
Find the terminal point of the vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] whose initial point is \[P(1,2)\] and whose components along x-axis and y-axis are \[ - 2\] and \[3\] respectively.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find the terminal or end point of the given vector. The x-component and y-component is given, using those from the vector. The initial point is also given use this point and the vector you formed using the given components to find the end point.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given a vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \]
Initial point of the vector is \[P(1,2)\]
x-component of the vector is \[x = - 2\]
y-component of the vector is \[y = 3\]
Therefore, the vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] can be written as, \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = - 2\widehat {\text{i}} + 3\widehat {\text{j}}\] (i)
Let the terminal point be \[Q(x,y)\]
Let us draw a diagram to understand the problem properly,
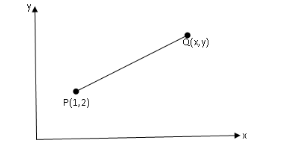
Now, observing the figure we can write the vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] in terms of their initial and final position vectors as,
\[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = \overrightarrow {\text{Q}} - \overrightarrow {\text{P}} \] (ii)
The initial point \[P(1,2)\] can be written in vector form as,
\[\overrightarrow {\text{P}} = 1\widehat {\text{i}} + 2\widehat {\text{j}}\] (iii)
The final point \[Q(x,y)\] can be written in vector form as,
\[\overrightarrow {\text{Q}} = x\widehat {\text{i}} + y\widehat {\text{j}}\] (iv)
Now, putting the values from equation (iii) and (iv) in equation (ii), we get
\[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = \left( {x\widehat {\text{i}} + y\widehat {\text{j}}} \right) - \left( {1\widehat {\text{i}} + 2\widehat {\text{j}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = (x - 1)\widehat {\text{i}} + (y - 2)\widehat {\text{j}} \]
Now, putting the value of \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] from equation (i), we get
\[ - 2\widehat {\text{i}} + 3\widehat {\text{j}} = (x - 1)\widehat {\text{i}} - (y - 2)\widehat {\text{j}}\]
Now, equating x-component we get,
\[- 2 = x - 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = - 1 \]
Equating y-component we get,
\[3 = y - 2 \\
\Rightarrow y = 5 \]
Therefore, the terminal point is \[Q( - 1,5)\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[Q( - 1,5)\] ”.
Note: A vector has a starting point and an ending or terminal point. The vector can be formed by subtracting the terminal position vector from the initial position vector. A vector has both magnitude and direction. Suppose we have a vector \[\overrightarrow {\text{A}} = a\widehat i + b\widehat j\] then its magnitude can be written as, \[{\text{A}} = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} \] . Always remember these basic concepts of vectors as you may have to use these in solving many problems.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given a vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \]
Initial point of the vector is \[P(1,2)\]
x-component of the vector is \[x = - 2\]
y-component of the vector is \[y = 3\]
Therefore, the vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] can be written as, \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = - 2\widehat {\text{i}} + 3\widehat {\text{j}}\] (i)
Let the terminal point be \[Q(x,y)\]
Let us draw a diagram to understand the problem properly,

Now, observing the figure we can write the vector \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] in terms of their initial and final position vectors as,
\[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = \overrightarrow {\text{Q}} - \overrightarrow {\text{P}} \] (ii)
The initial point \[P(1,2)\] can be written in vector form as,
\[\overrightarrow {\text{P}} = 1\widehat {\text{i}} + 2\widehat {\text{j}}\] (iii)
The final point \[Q(x,y)\] can be written in vector form as,
\[\overrightarrow {\text{Q}} = x\widehat {\text{i}} + y\widehat {\text{j}}\] (iv)
Now, putting the values from equation (iii) and (iv) in equation (ii), we get
\[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = \left( {x\widehat {\text{i}} + y\widehat {\text{j}}} \right) - \left( {1\widehat {\text{i}} + 2\widehat {\text{j}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} = (x - 1)\widehat {\text{i}} + (y - 2)\widehat {\text{j}} \]
Now, putting the value of \[\overrightarrow {{\text{PQ}}} \] from equation (i), we get
\[ - 2\widehat {\text{i}} + 3\widehat {\text{j}} = (x - 1)\widehat {\text{i}} - (y - 2)\widehat {\text{j}}\]
Now, equating x-component we get,
\[- 2 = x - 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = - 1 \]
Equating y-component we get,
\[3 = y - 2 \\
\Rightarrow y = 5 \]
Therefore, the terminal point is \[Q( - 1,5)\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[Q( - 1,5)\] ”.
Note: A vector has a starting point and an ending or terminal point. The vector can be formed by subtracting the terminal position vector from the initial position vector. A vector has both magnitude and direction. Suppose we have a vector \[\overrightarrow {\text{A}} = a\widehat i + b\widehat j\] then its magnitude can be written as, \[{\text{A}} = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} \] . Always remember these basic concepts of vectors as you may have to use these in solving many problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




