
Find the value of the following expression:
$\sin 690{}^\circ \cos 930{}^\circ +\tan \left( -765{}^\circ \right)\csc \left( -1170{}^\circ \right)$
Answer
603.6k+ views
Hint: Convert the angles into radians by multiplying the degree measure of angle with $\dfrac{\pi }{180}$. Use the rules of conversion of $T\left( n\dfrac{\pi }{2}\pm x \right)\to T'\left( x \right),n\in \mathbb{Z}$, where T and T’ are trigonometric ratios. Use the values of sine cosine tangent cotangent secant and cosecant at angles $0,\dfrac{\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and hence find the value of the given expression.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Converting angles in degrees to angles in radians:
We have
[a] $690{}^\circ =\dfrac{690}{180}\times \pi =\dfrac{23\pi }{6}$ radians
[b] $930{}^\circ =\dfrac{930}{180}\pi =\dfrac{31}{6}\pi $ radians
[c] $765{}^\circ =\dfrac{765\pi }{180}=\dfrac{17\pi }{4}$
[d] $1170{}^\circ =\dfrac{1170\pi }{180}=\dfrac{13\pi }{2}$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin 690{}^\circ \cos 930{}^\circ +\tan \left( -765{}^\circ \right)\csc \left( -1170{}^\circ \right)=\sin \dfrac{23\pi }{6}\cos \dfrac{31\pi }{6}+\tan \left( -\dfrac{17\pi }{4} \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{-13\pi }{2} \right)$
We know that $\tan \left( -x \right)=-\tan x$ and $\csc \left( -x \right)=-\csc x$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin \dfrac{23\pi }{6}\cos \dfrac{31\pi }{6}+\tan \dfrac{17\pi }{4}\csc \dfrac{13\pi }{2}$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin \left( 4\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\cos \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+\tan \left( 4\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\csc \left( 6\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$
We know that $\sin \left( 4\pi -x \right)=-\sin x,\cos \left( 5\pi +x \right)=-\cos x,\tan \left( 4\pi +x \right)=\tan x,\csc \left( 6\pi +x \right)=\csc x$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}+\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}\csc \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
We have the following table for the trigonometric ratios of $0,\dfrac{\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
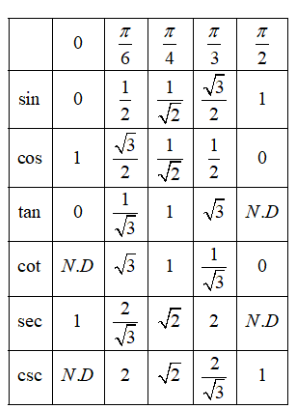
From the table, we have
$\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{1}{2},\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2},\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}=1$ and $\csc \dfrac{\pi }{2}=1$
Hence, we have
$S=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+1\times 1=1+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}$
Note: Rule for converting $T\left( n\dfrac{\pi }{2}\pm x \right)$ to $T'\left( x \right)$, where T and T’ are trigonometric ratios.
If n is even the final expression will be of T. If n is odd, the final expression will contain the complement of T.
The complement of sin is cos and vice versa
The complement of tan is cot and vice versa
The complement of cosec is sec and vice versa.
Sign of the final expression is determined by the quadrant in which $n\dfrac{\pi }{2}\pm x$ falls.
Keeping the above points in consideration, we have
$\sin \left( 4\pi -x \right)=\sin \left( 8\dfrac{\pi }{2}-x \right)$
Now 8 is even, hence the final expression will be of sinx.
Also, $4\pi -x$ falls in the fourth quadrant in which sinx is negative
Hence, we have
$\sin \left( 4\pi -x \right)=-\sin x$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Converting angles in degrees to angles in radians:
We have
[a] $690{}^\circ =\dfrac{690}{180}\times \pi =\dfrac{23\pi }{6}$ radians
[b] $930{}^\circ =\dfrac{930}{180}\pi =\dfrac{31}{6}\pi $ radians
[c] $765{}^\circ =\dfrac{765\pi }{180}=\dfrac{17\pi }{4}$
[d] $1170{}^\circ =\dfrac{1170\pi }{180}=\dfrac{13\pi }{2}$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin 690{}^\circ \cos 930{}^\circ +\tan \left( -765{}^\circ \right)\csc \left( -1170{}^\circ \right)=\sin \dfrac{23\pi }{6}\cos \dfrac{31\pi }{6}+\tan \left( -\dfrac{17\pi }{4} \right)\csc \left( \dfrac{-13\pi }{2} \right)$
We know that $\tan \left( -x \right)=-\tan x$ and $\csc \left( -x \right)=-\csc x$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin \dfrac{23\pi }{6}\cos \dfrac{31\pi }{6}+\tan \dfrac{17\pi }{4}\csc \dfrac{13\pi }{2}$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin \left( 4\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\cos \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+\tan \left( 4\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)\csc \left( 6\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$
We know that $\sin \left( 4\pi -x \right)=-\sin x,\cos \left( 5\pi +x \right)=-\cos x,\tan \left( 4\pi +x \right)=\tan x,\csc \left( 6\pi +x \right)=\csc x$
Hence, we have
$S=\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}+\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}\csc \dfrac{\pi }{2}$
We have the following table for the trigonometric ratios of $0,\dfrac{\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{\pi }{2}$

From the table, we have
$\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{1}{2},\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2},\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}=1$ and $\csc \dfrac{\pi }{2}=1$
Hence, we have
$S=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+1\times 1=1+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}$
Note: Rule for converting $T\left( n\dfrac{\pi }{2}\pm x \right)$ to $T'\left( x \right)$, where T and T’ are trigonometric ratios.
If n is even the final expression will be of T. If n is odd, the final expression will contain the complement of T.
The complement of sin is cos and vice versa
The complement of tan is cot and vice versa
The complement of cosec is sec and vice versa.
Sign of the final expression is determined by the quadrant in which $n\dfrac{\pi }{2}\pm x$ falls.
Keeping the above points in consideration, we have
$\sin \left( 4\pi -x \right)=\sin \left( 8\dfrac{\pi }{2}-x \right)$
Now 8 is even, hence the final expression will be of sinx.
Also, $4\pi -x$ falls in the fourth quadrant in which sinx is negative
Hence, we have
$\sin \left( 4\pi -x \right)=-\sin x$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




