
How do you find the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$?
Answer
544.8k+ views
Hint: We have to find the vertex for $f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 2x + 2$. First rewrite the equation in vertex form. Next, use the vertex form of parabola, to determine the values of $a$, $h$, and $k$. Next, find the vertex by putting the value of $h$ and $k$.
Vertex form of a parabola: $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
$d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$
$e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$
Vertex form: $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
Vertex: $\left( {h,k} \right)$
$p = \dfrac{1}{{4a}}$
Focus: $\left( {h,k + p} \right)$
Directrix: $y = k - p$
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the vertex for $f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 2x + 2$.
So, compare ${x^2} + 2x + 2$ with $a{x^2} + bx + c$.
So, first rewrite the equation in vertex form.
For this, complete the square for ${x^2} + 2x + 2$.
Use the form $a{x^2} + bx + c$, to find the values of $a$, $b$, and $c$.
$a = 1,b = 2,c = 2$
Consider the vertex form of a parabola.
$a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
Now, substitute the values of $a$ and $b$ into the formula $d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$.
$d = \dfrac{2}{{2 \times 1}}$
Simplify the right side.
$ \Rightarrow d = 1$
Find the value of $e$ using the formula $e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$.
$e = 2 - \dfrac{{{2^2}}}{{4 \times 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow e = 1$
Now, substitute the values of $a$, $d$, and $e$ into the vertex form $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$.
${\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} + 1$
Set $y$ equal to the new right side.
$y = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} + 1$
Now, use the vertex form, $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$, to determine the values of $a$, $h$, and $k$.
$a = 1$
$h = 1$
$k = 1$
Since the value of $a$ is positive, the parabola opens up.
Opens Up
Find the vertex $\left( {h,k} \right)$.
$\left( { - 1,1} \right)$
Hence, the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ is at $\left( { - 1,1} \right)$.
Note: We can also determine the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ by plotting it.
Graph of $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$:
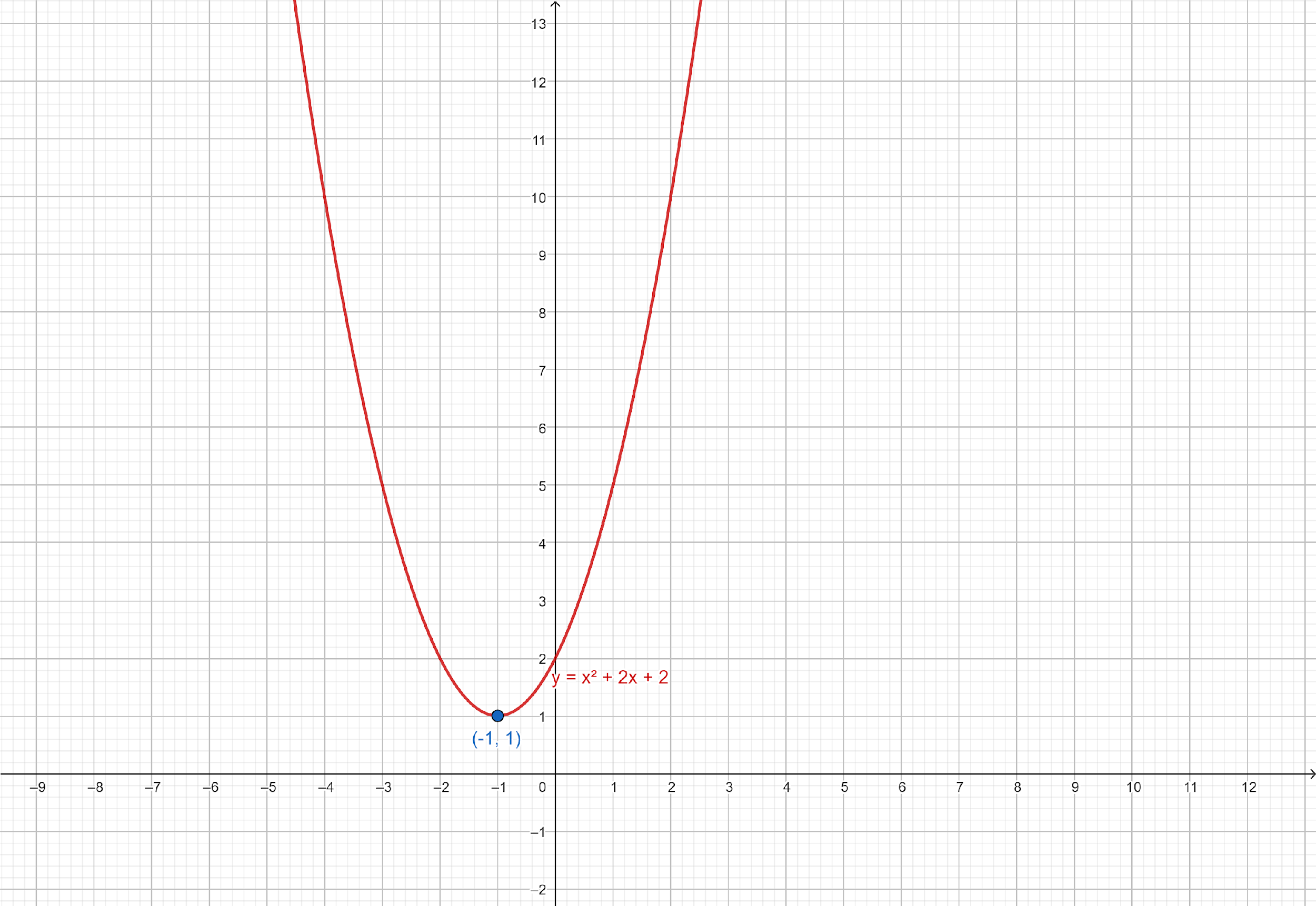
Hence, the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ is at $\left( { - 1,1} \right)$.
2. We can also determine the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ by converting to Vertex Form
Vertex form can be represented as $y = {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
where the point $\left( {h,k} \right)$ is the vertex.
To do that, we should complete the square
$y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$
First, we should try to change the last number in a way so we can factor the entire thing
⇒ we should aim for $y = {x^2} + 2x + 1$
to make it look like $y = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2}$
If we notice, the only difference between the original $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ and the factor-able $y = {x^2} + 2x + 1$ is simply changing the 2 to a 1.
Since we can't randomly change the 2 to a 1, we can add 1 and subtract a 1 to the equation at the same time to keep it balanced.
So, we get
$y = {x^2} + 2x + 1 + 2 - 1$
Organizing
$y = \left( {{x^2} + 2x + 1} \right) + 2 - 1$
Add like terms
$2 - 1 = 1$
Factor
$y = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} + 1$
Now comparing it to $y = {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
We can see that the vertex would be $\left( { - 1,1} \right)$.
Vertex form of a parabola: $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
$d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$
$e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$
Vertex form: $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
Vertex: $\left( {h,k} \right)$
$p = \dfrac{1}{{4a}}$
Focus: $\left( {h,k + p} \right)$
Directrix: $y = k - p$
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the vertex for $f\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 2x + 2$.
So, compare ${x^2} + 2x + 2$ with $a{x^2} + bx + c$.
So, first rewrite the equation in vertex form.
For this, complete the square for ${x^2} + 2x + 2$.
Use the form $a{x^2} + bx + c$, to find the values of $a$, $b$, and $c$.
$a = 1,b = 2,c = 2$
Consider the vertex form of a parabola.
$a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
Now, substitute the values of $a$ and $b$ into the formula $d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$.
$d = \dfrac{2}{{2 \times 1}}$
Simplify the right side.
$ \Rightarrow d = 1$
Find the value of $e$ using the formula $e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$.
$e = 2 - \dfrac{{{2^2}}}{{4 \times 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow e = 1$
Now, substitute the values of $a$, $d$, and $e$ into the vertex form $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$.
${\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} + 1$
Set $y$ equal to the new right side.
$y = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} + 1$
Now, use the vertex form, $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$, to determine the values of $a$, $h$, and $k$.
$a = 1$
$h = 1$
$k = 1$
Since the value of $a$ is positive, the parabola opens up.
Opens Up
Find the vertex $\left( {h,k} \right)$.
$\left( { - 1,1} \right)$
Hence, the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ is at $\left( { - 1,1} \right)$.
Note: We can also determine the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ by plotting it.
Graph of $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$:

Hence, the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ is at $\left( { - 1,1} \right)$.
2. We can also determine the vertex of the parabola: $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ by converting to Vertex Form
Vertex form can be represented as $y = {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
where the point $\left( {h,k} \right)$ is the vertex.
To do that, we should complete the square
$y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$
First, we should try to change the last number in a way so we can factor the entire thing
⇒ we should aim for $y = {x^2} + 2x + 1$
to make it look like $y = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2}$
If we notice, the only difference between the original $y = {x^2} + 2x + 2$ and the factor-able $y = {x^2} + 2x + 1$ is simply changing the 2 to a 1.
Since we can't randomly change the 2 to a 1, we can add 1 and subtract a 1 to the equation at the same time to keep it balanced.
So, we get
$y = {x^2} + 2x + 1 + 2 - 1$
Organizing
$y = \left( {{x^2} + 2x + 1} \right) + 2 - 1$
Add like terms
$2 - 1 = 1$
Factor
$y = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} + 1$
Now comparing it to $y = {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
We can see that the vertex would be $\left( { - 1,1} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




