrac{{{P}_{t}}-{{P}_{0}}}{2})}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{t}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{3{{P}_{0}}-{{P}_{t}}}$
$-Kt+\ln 2{{P}_{0}}=\ln (3{{P}_{0}}-{{P}_{t}})$
And ${{t}_{1/3}}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln \dfrac{{{P}_{0}}}{{{P}_{0}}/3}=\dfrac{1}{K}\ln 3$this would be equal to constant. Then the correct options for this term will be A and D, as rate constants do not depend on concentration.
Note:
A first-order reaction can also be defined as a chemical reaction for which the reaction rate is purely dependent on the concentration of only one reactant and in these reactions if the concentration of the first order reactant is doubled then the rate of reaction is also doubled.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




