
Find the values of \[\theta \] and p, if the equation \[xcos\theta +ysin\theta =p~\] is the normal form of the line \[\sqrt{3}x+y+2=0\]
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: In geometry, a line can be defined as a straight one- dimensional figure that has no thickness and extends endlessly in both directions. It is often described as the shortest distance between any two points.
Complete step-by-step solution
The equation of the straight line upon which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is p and this perpendicular makes an angle α with the x-axis is $x\cos \alpha +y\sin \alpha =p$.
In the below diagram, we have shown the equation of a line $x\cos \alpha +y\sin \alpha =p$.
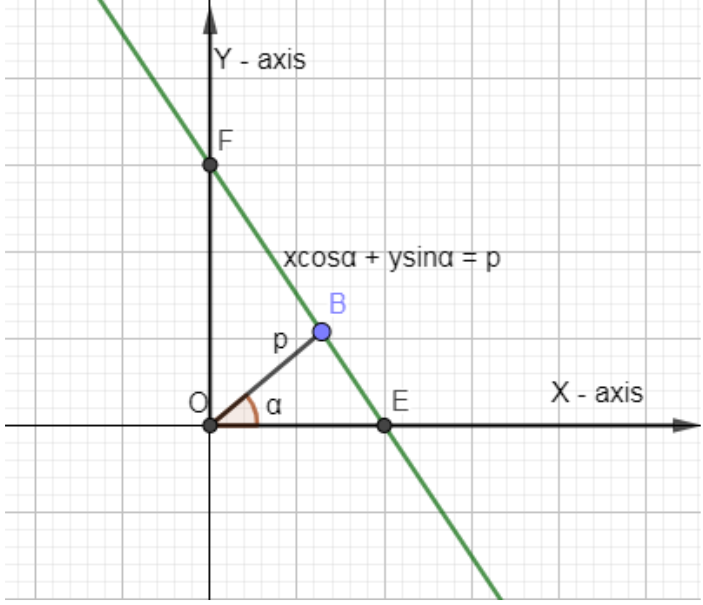
If the line length of the perpendicular drawn from the origin upon a line and the angle that the perpendicular makes with the positive direction of the x-axis be given then to find the equation of the line.
This is the normal form of a line.
As mentioned in the question, we have to find the values of \[\theta \] and p for the given line when it is converted into the normal form of a line.
Now, to convert the given equation into the normal form, we can do the following:-
Firstly, we will divide the equation that is both sides of the equation with 2, and then we will observe the equation that is obtained as follows
\[-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}x-\dfrac{1}{2}y=1\]
Now, we can observe that the coefficients of x and y can be converted as sin and cos form as follows
\[\begin{align}
& x\cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+y\sin \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=1 \\
& x\cos \dfrac{7\pi }{6}+y\sin \dfrac{7\pi }{6}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, on comparing this equation with the normal form of a line, we get the following result as \[\theta =\dfrac{7\pi }{6}\] and p=1.
Note: The mistake that you could make is that even after writing \[\sqrt{3}x+y+2=0\] in the form of \[xcos\theta +ysin\theta =p~\], you might be wrong if you don’t know the value of $\cos \theta \And \sin \theta $ lies from -1 to 1.
Rewriting \[\sqrt{3}x+y+2=0\] we get,
\[\sqrt{3}x+y=-2\]
Now, you can write the value of $\cos \theta =\sqrt{3}\And \sin \theta =1$ if you don’t know that “p” is the length of the perpendicular from the origin and we know that length cannot be negative. Also, if you don’t know the value of $\cos \theta \And \sin \theta $ lies from -1 to 1 then also you can write these values of $\cos \theta \And \sin \theta $ so make sure you won’t make such mistakes.
Complete step-by-step solution
The equation of the straight line upon which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is p and this perpendicular makes an angle α with the x-axis is $x\cos \alpha +y\sin \alpha =p$.
In the below diagram, we have shown the equation of a line $x\cos \alpha +y\sin \alpha =p$.

If the line length of the perpendicular drawn from the origin upon a line and the angle that the perpendicular makes with the positive direction of the x-axis be given then to find the equation of the line.
This is the normal form of a line.
As mentioned in the question, we have to find the values of \[\theta \] and p for the given line when it is converted into the normal form of a line.
Now, to convert the given equation into the normal form, we can do the following:-
Firstly, we will divide the equation that is both sides of the equation with 2, and then we will observe the equation that is obtained as follows
\[-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}x-\dfrac{1}{2}y=1\]
Now, we can observe that the coefficients of x and y can be converted as sin and cos form as follows
\[\begin{align}
& x\cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+y\sin \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=1 \\
& x\cos \dfrac{7\pi }{6}+y\sin \dfrac{7\pi }{6}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, on comparing this equation with the normal form of a line, we get the following result as \[\theta =\dfrac{7\pi }{6}\] and p=1.
Note: The mistake that you could make is that even after writing \[\sqrt{3}x+y+2=0\] in the form of \[xcos\theta +ysin\theta =p~\], you might be wrong if you don’t know the value of $\cos \theta \And \sin \theta $ lies from -1 to 1.
Rewriting \[\sqrt{3}x+y+2=0\] we get,
\[\sqrt{3}x+y=-2\]
Now, you can write the value of $\cos \theta =\sqrt{3}\And \sin \theta =1$ if you don’t know that “p” is the length of the perpendicular from the origin and we know that length cannot be negative. Also, if you don’t know the value of $\cos \theta \And \sin \theta $ lies from -1 to 1 then also you can write these values of $\cos \theta \And \sin \theta $ so make sure you won’t make such mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




