
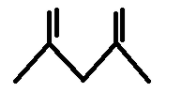
Find total number of allylic H in the following
i)
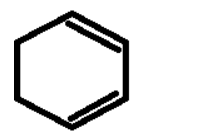
ii)
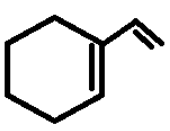
iii)
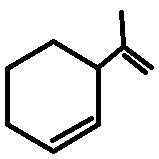
iv)
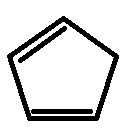
v)

vi)

vii)

viii)








Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:In the carbon compounds consisting of hydrogens and carbons which are hydrocarbons are further divided into saturated and unsaturated compounds, where there are different types of carbon and hydrogen atoms depending upon their degrees.
Complete answer:
out of the unsaturated hydrocarbons, the open chain hydrocarbons which contain carbon-carbon double bonds in their molecules are termed as alkenes. Alkenes have their naming rules similar to the naming rules of alkanes which are saturated compounds. But in alkenes various locations and positions have been given different terms such as allylic and vinylic positions before we understand what these positions are we should know that alkenes have a C=C which consists of a σ and a π bond, in a plane at right angles to the plane of the single σ bonds to each C. The π bond is weaker and more reactive than the σ bond.
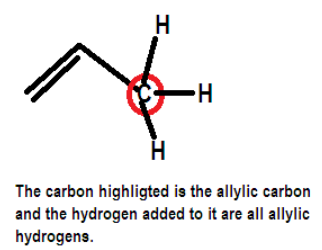
The position allylic is referred to the carbon attached adjacent to the C=C therefore the hydrogen attached to that carbon will be an allylic hydrogen. One can understand it clearly from the diagram given below:
Now let us determine the number of allylic hydrogens in all the compounds by counting them,
Therefore the compound 1 has 4 allylic hydrogens attached to the two highlighted carbons and since we know that all the carbons form four bonds, the other two bonds that complete the carbon’s configuration are two C-H bonds.
Similarly the second compound will also have four allylic hydrogens attached to the two highlighted allylic carbons.
The third compound has six, fourth compound has two, and the fifth compound has two allylic hydrogens attached to their respective highlighted carbons as shown below.
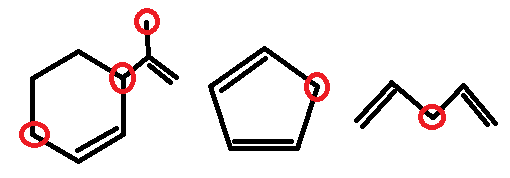
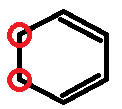
Sixth compound has no allylic hydrogen as there is no allylic carbon.

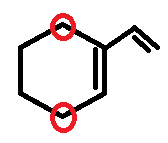
Seventh compound has sixth and eighth has eight allylic hydrogens as shown below,
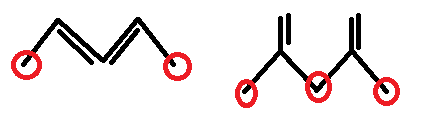
Note:
Similar to the allylic position one other classification in the position of alkenes is vinylic position it can be understood that any of the elements attached to the C=C be it halide or hydrogen it is at the vinylic position.
Complete answer:
out of the unsaturated hydrocarbons, the open chain hydrocarbons which contain carbon-carbon double bonds in their molecules are termed as alkenes. Alkenes have their naming rules similar to the naming rules of alkanes which are saturated compounds. But in alkenes various locations and positions have been given different terms such as allylic and vinylic positions before we understand what these positions are we should know that alkenes have a C=C which consists of a σ and a π bond, in a plane at right angles to the plane of the single σ bonds to each C. The π bond is weaker and more reactive than the σ bond.
The position allylic is referred to the carbon attached adjacent to the C=C therefore the hydrogen attached to that carbon will be an allylic hydrogen. One can understand it clearly from the diagram given below:

Now let us determine the number of allylic hydrogens in all the compounds by counting them,
Therefore the compound 1 has 4 allylic hydrogens attached to the two highlighted carbons and since we know that all the carbons form four bonds, the other two bonds that complete the carbon’s configuration are two C-H bonds.

Similarly the second compound will also have four allylic hydrogens attached to the two highlighted allylic carbons.

The third compound has six, fourth compound has two, and the fifth compound has two allylic hydrogens attached to their respective highlighted carbons as shown below.

Sixth compound has no allylic hydrogen as there is no allylic carbon.

Seventh compound has sixth and eighth has eight allylic hydrogens as shown below,

Note:
Similar to the allylic position one other classification in the position of alkenes is vinylic position it can be understood that any of the elements attached to the C=C be it halide or hydrogen it is at the vinylic position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




