
Find the top of a \[7m\] height building, the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is \[{60^\circ }\] and angle of depression of the tower is \[{45^\circ }\]. Find the height of the tower.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: This sum is solved by using trigonometry, in this section, we will see how trigonometry is used for finding the heights and distances of various objects without actually measuring them.
Here they give an angle of elevation, it is an angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point being viewed is above the horizontal level, that is, the case when we raise our head to look at the object.
The angle of depression is an angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point is below the horizontal level, that is, the case when we lower our head to look at the point being viewed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given the angle of elevation is \[{60^\circ }\] and the angle of depression is \[{45^\circ }\]
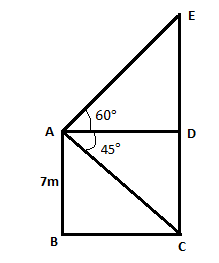
Let the building be \[AB\] and tower be \[CE\]
Also given that the height of building = \[AB\]=\[7m\]
From the top of building angle of elevation of top of tower=\[{60^\circ }\]
\[\angle EAD = {60^\circ }\]
Angle of depression of the foot of the tower=\[{45^\circ }\]
\[\angle CAD\]=\[{45^\circ }\]
We need to find height of tower
That is, \[CE\]
Collect all the possible information from the diagram for the sum
\[AB\] is parallel to \[CE\]
Since \[AB\] and \[CD\] are also parallel.
\[CD\]=\[AB\]=\[7m\]
Also,
\[AD\] and \[BC\] are parallel
So we can write \[AD\]=\[BC\]
Since tower and building are vertical to the ground
\[\angle ABC = {90^\circ }\] and \[\angle EDA = {90^\circ }\]
Since, \[AD\] and \[BC\] are parallel,
So we take \[AC\] as transversal
\[\angle ACB\]=\[\angle DAC\] (alternate angles)
\[\angle ACB\]=\[{45^\circ }\]
In right angle triangle\[ABC\],
\[\tan C = \dfrac{{\;side{\text{ }}opposite{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}C}}{{side{\text{ }}adjacent{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}C}}\]
\[\tan {45^\circ } = \dfrac{{\;AB}}{{BC}}\]
Here the value of \[\tan {45^\circ } = 1\]
\[1 = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\]
\[AB = 7m\]
\[1 = \dfrac{7}{{BC}}\]
\[BC\] =\[7m\]
Since we have to know that \[BC = AD\]
So, \[AD = 7m\]
Now, in a right angle triangle\[ADE\],
\[\tan A = \dfrac{{\;side{\text{ }}opposite{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}A}}{{side{\text{ }}adjacent{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}A}}\]
\[\tan {60^\circ } = \dfrac{{ED}}{{AD}}\]
Here, \[\tan {60^\circ } = \sqrt 3 \]
\[\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{ED}}{{AD}}\]
\[\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{ED}}{7}\]
\[7\sqrt 3 = ED\]
\[ED = 7\sqrt 3 m\]
Hence, height of tower = \[CE\]
In the diagram we can say that \[CE = CD + DE\]
Already we have the value of \[CD = 7m\] and \[ED = 7\sqrt 3 m\]
So we can write it as,
\[CE = 7\sqrt 3 + 7\]
Height of tower=\[7(\sqrt 3 + 1)m\]
Note: The process of finding heights and distances is the best example of applying trigonometry in real life situations.
Here some uses,
It is used in oceanography in calculating the height of tides in oceans.
The sine and cosine functions are fundamental to the theory of periodic functions, those that describe the sound and light waves.
Here they give an angle of elevation, it is an angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point being viewed is above the horizontal level, that is, the case when we raise our head to look at the object.
The angle of depression is an angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point is below the horizontal level, that is, the case when we lower our head to look at the point being viewed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given the angle of elevation is \[{60^\circ }\] and the angle of depression is \[{45^\circ }\]

Let the building be \[AB\] and tower be \[CE\]
Also given that the height of building = \[AB\]=\[7m\]
From the top of building angle of elevation of top of tower=\[{60^\circ }\]
\[\angle EAD = {60^\circ }\]
Angle of depression of the foot of the tower=\[{45^\circ }\]
\[\angle CAD\]=\[{45^\circ }\]
We need to find height of tower
That is, \[CE\]
Collect all the possible information from the diagram for the sum
\[AB\] is parallel to \[CE\]
Since \[AB\] and \[CD\] are also parallel.
\[CD\]=\[AB\]=\[7m\]
Also,
\[AD\] and \[BC\] are parallel
So we can write \[AD\]=\[BC\]
Since tower and building are vertical to the ground
\[\angle ABC = {90^\circ }\] and \[\angle EDA = {90^\circ }\]
Since, \[AD\] and \[BC\] are parallel,
So we take \[AC\] as transversal
\[\angle ACB\]=\[\angle DAC\] (alternate angles)
\[\angle ACB\]=\[{45^\circ }\]
In right angle triangle\[ABC\],
\[\tan C = \dfrac{{\;side{\text{ }}opposite{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}C}}{{side{\text{ }}adjacent{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}C}}\]
\[\tan {45^\circ } = \dfrac{{\;AB}}{{BC}}\]
Here the value of \[\tan {45^\circ } = 1\]
\[1 = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\]
\[AB = 7m\]
\[1 = \dfrac{7}{{BC}}\]
\[BC\] =\[7m\]
Since we have to know that \[BC = AD\]
So, \[AD = 7m\]
Now, in a right angle triangle\[ADE\],
\[\tan A = \dfrac{{\;side{\text{ }}opposite{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}A}}{{side{\text{ }}adjacent{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}angle{\text{ }}A}}\]
\[\tan {60^\circ } = \dfrac{{ED}}{{AD}}\]
Here, \[\tan {60^\circ } = \sqrt 3 \]
\[\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{ED}}{{AD}}\]
\[\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{ED}}{7}\]
\[7\sqrt 3 = ED\]
\[ED = 7\sqrt 3 m\]
Hence, height of tower = \[CE\]
In the diagram we can say that \[CE = CD + DE\]
Already we have the value of \[CD = 7m\] and \[ED = 7\sqrt 3 m\]
So we can write it as,
\[CE = 7\sqrt 3 + 7\]
Height of tower=\[7(\sqrt 3 + 1)m\]
Note: The process of finding heights and distances is the best example of applying trigonometry in real life situations.
Here some uses,
It is used in oceanography in calculating the height of tides in oceans.
The sine and cosine functions are fundamental to the theory of periodic functions, those that describe the sound and light waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




