
Fluorine is a non-metal. Will it give or take electrons?
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: Non-metals are elements which are present at the left side of the periodic table. There is some basic difference between them, non-metal is generally dull in appearance and less reactive than metals. Halogens come under the category of non-metals.
Complete answer:
In the periodic table, metal and nonmetal are placed at different places. However, specific differentiation between them is not done yet. Fluorine is the first member of the halogen family and known as non-metal. Atomic number of fluorine is $9$, so when we write the electronic configuration of it according to Aufbau principle and Pauli exclusion principle, it will be represented as:
Electronic configuration of fluorine: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^5}$
From the electronic configuration we see that, fluorine atom contains $7$ electrons in its outermost shell. The outermost shell of fluorine is $2s$ and $2p$. According to octet rule, every atom undergoes the chemical reaction to complete its outermost shell with $8$ electrons to attain noble gas configuration. So as from the electronic configuration it is clear that a fluorine atom requires only one more electron to complete its octet to attain configuration of neon noble gas which is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}$.
Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is also very high so it is capable of attracting one electron from another atom to complete its octet.
Fluorine accepts one electron either by sharing to form a covalent bond or by attracting the electron from a less electronegative element to form fluoride ion.
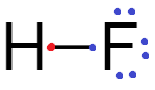
Therefore, fluorine atoms have a tendency to accept electrons.
Note:
Fluorine is highly reactive in nature and forms the strongest hydrogen bonding with hydrogen atoms. Fluorine has a tendency to react with non-metal like hydrogen as well as with metals like iron to form halides of halogen.
Complete answer:
In the periodic table, metal and nonmetal are placed at different places. However, specific differentiation between them is not done yet. Fluorine is the first member of the halogen family and known as non-metal. Atomic number of fluorine is $9$, so when we write the electronic configuration of it according to Aufbau principle and Pauli exclusion principle, it will be represented as:
Electronic configuration of fluorine: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^5}$
From the electronic configuration we see that, fluorine atom contains $7$ electrons in its outermost shell. The outermost shell of fluorine is $2s$ and $2p$. According to octet rule, every atom undergoes the chemical reaction to complete its outermost shell with $8$ electrons to attain noble gas configuration. So as from the electronic configuration it is clear that a fluorine atom requires only one more electron to complete its octet to attain configuration of neon noble gas which is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}$.
Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is also very high so it is capable of attracting one electron from another atom to complete its octet.
Fluorine accepts one electron either by sharing to form a covalent bond or by attracting the electron from a less electronegative element to form fluoride ion.
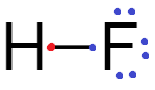
Therefore, fluorine atoms have a tendency to accept electrons.
Note:
Fluorine is highly reactive in nature and forms the strongest hydrogen bonding with hydrogen atoms. Fluorine has a tendency to react with non-metal like hydrogen as well as with metals like iron to form halides of halogen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




