
How do you find the vertex of \[y={{x}^{2}}+8x-9\] ?
Answer
549k+ views
Hint: These types of problems are very simple and easy to solve. The problem is of coordinate geometry of sub-topic parabola, and for solving these types of problems we need to first understand what the different general forms of parabolas are possible in geometry. There are four general types of parabola and for each of them, the corresponding vertex and foci are as follows,
Complete step by step answer:
Now, starting off with the solution of our given problem, we can first of all rearrange the left and right hand side of the given parabolic equation to make it look like one of the standardized form of general equation. So rearranging all the terms we get,
\[y+9={{x}^{2}}+8x\]
Now, since the \[x\] term of the equation has coefficient \[8\] , which is basically \[2\times 4\] , we add \[{{4}^{2}}\], which is basically \[16\], on both sides of the equation, so that the right hand side of the equation becomes a perfect square. We do the operation as,
\[\Rightarrow y+9+16={{x}^{2}}+8x+16\]
Evaluating the values, we write,
\[\Rightarrow y+25={{x}^{2}}+8x+16\] ,
Now, representing the right hand side of the equation as a perfect square, we get,
\[\Rightarrow y+25={{\left( x+4 \right)}^{2}}\]
Rearranging the terms we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( x+4 \right)}^{2}}=y+25\]
We can clearly observe that the above equation is of the form \[{{x}^{2}}=4by\] , where we can say, \[b=\dfrac{1}{4}\] .
We can however rewrite the general parabolic equation as,
\[{{\left( x-0 \right)}^{2}}=4b\left( y-0 \right)\] and from this it is very clear that for this equation \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] is the vertex.
From the formed equation we can get the values of the \[x\] and \[y\] coordinates of vertex as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-4 \\
\end{align}\] and \[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y+25=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-25 \\
\end{align}\]
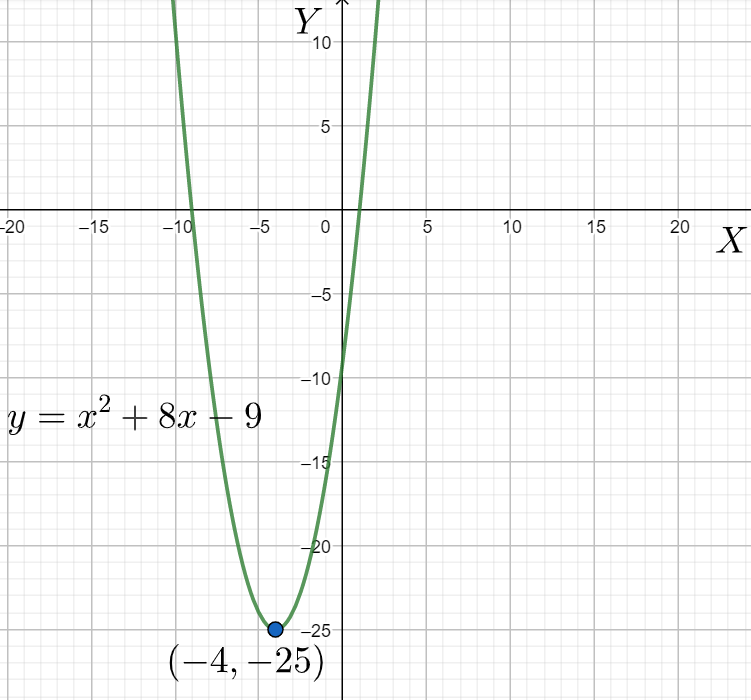
Thus, we can very clearly say that the vertex of the given parabola is, \[\left( -4,-25 \right)\].
Note: We can solve the above given problem using another method, known as the method of shifting of origin or origin transformation, but it is a very complex as well as a long process. In such a process, we transfer the parabolic equation to some other coordinate system. We then find the value of the coordinates in the new system. After that, we revert back to our original coordinate system and evaluate the coordinates in our original system. The solution shown above is the simplest one.
| Equation | Vertex | Foci |
| \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] | \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] | \[\left( a,0 \right)\] |
| \[{{y}^{2}}=-4ax\] | \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] | \[\left( -a,0 \right)\] |
| \[{{x}^{2}}=4by\] | \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] | \[\left( 0,b \right)\] |
| \[{{x}^{2}}=-4by\] | \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] | \[\left( 0,-b \right)\] |
Complete step by step answer:
Now, starting off with the solution of our given problem, we can first of all rearrange the left and right hand side of the given parabolic equation to make it look like one of the standardized form of general equation. So rearranging all the terms we get,
\[y+9={{x}^{2}}+8x\]
Now, since the \[x\] term of the equation has coefficient \[8\] , which is basically \[2\times 4\] , we add \[{{4}^{2}}\], which is basically \[16\], on both sides of the equation, so that the right hand side of the equation becomes a perfect square. We do the operation as,
\[\Rightarrow y+9+16={{x}^{2}}+8x+16\]
Evaluating the values, we write,
\[\Rightarrow y+25={{x}^{2}}+8x+16\] ,
Now, representing the right hand side of the equation as a perfect square, we get,
\[\Rightarrow y+25={{\left( x+4 \right)}^{2}}\]
Rearranging the terms we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( x+4 \right)}^{2}}=y+25\]

We can clearly observe that the above equation is of the form \[{{x}^{2}}=4by\] , where we can say, \[b=\dfrac{1}{4}\] .
We can however rewrite the general parabolic equation as,
\[{{\left( x-0 \right)}^{2}}=4b\left( y-0 \right)\] and from this it is very clear that for this equation \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] is the vertex.
From the formed equation we can get the values of the \[x\] and \[y\] coordinates of vertex as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-4 \\
\end{align}\] and \[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y+25=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-25 \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, we can very clearly say that the vertex of the given parabola is, \[\left( -4,-25 \right)\].
Note: We can solve the above given problem using another method, known as the method of shifting of origin or origin transformation, but it is a very complex as well as a long process. In such a process, we transfer the parabolic equation to some other coordinate system. We then find the value of the coordinates in the new system. After that, we revert back to our original coordinate system and evaluate the coordinates in our original system. The solution shown above is the simplest one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




