
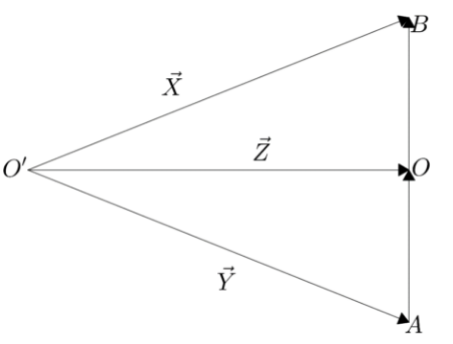
Five vectors $\overrightarrow{X}$ , $\overrightarrow{Y}$ , $\overrightarrow{Z}$ , $\overrightarrow{OA}$ , and $\overrightarrow{OB}$ are connected as shown in figure. If $\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{AO}$, then which of the following options is correct.
A. $\overrightarrow{X}+\overrightarrow{Y}=2\overrightarrow{Z}$
B. $\overrightarrow{X}-\overrightarrow{Y}=2\overrightarrow{Z}$
C. $\overrightarrow{X}-\overrightarrow{Y}=3\overrightarrow{Z}$
D. $\overrightarrow{Y}+\overrightarrow{Z}=2\overrightarrow{X}$

Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: Use triangle law of vector addition and properties of vector like associative law, commutative law, identity law, additive inverse etc. Vector is a physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is represented by an arrow whose direction is same as that of quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, as we are given vectors, we can use the triangle law of vector addition. According to triangle law of vector addition, when two vectors are represented as two sides of the triangle with order of magnitude and direction, then the third side of the triangle represents the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.Let us consider the triangle $\Delta O'OB$ . For this triangle, using triangle law of vector addition we can understand that $\overrightarrow{Z}+\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{X}$
Rearranging the equation as $\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{X}-\overrightarrow{Z}$ …… $(1)$
Similarly for the triangle $\Delta O'AO$ , using the triangle law of vector addition, we can obtain the relation as $\overrightarrow{Y}+\overrightarrow{OA}=\overrightarrow{Z}$
Rearranging the equation as $\overrightarrow{OA}=\overrightarrow{Z}-\overrightarrow{Y}$ …… $(2)$
Now, we are given here that $\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{AO}$
Hence, we can say that the left hand side of the equations are equal.
Thus, we can equate the right hand sides of both equations
$\overrightarrow{X}-\overrightarrow{Z}=\overrightarrow{Z}-\overrightarrow{Y}$
$\therefore \overrightarrow{X}+\overrightarrow{Y}=2\overrightarrow{Z}$
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: For triangle law of vector addition, we must remember to consider the vector which starts from the head of the first vector as the second vector. And the resultant vector will be the vector which starts from the origin of the first vector and intersects at the head of the second vector.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, as we are given vectors, we can use the triangle law of vector addition. According to triangle law of vector addition, when two vectors are represented as two sides of the triangle with order of magnitude and direction, then the third side of the triangle represents the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.Let us consider the triangle $\Delta O'OB$ . For this triangle, using triangle law of vector addition we can understand that $\overrightarrow{Z}+\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{X}$
Rearranging the equation as $\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{X}-\overrightarrow{Z}$ …… $(1)$
Similarly for the triangle $\Delta O'AO$ , using the triangle law of vector addition, we can obtain the relation as $\overrightarrow{Y}+\overrightarrow{OA}=\overrightarrow{Z}$
Rearranging the equation as $\overrightarrow{OA}=\overrightarrow{Z}-\overrightarrow{Y}$ …… $(2)$
Now, we are given here that $\overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{AO}$
Hence, we can say that the left hand side of the equations are equal.
Thus, we can equate the right hand sides of both equations
$\overrightarrow{X}-\overrightarrow{Z}=\overrightarrow{Z}-\overrightarrow{Y}$
$\therefore \overrightarrow{X}+\overrightarrow{Y}=2\overrightarrow{Z}$
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: For triangle law of vector addition, we must remember to consider the vector which starts from the head of the first vector as the second vector. And the resultant vector will be the vector which starts from the origin of the first vector and intersects at the head of the second vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




