
For $0 \cdot 90{\text{ gm}}$of an organic compound ${C_4}{H_{10}}{O_2}$, ${\text{A}}$, when treated with Sodium gives $224{\text{ ml}}$ of hydrogen at ${\text{NTP}}$. Compound $A$ can be separated into fractions ${\text{B and C}}$ by crystallisation of which the fraction ${\text{B}}$ is resolved into optical isomers ${\text{D and E}}$. Write down the structural formula of ${\text{A and E}}$ with proper reasoning.
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:Compound ${\text{A}}$ must be containing active hydrogens to give ${H_2}$ when treated with ${\text{Na}}$. It should be symmetrical as it can be fractionated into two. Optical isomers are enantiomers. Hence, ${\text{D and E}}$ will be the mirror image of each other.
Complete step by step answer:
Step (1):
The given compound is ${C_4}{H_{10}}{O_2}$. Its molecular mass will be:
$\left( {4 \times {\text{Mass of Carbon + 10}} \times {\text{ Mass of Hydrogen + 2}} \times {\text{Mass of Oxygen}}} \right)$
= $\left( {4 \times 12 + 10 \times 1 + 2 \times 16} \right)$
= $90{\text{ gm mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Step (2):
Given mass of compound is $0 \cdot 90{\text{ gm}}$.
So, Number of moles of the compound = $\dfrac{{{\text{Given mass}}}}{{{\text{Molar mass}}}}$
${\text{ = }}\dfrac{{0 \cdot 90}}{{90}}$
= $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$
So, Number of moles of the compound is $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$.
Step (3):
It is given that $224{\text{ ml}}$ of ${H_2}$ is released. Molar volume of ${H_2}$ at ${\text{NTP}}$ is $22 \cdot 4{\text{ L}}$.
So, Number of Moles of ${H_2}$ = $\dfrac{{{\text{Given Volume}}}}{{{\text{Molar volume}}}}$
= $\dfrac{{224{\text{ ml}}}}{{22400{\text{ ml}}}}$
$ = 0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$
Since, $1{\text{ mole}}$ of ${H_2}$ contains ${\text{2 moles of H}}$. So, $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$ of ${H_2}$ contains $0 \cdot 02{\text{ moles of H}}$.
Step (4):
As the compound contains active hydrogen to undergo reaction with Sodium, it must contain some $\left( {{\text{ - OH}}} \right)$ group to provide those active hydrogens. The reaction will be:
$2{C_4}{H_{10}}{O_2} + 2Na \to 2{C_4}{H_9}{O_2}Na + {H_2}$
As there are $0 \cdot 02{\text{ moles of active H}}$ present in $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$ of compound. So, the compound must contain ${\text{2 ( - OH) }}$ groups. Hence, the structural formula of $A$ will be ${C_4}{H_8}{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$.
Following are the possible structures of ${\text{A}}$:
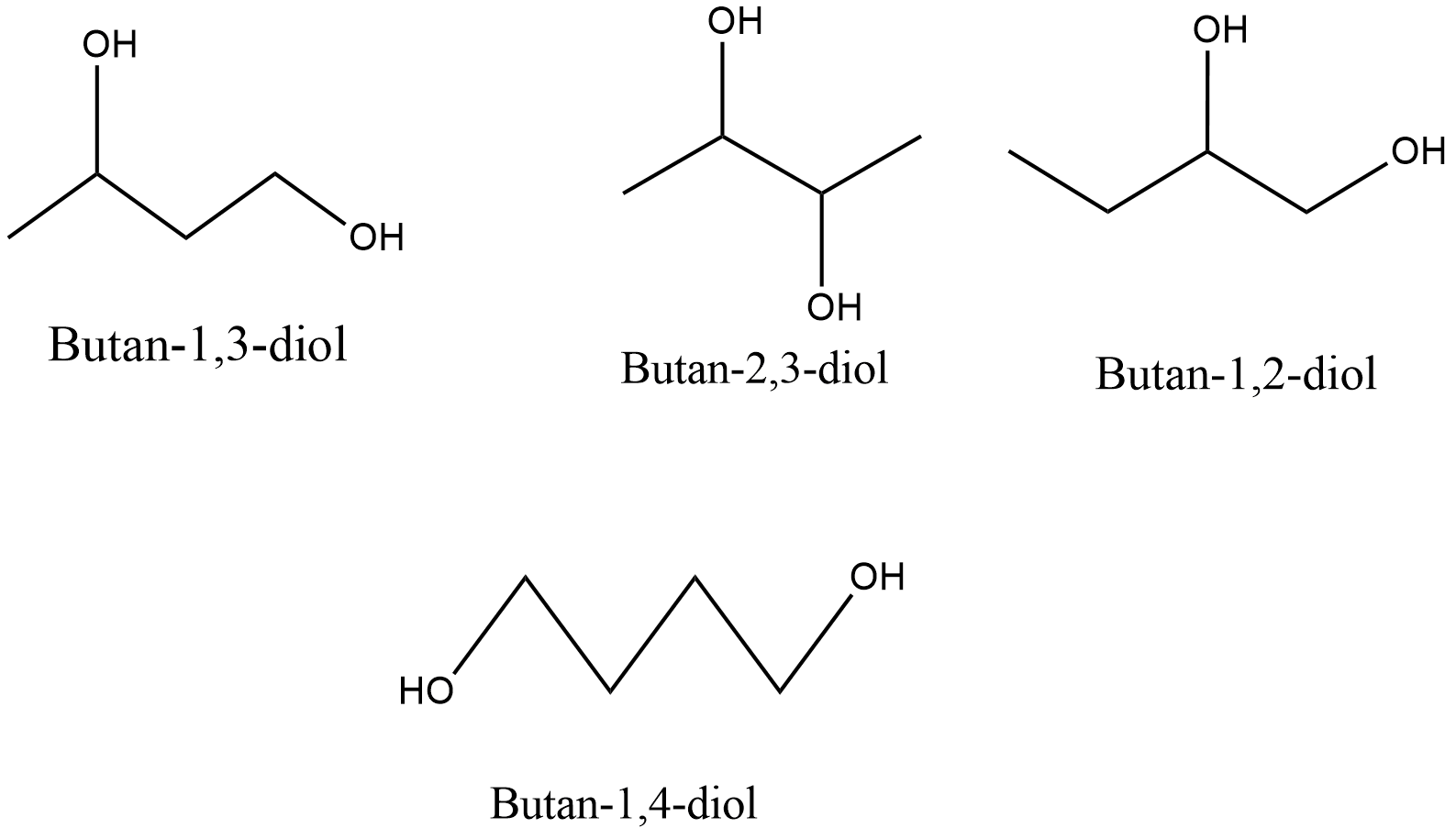
Among above all only ${\text{Butan - 2,3 - diol}}$ can be possible because for rest, Fisher projections cannot be drawn to see the symmetry for further answering the question which says, ${\text{A}}$ can be fractionated into
${\text{B and C}}$ whose structures will be:
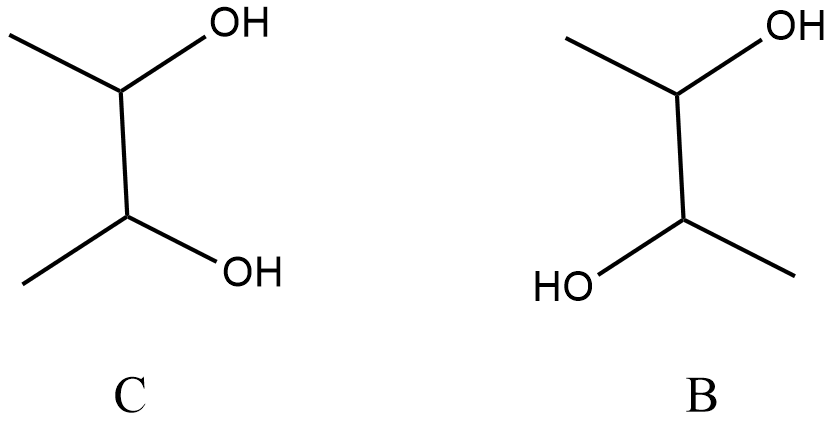
Step (5):
It is given that ${\text{B}}$ can be resolved into two optical isomers ${\text{D and E}}$, and optical isomers are enantiomers which are mirror images of each other. That means B should not be a meso compound, so ${\text{C}}$ is taken as a meso compound. The structure of ${\text{D and E}}$ will be:
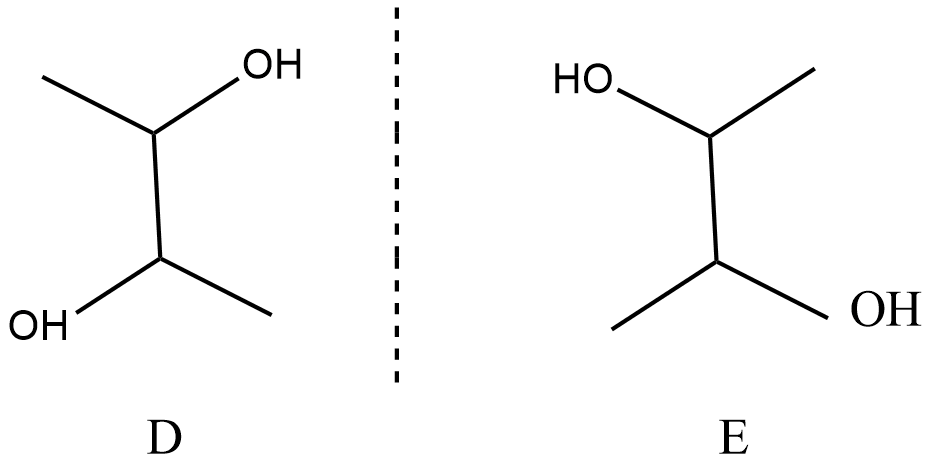
Hence, the Structural formula for ${\text{A and E}}$ is the same as ${C_4}{H_8}{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$ .
Note:
For optically active compounds, it should have the same type of ligand on the same side of the molecule, as in case of ${\text{C}}$ here, which is a meso compound or repeated pair of ligands. Plane of symmetry is a sign of optically inactive compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Step (1):
The given compound is ${C_4}{H_{10}}{O_2}$. Its molecular mass will be:
$\left( {4 \times {\text{Mass of Carbon + 10}} \times {\text{ Mass of Hydrogen + 2}} \times {\text{Mass of Oxygen}}} \right)$
= $\left( {4 \times 12 + 10 \times 1 + 2 \times 16} \right)$
= $90{\text{ gm mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Step (2):
Given mass of compound is $0 \cdot 90{\text{ gm}}$.
So, Number of moles of the compound = $\dfrac{{{\text{Given mass}}}}{{{\text{Molar mass}}}}$
${\text{ = }}\dfrac{{0 \cdot 90}}{{90}}$
= $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$
So, Number of moles of the compound is $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$.
Step (3):
It is given that $224{\text{ ml}}$ of ${H_2}$ is released. Molar volume of ${H_2}$ at ${\text{NTP}}$ is $22 \cdot 4{\text{ L}}$.
So, Number of Moles of ${H_2}$ = $\dfrac{{{\text{Given Volume}}}}{{{\text{Molar volume}}}}$
= $\dfrac{{224{\text{ ml}}}}{{22400{\text{ ml}}}}$
$ = 0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$
Since, $1{\text{ mole}}$ of ${H_2}$ contains ${\text{2 moles of H}}$. So, $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$ of ${H_2}$ contains $0 \cdot 02{\text{ moles of H}}$.
Step (4):
As the compound contains active hydrogen to undergo reaction with Sodium, it must contain some $\left( {{\text{ - OH}}} \right)$ group to provide those active hydrogens. The reaction will be:
$2{C_4}{H_{10}}{O_2} + 2Na \to 2{C_4}{H_9}{O_2}Na + {H_2}$
As there are $0 \cdot 02{\text{ moles of active H}}$ present in $0 \cdot 01{\text{ mol}}$ of compound. So, the compound must contain ${\text{2 ( - OH) }}$ groups. Hence, the structural formula of $A$ will be ${C_4}{H_8}{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$.
Following are the possible structures of ${\text{A}}$:

Among above all only ${\text{Butan - 2,3 - diol}}$ can be possible because for rest, Fisher projections cannot be drawn to see the symmetry for further answering the question which says, ${\text{A}}$ can be fractionated into
${\text{B and C}}$ whose structures will be:

Step (5):
It is given that ${\text{B}}$ can be resolved into two optical isomers ${\text{D and E}}$, and optical isomers are enantiomers which are mirror images of each other. That means B should not be a meso compound, so ${\text{C}}$ is taken as a meso compound. The structure of ${\text{D and E}}$ will be:

Hence, the Structural formula for ${\text{A and E}}$ is the same as ${C_4}{H_8}{\left( {OH} \right)_2}$ .
Note:
For optically active compounds, it should have the same type of ligand on the same side of the molecule, as in case of ${\text{C}}$ here, which is a meso compound or repeated pair of ligands. Plane of symmetry is a sign of optically inactive compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




