
How do you find which quadrant each question is referring to if $0 < a < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $\dfrac{3\pi }{2} < a < 2\pi $?
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: We explain the central angle around a point. Then we discuss the algebraic and geometric versions of the quadrants. We also find different quadrants and their characteristics. Then we find the solutions for the angles $0 < a < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $\dfrac{3\pi }{2} < a < 2\pi $.
Complete step by step answer:
The central angle around a point is always equal to ${{360}^{\circ }}$.
The total angle is divided into four parts or quadrant as they are called. These quadrants are named in roman numerals of $I,II,III,IV$.
In case of algebraic sense these quadrants give the signs of the x and y coordinates.
These quadrants are also called as the first, second, third and fourth quadrant.
The respective signs for the coordinates of $\left( x,y \right)$ will be \[\left( +,+ \right),\left( -,+ \right),\left( -,- \right),\left( +,- \right)\] respectively for the quadrants.
Now we look for the geometric side of the quadrants where we deal with the angle of the trigonometric ratios.
The total circular angle of $2\pi $ can be divided into four parts. Each part is of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Therefore, the first quadrant is the interval of $\left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$. The second quadrant is the interval of $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi \right)$. The third quadrant is the interval of $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right)$. The fourth quadrant is the interval of $\left( \dfrac{3\pi }{2},2\pi \right)$. The $0,\dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$ indicates the axes.
Now we find for the quadrants $0 < a < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $\dfrac{3\pi }{2} < a < 2\pi $.
When the angle $0 < a < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$, the quadrant is first and when the angle $\dfrac{3\pi }{2} < a < 2\pi $, the quadrant is fourth.
Note:
We can also represent the quadrants with respect to the image form of both algebraic and geometric versions.
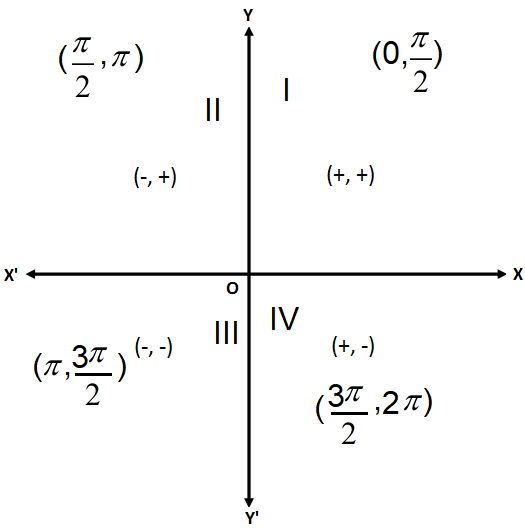
The rotation of the coordinates happens anti-clockwise.
Complete step by step answer:
The central angle around a point is always equal to ${{360}^{\circ }}$.
The total angle is divided into four parts or quadrant as they are called. These quadrants are named in roman numerals of $I,II,III,IV$.
In case of algebraic sense these quadrants give the signs of the x and y coordinates.
These quadrants are also called as the first, second, third and fourth quadrant.
The respective signs for the coordinates of $\left( x,y \right)$ will be \[\left( +,+ \right),\left( -,+ \right),\left( -,- \right),\left( +,- \right)\] respectively for the quadrants.
Now we look for the geometric side of the quadrants where we deal with the angle of the trigonometric ratios.
The total circular angle of $2\pi $ can be divided into four parts. Each part is of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Therefore, the first quadrant is the interval of $\left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$. The second quadrant is the interval of $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi \right)$. The third quadrant is the interval of $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right)$. The fourth quadrant is the interval of $\left( \dfrac{3\pi }{2},2\pi \right)$. The $0,\dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$ indicates the axes.
Now we find for the quadrants $0 < a < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $\dfrac{3\pi }{2} < a < 2\pi $.
When the angle $0 < a < \dfrac{\pi }{2}$, the quadrant is first and when the angle $\dfrac{3\pi }{2} < a < 2\pi $, the quadrant is fourth.
Note:
We can also represent the quadrants with respect to the image form of both algebraic and geometric versions.
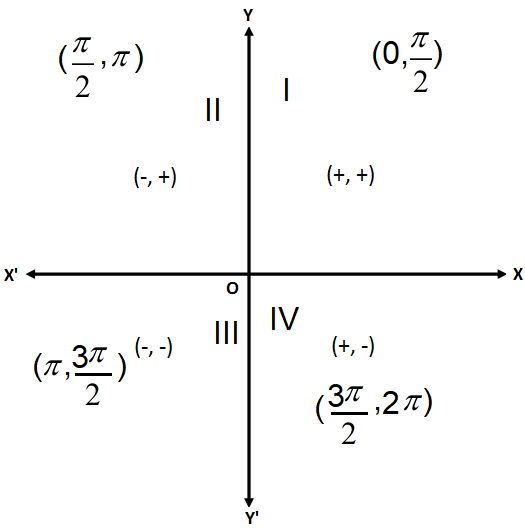
The rotation of the coordinates happens anti-clockwise.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




