
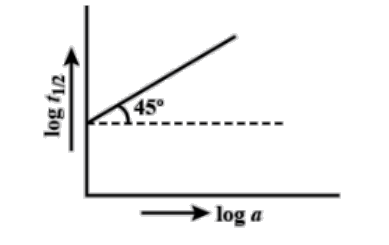
Following is the graph between log ${{T}_{{1}/{2}\;}}$ and log a (a = initial concentration) for a given reaction at ${{27}^{{}^\circ }}C$ . Hence, the order is:
[A] 0
[B] 1
[C] 2
[D] 3

Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you can use the relation between half-life and initial concentration of the reactant \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\].Then try to find out the slope of the graph given above. Compare the above relation with the straight line equation and find ‘n’, which is the order of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that order of a reaction is the relation between the rate of the reaction and the concentration of the reactants in it. It tells us how the reaction rate is affected by the concentration of the involved reactants.
If we have a zero order reaction, it means that the concentration of the reactants do not affect the rate of the reaction. Similarly, for a first order reaction, the concentration of one of the reactant species affects the reaction rate.
We can determine the order of a reaction from a graph of the initial concentration versus time.
We know that half-life of a species of the time taken by it to reach the half value of its initial concentration.
Here, the graph of initial concentration versus the half-life of the reaction is given to us and we have to find the order of the reaction.
The half-life of the reaction is inversely proportional to the initial concentration of the reaction to the power (1 – order of the reaction). Symbolically, we can write this relation as-
\[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}\propto {{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\]
If we introduce a proportionality constant, we can write the relation as-
\[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\]
Where, \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}\] is the half-life, ‘a’ is the initial concentration and n is the order of the reaction.
The graph which is given to us is linear. Therefore, the equation of the graph is y = mx + c where, ‘c’ is the intercept, ‘m’ is the slope and ‘x’ and ‘y’ denote the two axes.
In the graph, x-axis is the concentration and y-axis is the half-life and the straight line is at an angle of ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$ . We know that the slope is given by tan theta. Here, theta is ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$.
Therefore, slope = m = $\tan \theta =\tan {{45}^{\circ }}=1$ .
Now, we can the equation \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\] as \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{a}^{n-1}}\]
if we take log on both sides in \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{a}^{n-1}}\], we will get-
\[\log {{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=\log K+\left( 1-n \right)\log a\]
Now, comparing it with the straight line equation, we will get that-
1-n = m
Or, 1 – n = 1 i.e. n = 0.
As we can see the order of the reaction is 0 i.e. it is a zero order reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The rate of a reaction depends upon several factors like the nature of the reactants, presence of catalyst, temperature at which the reaction is taking place and also on the presence of catalyst. Here, as the reaction is zero ordered, further the addition of reactants to increase the concentration of the reactant will not affect the rate of the reaction. The reaction will proceed at the same, constant speed.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that order of a reaction is the relation between the rate of the reaction and the concentration of the reactants in it. It tells us how the reaction rate is affected by the concentration of the involved reactants.
If we have a zero order reaction, it means that the concentration of the reactants do not affect the rate of the reaction. Similarly, for a first order reaction, the concentration of one of the reactant species affects the reaction rate.
We can determine the order of a reaction from a graph of the initial concentration versus time.
We know that half-life of a species of the time taken by it to reach the half value of its initial concentration.
Here, the graph of initial concentration versus the half-life of the reaction is given to us and we have to find the order of the reaction.
The half-life of the reaction is inversely proportional to the initial concentration of the reaction to the power (1 – order of the reaction). Symbolically, we can write this relation as-
\[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}\propto {{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\]
If we introduce a proportionality constant, we can write the relation as-
\[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\]
Where, \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}\] is the half-life, ‘a’ is the initial concentration and n is the order of the reaction.
The graph which is given to us is linear. Therefore, the equation of the graph is y = mx + c where, ‘c’ is the intercept, ‘m’ is the slope and ‘x’ and ‘y’ denote the two axes.
In the graph, x-axis is the concentration and y-axis is the half-life and the straight line is at an angle of ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$ . We know that the slope is given by tan theta. Here, theta is ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$.
Therefore, slope = m = $\tan \theta =\tan {{45}^{\circ }}=1$ .
Now, we can the equation \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{1-n}}\] as \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{a}^{n-1}}\]
if we take log on both sides in \[{{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=K{{a}^{n-1}}\], we will get-
\[\log {{t}_{{1}/{2}\;}}=\log K+\left( 1-n \right)\log a\]
Now, comparing it with the straight line equation, we will get that-
1-n = m
Or, 1 – n = 1 i.e. n = 0.
As we can see the order of the reaction is 0 i.e. it is a zero order reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The rate of a reaction depends upon several factors like the nature of the reactants, presence of catalyst, temperature at which the reaction is taking place and also on the presence of catalyst. Here, as the reaction is zero ordered, further the addition of reactants to increase the concentration of the reactant will not affect the rate of the reaction. The reaction will proceed at the same, constant speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




