
How do you find the zeros and use a sign chart to sketch the polynomial $F\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}$?
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint: Firstly, we have to determine the zeros of the given polynomial for which it has to be equated to zero so as to obtain the equation ${{x}^{3}}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=0$. By solving this equation, we will obtain the values $0$ and $-2$ so that we can divide the real number line into three intervals $x < -2$, $-2 < x < 0$ and $x>0$. For deducing the sign of the polynomial in different intervals, we can choose any value belonging to that interval and substitute it into the given polynomial.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The function given in the above question is
$\Rightarrow F\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}$
For determining the zeroes of the given function, we put it equal to zero to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( x \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{3}}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
By using the zero product rule, we can write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{3}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=0 \\
\end{align}$
And
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-2 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, we have found out the zeroes of the given function to be $-2$ and $0$. With reference to these points, we can divide the real number line into three intervals, which are $x < -2$, $-2 < x < 0$ and $x>0$.
We consider the first interval $x < -2$. For checking the sign of $F\left( x \right)$ in this interval, we can select any of the point belonging to this interval and substitute into the given function. Therefore, let us select $x=-3$ and substitute it into the given function to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( -3 \right)={{\left( -3 \right)}^{3}}{{\left( -3+2 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -3 \right)=-27{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -3 \right)=-27 \\
\end{align}$
Since we got a negative value, this means that $F\left( x \right)$ is negative in this interval.
Now, we consider the second interval $-2 < x < 0$. Let us choose $x=-1$ to substitute into the given function to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( -1 \right)={{\left( -1 \right)}^{3}}{{\left( -1+2 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -1 \right)=-1{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -1 \right)=-1 \\
\end{align}$
We again got a negative value. This means that $F\left( x \right)$ is negative in this interval too.
Finally, we consider the last interval $x>0$. Let us choose $x=1$ and substitute it in the given function to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( 1 \right)={{\left( 1 \right)}^{3}}{{\left( 1+2 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( 1 \right)=1{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( 1 \right)=9 \\
\end{align}$
Now, in this interval we got a positive value. Therefore, in this interval the function $F\left( x \right)$ is positive in this interval.
Thus the given function is negative in the intervals $x < -2$ and $-2 < x < 0$ and positive in the interval $x>0$. We can see this in the graph of $F\left( x \right)$ given below.
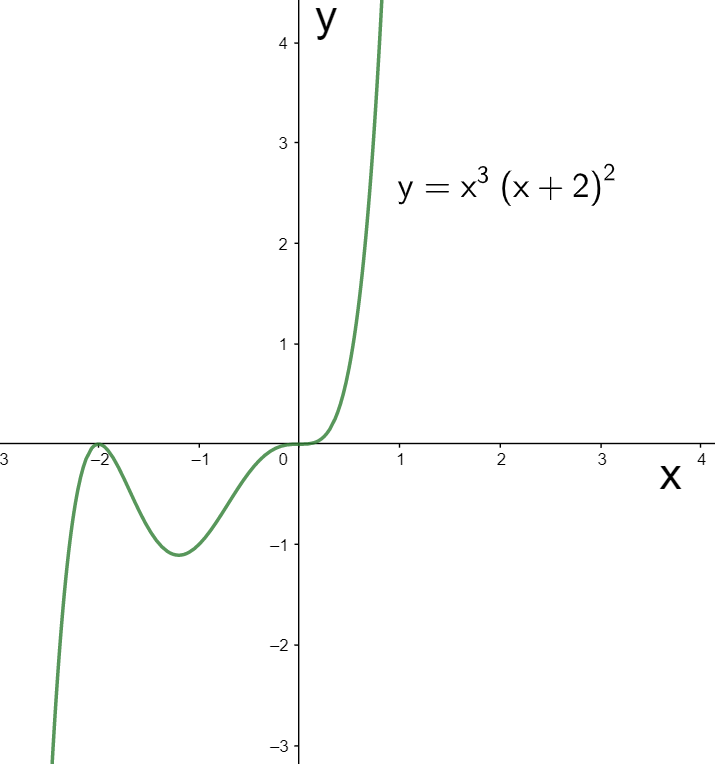
Note: We must note that we cannot draw any conclusion regarding the shape of the curve in a particular interval by knowing its sign in that interval. For this, we need the information regarding its derivative. Also, we can also use the wavy curve method to find out the signs of the function in the different intervals.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The function given in the above question is
$\Rightarrow F\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}$
For determining the zeroes of the given function, we put it equal to zero to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( x \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{3}}{{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
\end{align}$
By using the zero product rule, we can write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{3}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=0 \\
\end{align}$
And
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-2 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, we have found out the zeroes of the given function to be $-2$ and $0$. With reference to these points, we can divide the real number line into three intervals, which are $x < -2$, $-2 < x < 0$ and $x>0$.
We consider the first interval $x < -2$. For checking the sign of $F\left( x \right)$ in this interval, we can select any of the point belonging to this interval and substitute into the given function. Therefore, let us select $x=-3$ and substitute it into the given function to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( -3 \right)={{\left( -3 \right)}^{3}}{{\left( -3+2 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -3 \right)=-27{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -3 \right)=-27 \\
\end{align}$
Since we got a negative value, this means that $F\left( x \right)$ is negative in this interval.
Now, we consider the second interval $-2 < x < 0$. Let us choose $x=-1$ to substitute into the given function to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( -1 \right)={{\left( -1 \right)}^{3}}{{\left( -1+2 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -1 \right)=-1{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( -1 \right)=-1 \\
\end{align}$
We again got a negative value. This means that $F\left( x \right)$ is negative in this interval too.
Finally, we consider the last interval $x>0$. Let us choose $x=1$ and substitute it in the given function to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow F\left( 1 \right)={{\left( 1 \right)}^{3}}{{\left( 1+2 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( 1 \right)=1{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow F\left( 1 \right)=9 \\
\end{align}$
Now, in this interval we got a positive value. Therefore, in this interval the function $F\left( x \right)$ is positive in this interval.
Thus the given function is negative in the intervals $x < -2$ and $-2 < x < 0$ and positive in the interval $x>0$. We can see this in the graph of $F\left( x \right)$ given below.

Note: We must note that we cannot draw any conclusion regarding the shape of the curve in a particular interval by knowing its sign in that interval. For this, we need the information regarding its derivative. Also, we can also use the wavy curve method to find out the signs of the function in the different intervals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




