
What is the first step to occur during the process of replication?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Replication is a process that takes place at the time of reproduction at genetic level. This reproduction can either be for production of new cells or new organisms. It involves duplication of DNA so that uniformity of genes is maintained throughout the organism body.
Complete answer:
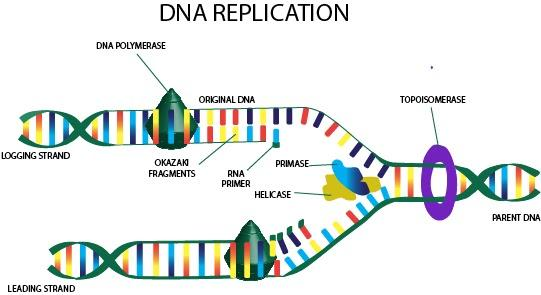
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) replication is a crucial and complex process. Unzipping of the helical structure is the first step which is concerned with breaking down the hydrogen bond between nitrogenous bases. It is possible only with the help of helicase enzyme that breaks these hydrogen bonds and separates the nitrogenous bases leading to formation of Y-shaped fork. Now this fork works as the foundation stone for formation of the new duplicate strand.
Binding of primers to form the duplicate strand is the second step of DNA replication. Replication process is actually initiated from this step. In this step, a primer (piece of RNA) is supposed to bind to the fork strand of DNA. Replication always takes place from the starting point of the DNA strand. However, this primer is formed by action of an enzyme called DNA primase.
Elongation is the third step of the DNA replication process. It involves formation of new contrasting nitrogenous bases alongside the already present nitrogenous bases in the fork strand body. These bases lead to elongation of the new strand into helical structure sonia called elongation. This action is initiated by several replication hormones such as polymerase III.
Note:
Termination is the last step of the DNA replication process. It is concerned with formation of two new DNA structures carrying one parent strand and one new daughter strand. This is possible by action of many enzymes. First an enzyme called exonuclease removes all the RNA primers to allow formation of full fledged daughter strands. Another such hormone does a proof reading to avoid mistakes. Another enzyme called DNA ligase leads to unification of the two strands. At last DNA telomerase breaks these strands to form individual helical structures. Thus, two new DNA strands are formed.
Complete answer:
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) replication is a crucial and complex process. Unzipping of the helical structure is the first step which is concerned with breaking down the hydrogen bond between nitrogenous bases. It is possible only with the help of helicase enzyme that breaks these hydrogen bonds and separates the nitrogenous bases leading to formation of Y-shaped fork. Now this fork works as the foundation stone for formation of the new duplicate strand.
Binding of primers to form the duplicate strand is the second step of DNA replication. Replication process is actually initiated from this step. In this step, a primer (piece of RNA) is supposed to bind to the fork strand of DNA. Replication always takes place from the starting point of the DNA strand. However, this primer is formed by action of an enzyme called DNA primase.
Elongation is the third step of the DNA replication process. It involves formation of new contrasting nitrogenous bases alongside the already present nitrogenous bases in the fork strand body. These bases lead to elongation of the new strand into helical structure sonia called elongation. This action is initiated by several replication hormones such as polymerase III.

Note:
Termination is the last step of the DNA replication process. It is concerned with formation of two new DNA structures carrying one parent strand and one new daughter strand. This is possible by action of many enzymes. First an enzyme called exonuclease removes all the RNA primers to allow formation of full fledged daughter strands. Another such hormone does a proof reading to avoid mistakes. Another enzyme called DNA ligase leads to unification of the two strands. At last DNA telomerase breaks these strands to form individual helical structures. Thus, two new DNA strands are formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




