
How do you find the value of \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{3}{5})\]?
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: We will use the trigonometric identity \[{\cos ^2} + {\sin ^2} = 1\]. We will use the Pythagoras theorem here, i.e. \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{P}{H}\] and \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{B}{H}\] where $P$ means perpendicular, B is base and H means hypotenuse. The inverse of sin function is denoted by Arcsine or \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let, \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{3}{5}) = \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
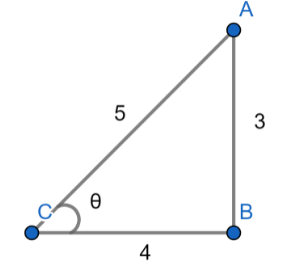
So the value of \[\theta \]will be \[\dfrac{{ - \pi }}{2} \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Since, we know that, \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{B}{H}\]
where $B$ is the base and H is the hypotenuse.
From the above diagram, the value of cos will be,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Another method to solve this is by using trigonometry identity.
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
So, apply the trigonometry identity here i.e.
\[{\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - {\sin ^2}\theta \]
Taking square root on both the sides, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {1 - {{\sin }^2}\theta } \]
Substituting the value, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {1 - {{(\dfrac{3}{5})}^2}} \]
Removing the brackets, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{9}{{25}}} \]
Simplify the above equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {\dfrac{{25 - 9}}{{25}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {\dfrac{{16}}{{25}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {{{(\dfrac{4}{5})}^2}} \]
\[ \therefore \cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Note: The expression \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}(x)\]is not the same as \[\dfrac{1}{{\sin (x)}}\]. In other words, \[ - 1\] is not an exponent. Instead, it simply means inverse function. The trigonometric functions sinx, cosx and tanx can be used to find an unknown side length of a right triangle, if one side length and an angle measure are known. The inverse trigonometric functions \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}x,{\cos ^{^{ - 1}}}x,{\tan ^{ - 1}}x\], are used to find the unknown measure of an angle of a right triangle when two side lengths are known. Pythagoras’ Theorem describes the mathematical relationship between three sides of a right-angled triangle. Trigonometry is a field of study in mathematics which observes the relationships of the sides and angles of triangles. The symbol \[\theta \] is used to describe an unknown angle. These functions are defined as the ratios of the different sides of a triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
Let, \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{3}{5}) = \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}\]

So the value of \[\theta \]will be \[\dfrac{{ - \pi }}{2} \leqslant \theta \leqslant \dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Since, we know that, \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{B}{H}\]
where $B$ is the base and H is the hypotenuse.
From the above diagram, the value of cos will be,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Another method to solve this is by using trigonometry identity.
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
So, apply the trigonometry identity here i.e.
\[{\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - {\sin ^2}\theta \]
Taking square root on both the sides, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {1 - {{\sin }^2}\theta } \]
Substituting the value, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {1 - {{(\dfrac{3}{5})}^2}} \]
Removing the brackets, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{9}{{25}}} \]
Simplify the above equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {\dfrac{{25 - 9}}{{25}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {\dfrac{{16}}{{25}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \sqrt {{{(\dfrac{4}{5})}^2}} \]
\[ \therefore \cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Note: The expression \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}(x)\]is not the same as \[\dfrac{1}{{\sin (x)}}\]. In other words, \[ - 1\] is not an exponent. Instead, it simply means inverse function. The trigonometric functions sinx, cosx and tanx can be used to find an unknown side length of a right triangle, if one side length and an angle measure are known. The inverse trigonometric functions \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}x,{\cos ^{^{ - 1}}}x,{\tan ^{ - 1}}x\], are used to find the unknown measure of an angle of a right triangle when two side lengths are known. Pythagoras’ Theorem describes the mathematical relationship between three sides of a right-angled triangle. Trigonometry is a field of study in mathematics which observes the relationships of the sides and angles of triangles. The symbol \[\theta \] is used to describe an unknown angle. These functions are defined as the ratios of the different sides of a triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




