
How do you find the vertical, horizontal and oblique asymptote for \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\]?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint:
In the given question, we have been asked to find the asymptotes. In order to solve the question, first we need to start by defining the asymptote and the types of asymptotes. Later by applying the properties of asymptote we will apply different conditions and evaluating different values of ‘x’ and ‘y’.
Complete step by step solution:
We have given that,
\[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\],
Let y = \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\]
Thus,
\[y=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\]
Simplify the given expression by using the property of\[{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)\], we get
\[y=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}=\dfrac{\left( x+3 \right)\left( x-3 \right)}{3x-6}\]
Now,
Finding the vertical asymptote:
Vertical asymptote occurs at rational function tends to zero i.e. denominator equals to zero.
Equating the denominator of the given expression equals to 0, we get
\[\Rightarrow 3x-6=0\]
Now solving for the value of ‘x’,
\[\Rightarrow 3x=6\]
\[\therefore x=2\]
Therefore, the vertical asymptote occurs at x = 2.
Now,
Finding the horizontal asymptote:
Since the highest degree of the numerator in the given expression is greater than the highest degree of the denominator in the given expression, thus there is no horizontal asymptote for the given expression.
Therefore, the horizontal asymptote does not occur.
Now,
Finding the oblique asymptote:
Since the highest degree of the numerator in the given expression is one greater than the highest degree of the denominator in the given expression, thus oblique asymptote occurs.
To finding the equation of oblique asymptote;
We have to perform long polynomial division.
After performing the long polynomial division,
We have,
Quotient = \[\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}\]
Remainder = \[\left( -\dfrac{5}{3x-6} \right)\]
Hence, the result is \[\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}+\left( -\dfrac{5}{3x-6} \right)\]
Thus,
The equation of oblique asymptote is;
\[y=\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}\]
Finding different values of ‘x’ and ‘y’,
Graph of the above asymptote is;
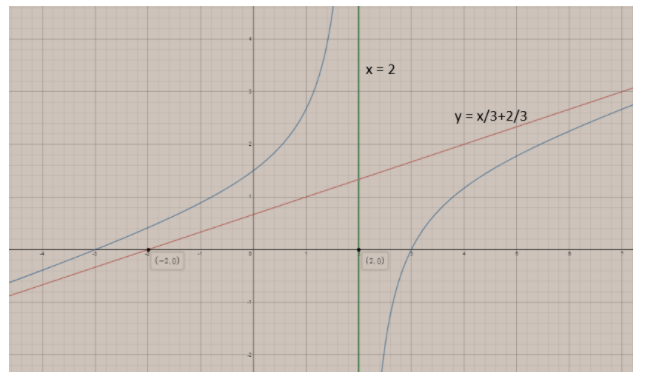
Therefore, we have all the required values of asymptote.
Note:
Students should always need to remember the concept of asymptote and very well know about the different types of conditions and their respective properties. Always make sure that all the terms are in the form of the same variable. Always plot the graph of the asymptote and remember that first draw the axis then mark the point and plot the graph.
In the given question, we have been asked to find the asymptotes. In order to solve the question, first we need to start by defining the asymptote and the types of asymptotes. Later by applying the properties of asymptote we will apply different conditions and evaluating different values of ‘x’ and ‘y’.
Complete step by step solution:
We have given that,
\[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\],
Let y = \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\]
Thus,
\[y=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}\]
Simplify the given expression by using the property of\[{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)\], we get
\[y=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}-9}{3x-6}=\dfrac{\left( x+3 \right)\left( x-3 \right)}{3x-6}\]
Now,
Finding the vertical asymptote:
Vertical asymptote occurs at rational function tends to zero i.e. denominator equals to zero.
Equating the denominator of the given expression equals to 0, we get
\[\Rightarrow 3x-6=0\]
Now solving for the value of ‘x’,
\[\Rightarrow 3x=6\]
\[\therefore x=2\]
Therefore, the vertical asymptote occurs at x = 2.
Now,
Finding the horizontal asymptote:
Since the highest degree of the numerator in the given expression is greater than the highest degree of the denominator in the given expression, thus there is no horizontal asymptote for the given expression.
Therefore, the horizontal asymptote does not occur.
Now,
Finding the oblique asymptote:
Since the highest degree of the numerator in the given expression is one greater than the highest degree of the denominator in the given expression, thus oblique asymptote occurs.
To finding the equation of oblique asymptote;
We have to perform long polynomial division.
After performing the long polynomial division,
We have,
Quotient = \[\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}\]
Remainder = \[\left( -\dfrac{5}{3x-6} \right)\]
Hence, the result is \[\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}+\left( -\dfrac{5}{3x-6} \right)\]
Thus,
The equation of oblique asymptote is;
\[y=\dfrac{x}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}\]
Finding different values of ‘x’ and ‘y’,
| x | Y |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
Graph of the above asymptote is;

Therefore, we have all the required values of asymptote.
Note:
Students should always need to remember the concept of asymptote and very well know about the different types of conditions and their respective properties. Always make sure that all the terms are in the form of the same variable. Always plot the graph of the asymptote and remember that first draw the axis then mark the point and plot the graph.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




