
Find the value of the following polynomial at the indicated value of the variable
$p\left( x \right)=5{{x}^{2}}-3x+7$ at x=1.
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: Substitute the value x = 1 in the expression for p(x). Calculate the value of each of the terms in p(x) and hence find the value of p(x) at x = 1. Alternatively, use synthetic division to calculate the value of p(x) at x = 1.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have $p\left( x \right)=5{{x}^{2}}-3x+7$
Calculating the value of each of the terms at x= 1:
Calculating the value of $5{{x}^{2}}:$
We have $5{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}=5\times 1=5$
Calculating the value of 3x:
We have $3\left( 1 \right)=3$
Hence, we have $p\left( 1 \right)=5-3+7=9$
Hence, the value of p(x) at x=1 is 9.
Note: Alternative method: Synthetic division: Best method.
Synthetic division method is a shorthand method of the polynomial division in the special case of dividing by a linear factor.
In this method, we start by writing coefficients of the polynomial in order from the highest degree to the constant term. If in between some degree terms are missing we set their coefficient as 0.
Consider the polynomial $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+x$ and we need to find the remainder on dividing p(x) by $g\left( x \right)=x-2$.
We will first write the missing powers of x between 4 and 0
Hence, $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}+0{{x}^{3}}+{{x}^{2}}+x+0$.
Then we write these coefficients inside the division symbol as shown below
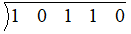
Now we put the zero of the divisor at the left. Here zero of the divisor is x= 2.
Hence, we write as follows
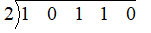
Under the first number inside the division symbol, we put 0 as shown

Now we add the numbers in the same column, as shown
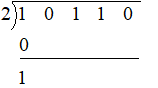
We call that number a carrydown. Here carrydown is 1.
Now we multiply the carrydown by the zero of the divisor and put it under the next coefficient as show
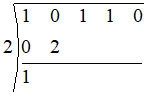
Again we add the two numbers in the same column, we get
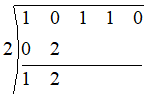
Multiplying the carry down by the zero, we get
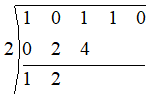
Continuing in this way we have the following table
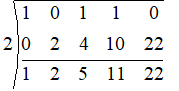
The last carrydown will be the remainder = 22.
This is also the value of $p\left( 2 \right)$.
Also if the divisor has leading coefficient 1(which in this case is true), then the quotient can be found from the carrydowns
We have the carrydowns(except the last) as $\begin{matrix}
1 & 2 & 5 & 11 \\
\end{matrix}$
Start by giving lowest degree(i.e. 0) to the right most carrydown and increase the degree by 1 as we move right to left.
Hence, we have
$\begin{matrix}
1{{x}^{3}} & 2{{x}^{2}} & 5x & 11 \\
\end{matrix}$
Add the resultant terms
Hence, we have
$q={{x}^{3}}+2{{x}^{2}}+5x+11$, which is the required coefficient of division.
Following similar procedure for $p\left( x \right)=5{{x}^{2}}-3x+7$, we create the following table
For x = 1:
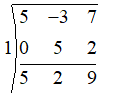
Since the last carrydown is 9, we have $p\left( 1 \right)=9$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have $p\left( x \right)=5{{x}^{2}}-3x+7$
Calculating the value of each of the terms at x= 1:
Calculating the value of $5{{x}^{2}}:$
We have $5{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}=5\times 1=5$
Calculating the value of 3x:
We have $3\left( 1 \right)=3$
Hence, we have $p\left( 1 \right)=5-3+7=9$
Hence, the value of p(x) at x=1 is 9.
Note: Alternative method: Synthetic division: Best method.
Synthetic division method is a shorthand method of the polynomial division in the special case of dividing by a linear factor.
In this method, we start by writing coefficients of the polynomial in order from the highest degree to the constant term. If in between some degree terms are missing we set their coefficient as 0.
Consider the polynomial $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{2}}+x$ and we need to find the remainder on dividing p(x) by $g\left( x \right)=x-2$.
We will first write the missing powers of x between 4 and 0
Hence, $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}+0{{x}^{3}}+{{x}^{2}}+x+0$.
Then we write these coefficients inside the division symbol as shown below
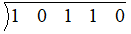
Now we put the zero of the divisor at the left. Here zero of the divisor is x= 2.
Hence, we write as follows
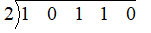
Under the first number inside the division symbol, we put 0 as shown

Now we add the numbers in the same column, as shown

We call that number a carrydown. Here carrydown is 1.
Now we multiply the carrydown by the zero of the divisor and put it under the next coefficient as show

Again we add the two numbers in the same column, we get

Multiplying the carry down by the zero, we get

Continuing in this way we have the following table

The last carrydown will be the remainder = 22.
This is also the value of $p\left( 2 \right)$.
Also if the divisor has leading coefficient 1(which in this case is true), then the quotient can be found from the carrydowns
We have the carrydowns(except the last) as $\begin{matrix}
1 & 2 & 5 & 11 \\
\end{matrix}$
Start by giving lowest degree(i.e. 0) to the right most carrydown and increase the degree by 1 as we move right to left.
Hence, we have
$\begin{matrix}
1{{x}^{3}} & 2{{x}^{2}} & 5x & 11 \\
\end{matrix}$
Add the resultant terms
Hence, we have
$q={{x}^{3}}+2{{x}^{2}}+5x+11$, which is the required coefficient of division.
Following similar procedure for $p\left( x \right)=5{{x}^{2}}-3x+7$, we create the following table
For x = 1:

Since the last carrydown is 9, we have $p\left( 1 \right)=9$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




