
How do you find the vertex and the intercepts for \[y = {x^2} + 8x + 15\] ?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: The equation of the form \[{(x - h)^2} = 4p(y - k)\] is the equation of a parabola. The value of \[x\] - coordinate of the vertex = \[ - \dfrac{b}{{2a}}\] and putting this value of \[x\] in the given equation, value of the \[y\] coordinate of the vertex can be determined.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let \[y = {x^2} + 8x + 15\] be considered as \[y = a{x^2} + bx + c\]
Now, \[x\] coordinate of vertex will be given by \[ - \dfrac{b}{{2a}}\] , i.e., \[x\] coordinate of vertex = \[ - \dfrac{8}{2} = - 4\]
Therefore, \[y\] -coordinate of the vertex will be (substituting the \[x\] coordinate in the equation)
\[ \Rightarrow y = {( - 4)^2} + 8( - 4) + 15\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 1\]
Hence, coordinates of the vertex are $\left( { - 4, - 1} \right)$ .
To find the \[y\] -intercept, put \[x = 0\] in the equation;
Hence, \[y\] intercept=15.
To find the \[x\] -intercept, put \[y = 0\] in the equation
\[{x^2} + 8x + 15 = 0\]
The above equation becomes a quadratic equation. We need to find the roots of this equation. Roots are those values for which the equation returns zero as a value. This equation can be written as
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + (3 + 5)x + (3 \times 5) = 0\]
Splitting the middle term so that we can find common and regroup them, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 3x + 5x + 15 = 0\]
Taking common and regrouping
\[ \Rightarrow x(x + 3) + 5(x + 3) = 0\]
Making factors,
\[ \Rightarrow (x + 3)(x + 5) = 0\]
Keeping each factor equal to 0,
\[ \Rightarrow x + 3 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 3\]
Now, we will keep another factor equal to 0,
\[ \Rightarrow x + 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 5\]
Finding the roots of the above equation we get,
\[x = - 3\] and \[ - 5\] .
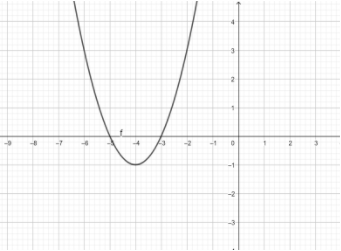
Hence, intercepts of \[x\] will be \[ - 3\] and \[ - 5\]. Hence, now we will plot these points on the graph.
Note: A parabola is a curve which is equidistant from a fixed point (called the focus) and a straight line (called the directrix).
The general equation of a parabola is of the form, \[y = {x^2}\] , when the vertex is at the origin \[(0,0)\] . The vertex is the point where the parabola is the sharpest.
\[{(x - h)^2} = 4p(y - k)\] is the equation of a parabola with vertex not at origin. The coordinates of the vertex are \[(h,k)\] . Axis of symmetry is determined by the value \[x = h\] .
The term \[p\] determines whether the parabola will be opening upwards or downwards. If \[p > 0\] , parabola opens upwards, else if, \[p < 0\] , parabola opens downwards.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let \[y = {x^2} + 8x + 15\] be considered as \[y = a{x^2} + bx + c\]
Now, \[x\] coordinate of vertex will be given by \[ - \dfrac{b}{{2a}}\] , i.e., \[x\] coordinate of vertex = \[ - \dfrac{8}{2} = - 4\]
Therefore, \[y\] -coordinate of the vertex will be (substituting the \[x\] coordinate in the equation)
\[ \Rightarrow y = {( - 4)^2} + 8( - 4) + 15\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 1\]
Hence, coordinates of the vertex are $\left( { - 4, - 1} \right)$ .
To find the \[y\] -intercept, put \[x = 0\] in the equation;
Hence, \[y\] intercept=15.
To find the \[x\] -intercept, put \[y = 0\] in the equation
\[{x^2} + 8x + 15 = 0\]
The above equation becomes a quadratic equation. We need to find the roots of this equation. Roots are those values for which the equation returns zero as a value. This equation can be written as
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + (3 + 5)x + (3 \times 5) = 0\]
Splitting the middle term so that we can find common and regroup them, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 3x + 5x + 15 = 0\]
Taking common and regrouping
\[ \Rightarrow x(x + 3) + 5(x + 3) = 0\]
Making factors,
\[ \Rightarrow (x + 3)(x + 5) = 0\]
Keeping each factor equal to 0,
\[ \Rightarrow x + 3 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 3\]
Now, we will keep another factor equal to 0,
\[ \Rightarrow x + 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = - 5\]
Finding the roots of the above equation we get,
\[x = - 3\] and \[ - 5\] .
Hence, intercepts of \[x\] will be \[ - 3\] and \[ - 5\]. Hence, now we will plot these points on the graph.

Note: A parabola is a curve which is equidistant from a fixed point (called the focus) and a straight line (called the directrix).
The general equation of a parabola is of the form, \[y = {x^2}\] , when the vertex is at the origin \[(0,0)\] . The vertex is the point where the parabola is the sharpest.
\[{(x - h)^2} = 4p(y - k)\] is the equation of a parabola with vertex not at origin. The coordinates of the vertex are \[(h,k)\] . Axis of symmetry is determined by the value \[x = h\] .
The term \[p\] determines whether the parabola will be opening upwards or downwards. If \[p > 0\] , parabola opens upwards, else if, \[p < 0\] , parabola opens downwards.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




