
How do we find the volume of a triangular pyramid?
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: A pyramid is a polyhedron which has a polygon at its base and a vertex (point) at the top.
Recall that the volume of a pyramid is $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × (Area of base). The base of a triangular pyramid is a triangle. How can we find the area of the base which is triangular in shape?
Complete step-by-step answer:
The volume of a pyramid is $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × (Area of base).
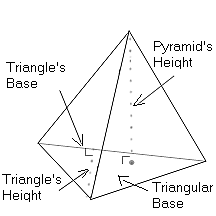
If the base is a triangle with the three sides equal to a, b and c units, then the area of the triangle can be calculated using the Heron's formula: Area = $ \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} $ square units, where s = $ \dfrac{a+b+c}{2} $ .
If instead, the lengths of a base of the triangle and its corresponding heights are known, then the area of the triangle can be calculated as Area = $ \dfrac{1}{2} $ × Height × Base. Note that this base is the "base of the triangle", NOT the "base of the pyramid" and that the height is the "height of the triangle (the perpendicular distance between the base side and its opposite vertex)", NOT the "height of the pyramid".
The base of the pyramid is a flat surface (the triangle in this case), whereas the base of the triangle is a line which is a side of a triangle. Also, the height of the pyramid is the perpendicular distance between the flat surface and the top vertex, whereas the height of the triangle is the perpendicular distance between the base side (line) and the vertex of the triangle which is opposite to the chosen base.
Note: Area of a shape is the number of squares of unit lengths that can fit inside it.
The volume of a solid is calculated as the number of unit cubes (square box) that can fit inside it. It follows that the volume of a right-angled prism is: (Area of base) × (Height) cubic units, which is simply the number of cubes of unit length that can fit on the base, multiplied by the number of unit lengths in the height.
There are two main types of solids based on the types of surfaces:
Polyhedron: It must have flat faces and straight edges. e.g. Parallelepiped (Cube/Cuboid), Tetrahedron etc.
Non-Polyhedron: Some face(s) may be curved. e.g. Cone, Cylinder, Sphere etc.
Right solids (vertically straight, not inclined at an angle) with a flat base and straight edges are of following types:
Prisms: Both the base and the top are identical flat surfaces.
Volume = Height × (Area of base)
Pyramids. The base is a flat surface, and the top is a point.
Volume = $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × (Area of base)
Frustum of a pyramid: Both the base and the top are similar flat surfaces, but not identical.
Volume = $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × $ \left( {{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}}+\sqrt{{{A}_{1}}{{A}_{2}}} \right) $ , where $ {{A}_{1}} $ and $ {{A}_{2}} $ are the areas of the top and base surfaces.
Euler's Formula: For a polyhedron: $ F+V-E=2 $ , where F is the number of faces, V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges.
Recall that the volume of a pyramid is $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × (Area of base). The base of a triangular pyramid is a triangle. How can we find the area of the base which is triangular in shape?
Complete step-by-step answer:
The volume of a pyramid is $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × (Area of base).

If the base is a triangle with the three sides equal to a, b and c units, then the area of the triangle can be calculated using the Heron's formula: Area = $ \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} $ square units, where s = $ \dfrac{a+b+c}{2} $ .
If instead, the lengths of a base of the triangle and its corresponding heights are known, then the area of the triangle can be calculated as Area = $ \dfrac{1}{2} $ × Height × Base. Note that this base is the "base of the triangle", NOT the "base of the pyramid" and that the height is the "height of the triangle (the perpendicular distance between the base side and its opposite vertex)", NOT the "height of the pyramid".
The base of the pyramid is a flat surface (the triangle in this case), whereas the base of the triangle is a line which is a side of a triangle. Also, the height of the pyramid is the perpendicular distance between the flat surface and the top vertex, whereas the height of the triangle is the perpendicular distance between the base side (line) and the vertex of the triangle which is opposite to the chosen base.
Note: Area of a shape is the number of squares of unit lengths that can fit inside it.
The volume of a solid is calculated as the number of unit cubes (square box) that can fit inside it. It follows that the volume of a right-angled prism is: (Area of base) × (Height) cubic units, which is simply the number of cubes of unit length that can fit on the base, multiplied by the number of unit lengths in the height.
There are two main types of solids based on the types of surfaces:
Polyhedron: It must have flat faces and straight edges. e.g. Parallelepiped (Cube/Cuboid), Tetrahedron etc.
Non-Polyhedron: Some face(s) may be curved. e.g. Cone, Cylinder, Sphere etc.
Right solids (vertically straight, not inclined at an angle) with a flat base and straight edges are of following types:
Prisms: Both the base and the top are identical flat surfaces.
Volume = Height × (Area of base)
Pyramids. The base is a flat surface, and the top is a point.
Volume = $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × (Area of base)
Frustum of a pyramid: Both the base and the top are similar flat surfaces, but not identical.
Volume = $ \dfrac{1}{3} $ × Height × $ \left( {{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{2}}+\sqrt{{{A}_{1}}{{A}_{2}}} \right) $ , where $ {{A}_{1}} $ and $ {{A}_{2}} $ are the areas of the top and base surfaces.
Euler's Formula: For a polyhedron: $ F+V-E=2 $ , where F is the number of faces, V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




