
How do I find the vertex, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept, $x$-intercept, domain and range of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$?
Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: We have to find the vertex, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept, $x$-intercept, domain and range of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$. First rewrite the equation in vertex form. Next, use the vertex form of parabola, to determine the values of $a$, $h$, and $k$. Next, find the vertex and the distance from the vertex to the focus. Then, find the focus, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept and $x$-intercept. Next, find the minimum value of the parabola by putting $x = - 4$ in $f\left( x \right) = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$. Finally, find the domain and range of the given equation.
Formula used:
Vertex form of a parabola: $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
$d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$
$e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$
Vertex form: $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
Vertex: $\left( {h,k} \right)$
$p = \dfrac{1}{{4a}}$
Focus: $\left( {h,k + p} \right)$
Directrix: $y = k - p$
Complete step by step solution:
We have to find the vertex, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept, $x$-intercept, domain and range of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$.
So, compare ${x^2} + 8x + 12$ with $a{x^2} + bx + c$.
So, first rewrite the equation in vertex form.
For this, complete the square for ${x^2} + 8x + 12$.
Use the form $a{x^2} + bx + c$, to find the values of $a$, $b$, and $c$.
$a = 1,b = 8,c = 12$
Consider the vertex form of a parabola.
$a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
Now, substitute the values of $a$ and $b$ into the formula $d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$.
$d = \dfrac{8}{{2 \times 1}}$
Simplify the right side.
$ \Rightarrow d = 4$
Find the value of $e$ using the formula $e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$.
$e = 12 - \dfrac{{{8^2}}}{{4 \times 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow e = - 4$
Now, substitute the values of $a$, $d$, and $e$ into the vertex form $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$.
${\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$
Set $y$ equal to the new right side.
$y = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$
Now, use the vertex form, $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$, to determine the values of $a$, $h$, and $k$.
$a = 1$
$h = - 4$
$k = - 4$
Since the value of $a$ is positive, the parabola opens up.
Opens Up
Find the vertex $\left( {h,k} \right)$.
$\left( { - 4, - 4} \right)$
Now, find $p$, the distance from the vertex to the focus.
Find the distance from the vertex to a focus of the parabola by using the following formula.
$\dfrac{1}{{4a}}$
Substitute the value of $a$ into the formula.
$\dfrac{1}{{4 \times 1}}$
Multiply $4$ by $1$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}$
Find the focus.
The focus of a parabola can be found by adding $p$ to the $y$-coordinate $k$ if the parabola opens up or down.
$\left( {h,k + p} \right)$
Now, substitute the known values of $h$, $p$, and $k$ into the formula and simplify.
$\left( { - 4, - \dfrac{{15}}{4}} \right)$
Find the axis of symmetry by finding the line that passes through the vertex and the focus.
$x = - 4$
Find the $y$-intercept.
Use the original equation, and substitute $0$ for $x$.
$f\left( 0 \right) = {\left( 0 \right)^2} + 8\left( 0 \right) + 12$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right) = 12$
Therefore, the $y$-intercept is $\left( {0,12} \right)$.
Find the $x$-intercept.
Use equation $y = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$, and substitute $0$ for $y$.
${\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} = 4$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} = {2^2}$
$ \Rightarrow x + 4 = \pm 2$
$ \Rightarrow x = - 2, - 6$
Therefore, the $x$-intercept is $\left( { - 2,0} \right),\left( { - 6,0} \right)$.
Find the minimum value of the parabola by putting $x = - 4$ in $f\left( x \right) = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$.
$f\left( { - 4} \right) = {\left( { - 4 + 4} \right)^2} - 4$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( { - 4} \right) = - 4$
The minimum value is $ - 4$.
The domain is all real numbers.
The range is all real numbers greater than or equal to the minimum value, or $\left\{ {f\left( x \right)|f\left( x \right) \geqslant - 4} \right\}$.
Hence, for $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$
Vertex: $\left( { - 4, - 4} \right)$
Axis of symmetry: $x = - 4$
$y$-intercept: $\left( {0,12} \right)$
$x$-intercept: $\left( { - 2,0} \right),\left( { - 6,0} \right)$
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ or $\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$
Range: $\left[ { - 4,\infty } \right)$
Note: We can also determine the vertex, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept, $x$-intercept, domain and range of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$ by plotting it.
Graph of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$:
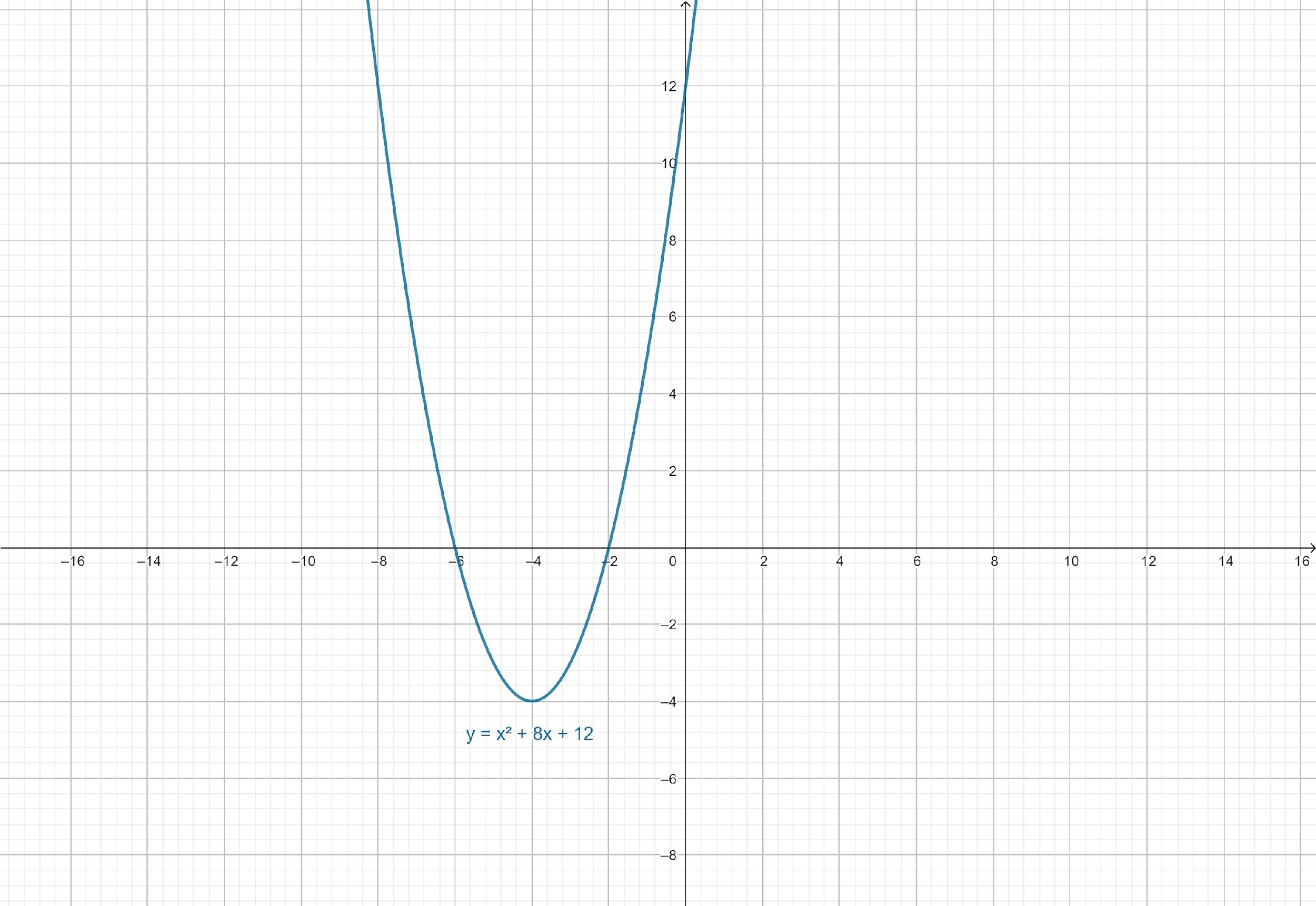
Hence, for $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$
Vertex: $\left( { - 4, - 4} \right)$
Axis of symmetry: $x = - 4$
$y$-intercept: $\left( {0,12} \right)$
$x$-intercept: $\left( { - 2,0} \right),\left( { - 6,0} \right)$
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ or $\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$
Range: $\left[ { - 4,\infty } \right)$
Formula used:
Vertex form of a parabola: $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
$d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$
$e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$
Vertex form: $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$
Vertex: $\left( {h,k} \right)$
$p = \dfrac{1}{{4a}}$
Focus: $\left( {h,k + p} \right)$
Directrix: $y = k - p$
Complete step by step solution:
We have to find the vertex, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept, $x$-intercept, domain and range of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$.
So, compare ${x^2} + 8x + 12$ with $a{x^2} + bx + c$.
So, first rewrite the equation in vertex form.
For this, complete the square for ${x^2} + 8x + 12$.
Use the form $a{x^2} + bx + c$, to find the values of $a$, $b$, and $c$.
$a = 1,b = 8,c = 12$
Consider the vertex form of a parabola.
$a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$
Now, substitute the values of $a$ and $b$ into the formula $d = \dfrac{b}{{2a}}$.
$d = \dfrac{8}{{2 \times 1}}$
Simplify the right side.
$ \Rightarrow d = 4$
Find the value of $e$ using the formula $e = c - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{4a}}$.
$e = 12 - \dfrac{{{8^2}}}{{4 \times 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow e = - 4$
Now, substitute the values of $a$, $d$, and $e$ into the vertex form $a{\left( {x + d} \right)^2} + e$.
${\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$
Set $y$ equal to the new right side.
$y = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$
Now, use the vertex form, $y = a{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + k$, to determine the values of $a$, $h$, and $k$.
$a = 1$
$h = - 4$
$k = - 4$
Since the value of $a$ is positive, the parabola opens up.
Opens Up
Find the vertex $\left( {h,k} \right)$.
$\left( { - 4, - 4} \right)$
Now, find $p$, the distance from the vertex to the focus.
Find the distance from the vertex to a focus of the parabola by using the following formula.
$\dfrac{1}{{4a}}$
Substitute the value of $a$ into the formula.
$\dfrac{1}{{4 \times 1}}$
Multiply $4$ by $1$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}$
Find the focus.
The focus of a parabola can be found by adding $p$ to the $y$-coordinate $k$ if the parabola opens up or down.
$\left( {h,k + p} \right)$
Now, substitute the known values of $h$, $p$, and $k$ into the formula and simplify.
$\left( { - 4, - \dfrac{{15}}{4}} \right)$
Find the axis of symmetry by finding the line that passes through the vertex and the focus.
$x = - 4$
Find the $y$-intercept.
Use the original equation, and substitute $0$ for $x$.
$f\left( 0 \right) = {\left( 0 \right)^2} + 8\left( 0 \right) + 12$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right) = 12$
Therefore, the $y$-intercept is $\left( {0,12} \right)$.
Find the $x$-intercept.
Use equation $y = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$, and substitute $0$ for $y$.
${\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} = 4$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} = {2^2}$
$ \Rightarrow x + 4 = \pm 2$
$ \Rightarrow x = - 2, - 6$
Therefore, the $x$-intercept is $\left( { - 2,0} \right),\left( { - 6,0} \right)$.
Find the minimum value of the parabola by putting $x = - 4$ in $f\left( x \right) = {\left( {x + 4} \right)^2} - 4$.
$f\left( { - 4} \right) = {\left( { - 4 + 4} \right)^2} - 4$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( { - 4} \right) = - 4$
The minimum value is $ - 4$.
The domain is all real numbers.
The range is all real numbers greater than or equal to the minimum value, or $\left\{ {f\left( x \right)|f\left( x \right) \geqslant - 4} \right\}$.
Hence, for $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$
Vertex: $\left( { - 4, - 4} \right)$
Axis of symmetry: $x = - 4$
$y$-intercept: $\left( {0,12} \right)$
$x$-intercept: $\left( { - 2,0} \right),\left( { - 6,0} \right)$
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ or $\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$
Range: $\left[ { - 4,\infty } \right)$
Note: We can also determine the vertex, axis of symmetry, $y$-intercept, $x$-intercept, domain and range of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$ by plotting it.
Graph of $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$:

Hence, for $y = {x^2} + 8x + 12$
Vertex: $\left( { - 4, - 4} \right)$
Axis of symmetry: $x = - 4$
$y$-intercept: $\left( {0,12} \right)$
$x$-intercept: $\left( { - 2,0} \right),\left( { - 6,0} \right)$
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ or $\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$
Range: $\left[ { - 4,\infty } \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




