
How do you find the vertices, asymptotes, foci and graph $100{{x}^{2}}-81{{y}^{2}}=8100$ ?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: To get the vertices, asymptotes, foci and graph of the given equation, first of all we will modify the given equation in the standard form $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ that will be the form of hyperbola. Then, we will use the different formulas for getting the values of vertices, asymptotes, foci and will draw the graph by using different values for variables.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the given question is:
$100{{x}^{2}}-81{{y}^{2}}=8100$
Now, we will convert it in the standard form of the hyperbola. So, we will divide in the given equation by $8100$ both sides so that can get $1$ right hand side of the equation as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{100{{x}^{2}}}{8100}-\dfrac{81{{y}^{2}}}{8100}=\dfrac{8100}{8100}$
Here, we will complete the division process by getting its quotient as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{81}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{100}=1$
Since, $81$ and $100$ are square of $9$ and $10$ respectively. So, we can write them below as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{9}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{10}^{2}}}=1$
Now, we will compare the obtained form of hyperbola with the standard form of hyperbola when its centre is $\left( 0,0 \right)$ , is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ . we will have:
$\Rightarrow a=9$ and $b=10$
Now, the vertex will be $\left( a,0 \right)$ and $\left( -a,0 \right)$ when its centre is $\left( 0,0 \right)$ . So, we will put the value of $a$ and $b$. Then, the vertex of the obtained hyperbola is:
$\Rightarrow \left( 9,0 \right)$ and $\left( -9,0 \right)$
Here, we will get the asymptotes with help of formula of asymptotes that is $y=\dfrac{b}{a}x$ and $y=-\dfrac{b}{a}x$ . Now, we will apply the required values as:
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{b}{a}x$ and $y=-\dfrac{b}{a}x$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{10}{9}x$ and $y=-\dfrac{10}{9}x$
And the foci of the hyperbola whose equation is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ , is $\left( \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$ and $\left( -\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$ . Now, we will apply the value of the $a$ and $b$ in the foci and will get the foci of the hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{9}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{10}^{2}}}=1$ as:
$\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$ and $\left( -\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{{{9}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}},0 \right)\] and $\left( -\sqrt{{{9}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}},0 \right)$
Now, we do the necessary calculation as:
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{81+100},0 \right)\] and $\left( -\sqrt{81+100},0 \right)$
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{181},0 \right)\] and $\left( -\sqrt{181},0 \right)$
The graph of the hyperbola according to the obtained equation as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{9}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{10}^{2}}}=1$ will be as:
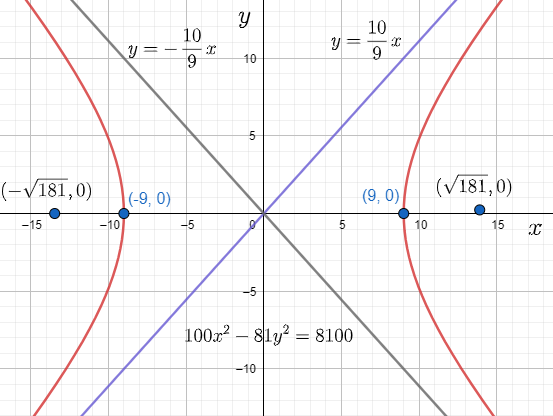
Hence, we got the final results related to the question.
Note: Here, I will write down all the formula to find vertices, asymptotes, foci and graph of hyperbola whose equation is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ , where $\left( h,k \right)$ is the centre of the hyperbola.
So, the vertices are $\left( h+a,k \right)$ and $\left( h-a,k \right)$ .
The asymptotes are $y=\dfrac{b}{a}\left( x-h \right)+k$ and $y=-\dfrac{b}{a}\left( x-h \right)+k$ .
And the foci are $\left( h+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},k \right)$ and $\left( h-\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},k \right)$ .
Complete step by step answer:
Since, the given question is:
$100{{x}^{2}}-81{{y}^{2}}=8100$
Now, we will convert it in the standard form of the hyperbola. So, we will divide in the given equation by $8100$ both sides so that can get $1$ right hand side of the equation as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{100{{x}^{2}}}{8100}-\dfrac{81{{y}^{2}}}{8100}=\dfrac{8100}{8100}$
Here, we will complete the division process by getting its quotient as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{81}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{100}=1$
Since, $81$ and $100$ are square of $9$ and $10$ respectively. So, we can write them below as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{9}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{10}^{2}}}=1$
Now, we will compare the obtained form of hyperbola with the standard form of hyperbola when its centre is $\left( 0,0 \right)$ , is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ . we will have:
$\Rightarrow a=9$ and $b=10$
Now, the vertex will be $\left( a,0 \right)$ and $\left( -a,0 \right)$ when its centre is $\left( 0,0 \right)$ . So, we will put the value of $a$ and $b$. Then, the vertex of the obtained hyperbola is:
$\Rightarrow \left( 9,0 \right)$ and $\left( -9,0 \right)$
Here, we will get the asymptotes with help of formula of asymptotes that is $y=\dfrac{b}{a}x$ and $y=-\dfrac{b}{a}x$ . Now, we will apply the required values as:
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{b}{a}x$ and $y=-\dfrac{b}{a}x$
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{10}{9}x$ and $y=-\dfrac{10}{9}x$
And the foci of the hyperbola whose equation is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ , is $\left( \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$ and $\left( -\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$ . Now, we will apply the value of the $a$ and $b$ in the foci and will get the foci of the hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{9}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{10}^{2}}}=1$ as:
$\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$ and $\left( -\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},0 \right)$
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{{{9}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}},0 \right)\] and $\left( -\sqrt{{{9}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}},0 \right)$
Now, we do the necessary calculation as:
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{81+100},0 \right)\] and $\left( -\sqrt{81+100},0 \right)$
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{181},0 \right)\] and $\left( -\sqrt{181},0 \right)$
The graph of the hyperbola according to the obtained equation as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{9}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{10}^{2}}}=1$ will be as:

Hence, we got the final results related to the question.
Note: Here, I will write down all the formula to find vertices, asymptotes, foci and graph of hyperbola whose equation is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ , where $\left( h,k \right)$ is the centre of the hyperbola.
So, the vertices are $\left( h+a,k \right)$ and $\left( h-a,k \right)$ .
The asymptotes are $y=\dfrac{b}{a}\left( x-h \right)+k$ and $y=-\dfrac{b}{a}\left( x-h \right)+k$ .
And the foci are $\left( h+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},k \right)$ and $\left( h-\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}},k \right)$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




