
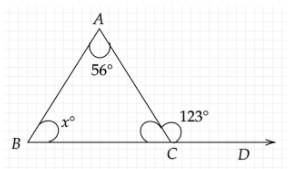
Find \[x^\circ \] in the given figure.

Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint:
We will approach the given problem by using the angle sum property of a triangle. First, we will apply the linear pair axiom to find the angle \[\angle ACB\]. Then, we will use the angle sum property to find the unknown angle.
Complete step by step solution:
We have a triangle ABC in which it is given that \[\angle BAC = 56^\circ \] and \[\angle ACD = 123^\circ \]. We are supposed to find the unknown angle \[x^\circ \].
We will use the angle sum property of a triangle and the linear pair axiom.
First, let us use the linear pair axiom and find out the measure of \[\angle ACB\].
By the linear pair axiom, “If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of the angles so formed is \[180^\circ \]”.
In the given figure, we will treat \[AC\] as the ray standing on the line \[BCD\].
According to the linear pair axiom,
\[\angle ACB + \angle ACD = 180^\circ \] ……….\[(1)\]
Now, let us substitute the value of \[\angle ACD\] in equation \[(1)\]. We have
\[\angle ACB + 123^\circ = 180^\circ \]
\[\]\[\therefore \angle ACB = 180^\circ - 123^\circ = 57^\circ \]
Now, we will use the angle sum property of a triangle which states that “the sum of the angles of a triangle is \[180^\circ \]”.
So, in triangle ABC, we have by the angle sum property,
\[\angle BAC + \angle ABC + \angle ACB = 180^\circ \] ………\[(2)\]
Let us substitute the measurements of \[\angle BAC\] and \[\angle ACB\] in equation \[(2)\]. Thus, equation \[(2)\] becomes
\[56^\circ + \angle ABC + 57^\circ = 180^\circ \]
\[\therefore \angle ABC = 180^\circ - 113^\circ = 67^\circ \]
In the given figure, \[\angle ABC = x^\circ \]. Therefore, \[x^\circ = 67^\circ \].
Note:
An alternate method to solve this problem is by using the exterior angle property of a triangle. This states that “If a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles”.
In the given figure, the side \[BC\] is produced and the exterior angle formed is \[\angle ACD\] whose measurement is given as \[123^\circ \]. By the exterior angle property,
\[\angle ACD = \angle BAC + \angle ABC\]
Substituting the known values, we get
\[123^\circ = 56^\circ + x^\circ \]
\[x^\circ = 123^\circ - 56^\circ = 67^\circ \]
We will approach the given problem by using the angle sum property of a triangle. First, we will apply the linear pair axiom to find the angle \[\angle ACB\]. Then, we will use the angle sum property to find the unknown angle.
Complete step by step solution:
We have a triangle ABC in which it is given that \[\angle BAC = 56^\circ \] and \[\angle ACD = 123^\circ \]. We are supposed to find the unknown angle \[x^\circ \].
We will use the angle sum property of a triangle and the linear pair axiom.
First, let us use the linear pair axiom and find out the measure of \[\angle ACB\].
By the linear pair axiom, “If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of the angles so formed is \[180^\circ \]”.
In the given figure, we will treat \[AC\] as the ray standing on the line \[BCD\].
According to the linear pair axiom,
\[\angle ACB + \angle ACD = 180^\circ \] ……….\[(1)\]
Now, let us substitute the value of \[\angle ACD\] in equation \[(1)\]. We have
\[\angle ACB + 123^\circ = 180^\circ \]
\[\]\[\therefore \angle ACB = 180^\circ - 123^\circ = 57^\circ \]
Now, we will use the angle sum property of a triangle which states that “the sum of the angles of a triangle is \[180^\circ \]”.
So, in triangle ABC, we have by the angle sum property,
\[\angle BAC + \angle ABC + \angle ACB = 180^\circ \] ………\[(2)\]
Let us substitute the measurements of \[\angle BAC\] and \[\angle ACB\] in equation \[(2)\]. Thus, equation \[(2)\] becomes
\[56^\circ + \angle ABC + 57^\circ = 180^\circ \]
\[\therefore \angle ABC = 180^\circ - 113^\circ = 67^\circ \]
In the given figure, \[\angle ABC = x^\circ \]. Therefore, \[x^\circ = 67^\circ \].
Note:
An alternate method to solve this problem is by using the exterior angle property of a triangle. This states that “If a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles”.
In the given figure, the side \[BC\] is produced and the exterior angle formed is \[\angle ACD\] whose measurement is given as \[123^\circ \]. By the exterior angle property,
\[\angle ACD = \angle BAC + \angle ABC\]
Substituting the known values, we get
\[123^\circ = 56^\circ + x^\circ \]
\[x^\circ = 123^\circ - 56^\circ = 67^\circ \]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





