
Finding pH of the following samples by using pH paper/universal indicator:
a.) Dilute Hydrochloric Acid
b.) Dilute NaOH solution
c.) Dilute Ethanoic Acid solution
d.) Lemon juice
e.) Water
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: The nature of the chemicals used in laboratories is either basic, acidic or neutral. This characteristic depends on the ions they release. A chemical is said to be acidic if it releases H+ ions and basic if it releases OH– ions in its aqueous solutions.
Complete step by step answer:
- The pH is the measure of the acidic or basic power of a solution. It is a scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
- The pH scale varies from 0 to 14. Neutral solution has a pH of 7.
- pH is defined as the negative logarithm of \[{{H}^{+}}\] ions. It can be mathematically represented as
\[pH=-{{\log }_{10}}[{{H}^{+}}]\]
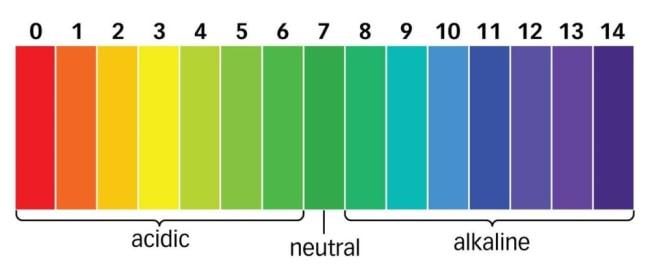
- To find the pH of the given chemicals, the apparatus required is as follows:
Test tubes
Test tube stand
Dropper
Glass rod
pH paper strips
pH paper colour chart
- First of all, arrange all the chemicals in clean, dry test tubes on the test tube stand.
- Secondly, put one or two drops of each test solution on pH paper strips using a glass rod.
- We will compare the pH using the pH scale chart from the observations given below:
Note: As pH depends upon ${{H}^{+}}$ concentration and in an aqueous solution ${{H}^{+}}$ and $O{{H}^{-}}$ ion concentrations are correlated, Therefore, every acidic and basic solution shows different colour at different pH .
Complete step by step answer:
- The pH is the measure of the acidic or basic power of a solution. It is a scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
- The pH scale varies from 0 to 14. Neutral solution has a pH of 7.
- pH is defined as the negative logarithm of \[{{H}^{+}}\] ions. It can be mathematically represented as
\[pH=-{{\log }_{10}}[{{H}^{+}}]\]

pH scale
- To find the pH of the given chemicals, the apparatus required is as follows:
Test tubes
Test tube stand
Dropper
Glass rod
pH paper strips
pH paper colour chart
- First of all, arrange all the chemicals in clean, dry test tubes on the test tube stand.
- Secondly, put one or two drops of each test solution on pH paper strips using a glass rod.
- We will compare the pH using the pH scale chart from the observations given below:
| Sr. No. | Sample Solution | Colour appeared on pH paper | pH of the solution | Inference |
| 1. | Dilute HCl | Red | 1 | Strong acid |
| 2. | Dilute NaOH solution | Purple | 14 | Strong alkali |
| 3. | Dilute Ethanoic Acid solution | Yellow | 3 | Weak acid |
| 4. | Lemon Juice | Orange | 2 | Acid |
| 5. | Water | Green | 7 | Weak alkali |
Note: As pH depends upon ${{H}^{+}}$ concentration and in an aqueous solution ${{H}^{+}}$ and $O{{H}^{-}}$ ion concentrations are correlated, Therefore, every acidic and basic solution shows different colour at different pH .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




