
How do you find the values of six trigonometric functions given $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{4}{5}$ and $\theta $ lies in Quadrant III?
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: We have given the value of one of the trigonometric functions i.e. $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{4}{5}$ and we are asked to find the other six trigonometric functions. The other 5 trigonometric functions are: $\sin \theta ,\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\sec \theta \And \csc \theta $. From the right angled triangle, we are going to find the $\sin \theta $ from the given $\cos \theta $. And then find the other trigonometric functions.
Complete step by step solution:
In the above problem, we have given the value of $\cos \theta $ as follows:
$\cos \theta =-\dfrac{4}{5}$
It is also given that $\theta $ lies in Quadrant III so accordingly put the signs in front of trigonometric functions.
In the below figure, we have drawn a right angled triangle with angle $\theta $.
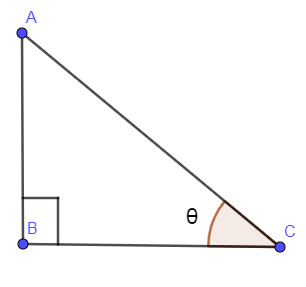
We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{B}{H}$ where “B” is the base corresponding to angle $\theta $ and “H” is the hypotenuse of the right triangle. Now, we have given $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{4}{5}$, let us forget the negative sign and just concentrate on the absolute value then,
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{B}{H}$
We can calculate the value of perpendicular (“P”) by using the Pythagoras theorem which is equal to:
$H=\sqrt{{{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}$
Now, substituting the value of “H” and “B” in the above equation we get,
$5=\sqrt{{{P}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}}$
Squaring on both the sides we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 25={{P}^{2}}+16 \\
& \Rightarrow 25-16={{P}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 9={{P}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking square root on both the sides we get,
$3=P$
Now, we know that:
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}$
Substituting the value of “P” and “H” which we have calculated above we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}$
Now, as $\theta $ lies in Quadrant III and we know that sine is also negative in third quadrant so the in the above value of sine we have to put negative sign and we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \theta =-\dfrac{3}{5}$
And we also that:
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B}$
Substituting the value of “P” and “B” in the above equation we get,
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$
And we know that tangent is positive in the third quadrant so we don’t have to make any changes in the above equation.
And we know that $\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ so substituting the value of $\tan \theta $ in this cot expression we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Also, $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$ so substituting the value of $\sin \theta $ in this csc expression we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{-\dfrac{3}{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow \csc \theta =-\dfrac{5}{3} \\
\end{align}$
And we know that $\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }$ then substituting the value of $\cos \theta $ in this expression we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{-\dfrac{4}{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sec \theta =-\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we have found all the trigonometric functions corresponding to given $\cos \theta $.
Note: The plausible mistake that could be possible is that you might forgetful of the signs corresponding to the trigonometric functions like $\sin ,\cos ,\sec ,\csc $ are negative in the third quadrant whereas $\tan \And \cot $ are positive in the third quadrant so make sure you won’t make this mistake in the examination.
Complete step by step solution:
In the above problem, we have given the value of $\cos \theta $ as follows:
$\cos \theta =-\dfrac{4}{5}$
It is also given that $\theta $ lies in Quadrant III so accordingly put the signs in front of trigonometric functions.
In the below figure, we have drawn a right angled triangle with angle $\theta $.

We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{B}{H}$ where “B” is the base corresponding to angle $\theta $ and “H” is the hypotenuse of the right triangle. Now, we have given $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{4}{5}$, let us forget the negative sign and just concentrate on the absolute value then,
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{B}{H}$
We can calculate the value of perpendicular (“P”) by using the Pythagoras theorem which is equal to:
$H=\sqrt{{{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}$
Now, substituting the value of “H” and “B” in the above equation we get,
$5=\sqrt{{{P}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}}}$
Squaring on both the sides we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 25={{P}^{2}}+16 \\
& \Rightarrow 25-16={{P}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 9={{P}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking square root on both the sides we get,
$3=P$
Now, we know that:
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}$
Substituting the value of “P” and “H” which we have calculated above we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}$
Now, as $\theta $ lies in Quadrant III and we know that sine is also negative in third quadrant so the in the above value of sine we have to put negative sign and we get,
$\Rightarrow \sin \theta =-\dfrac{3}{5}$
And we also that:
$\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B}$
Substituting the value of “P” and “B” in the above equation we get,
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$
And we know that tangent is positive in the third quadrant so we don’t have to make any changes in the above equation.
And we know that $\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ so substituting the value of $\tan \theta $ in this cot expression we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Also, $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$ so substituting the value of $\sin \theta $ in this csc expression we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{-\dfrac{3}{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow \csc \theta =-\dfrac{5}{3} \\
\end{align}$
And we know that $\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }$ then substituting the value of $\cos \theta $ in this expression we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{-\dfrac{4}{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sec \theta =-\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we have found all the trigonometric functions corresponding to given $\cos \theta $.
Note: The plausible mistake that could be possible is that you might forgetful of the signs corresponding to the trigonometric functions like $\sin ,\cos ,\sec ,\csc $ are negative in the third quadrant whereas $\tan \And \cot $ are positive in the third quadrant so make sure you won’t make this mistake in the examination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




