
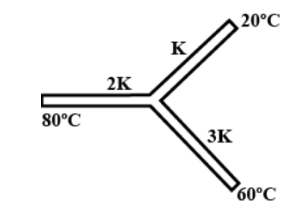
Find the temperature of the junction a shown in the figure for three rods; identical in dimensions:

Answer
513k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we first need to understand what temperature is. Temperature is a physical number that describes how hot or cold something is. When a body comes into contact with another that is colder or hotter, it is the manifestation of thermal energy, which is present in all matter and is the source of the occurrence of heat, a flow of energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Junction temperature: The highest operating temperature of the real semiconductor in an electronic device is known as junction temperature (short for transistor junction temperature). It is higher than the case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior when it is in use.
Heat energy: Heat is a type of energy that is transmitted between systems or things of various temperatures (flowing from the high-temperature system to the low-temperature system). Also known as thermal energy or heat energy. But, calories, and joules are the most common units of heat measurement.
Formula of heat energy in a bar is
$Q = \dfrac{{kA(\Delta T)}}{l}$
Here $k$ is the heat constant, $A$ is the cross-section area of bar,$l$ is the length of the bar and $\Delta T$ is the temperature difference between the endpoints of bar.
Let the temperature at the junction be $T$.
${Q_1} + {Q_2} = {Q_3}$ (Here, Q is the heat energy in each branch)
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2kA}}{l}(80 - t) + \dfrac{{3kA}}{l}(60 - T) = \dfrac{{kA}}{l}(T - 20)$
$\Rightarrow 160 - 2T + 180 - 3T = T - 2 \\
\Rightarrow 6T = 360 \\
\therefore T = {60^0}C \\ $
Hence, the final temperature of the junction is 60 degrees.
Note: According to Energy Education, heat is energy transmitted between substances or systems due to a temperature differential between them. Heat is a kind of energy that can't be made or destroyed, hence it can't be made or destroyed. However, it can be moved from one location to another.
Complete step by step answer:
Junction temperature: The highest operating temperature of the real semiconductor in an electronic device is known as junction temperature (short for transistor junction temperature). It is higher than the case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior when it is in use.
Heat energy: Heat is a type of energy that is transmitted between systems or things of various temperatures (flowing from the high-temperature system to the low-temperature system). Also known as thermal energy or heat energy. But, calories, and joules are the most common units of heat measurement.
Formula of heat energy in a bar is
$Q = \dfrac{{kA(\Delta T)}}{l}$
Here $k$ is the heat constant, $A$ is the cross-section area of bar,$l$ is the length of the bar and $\Delta T$ is the temperature difference between the endpoints of bar.
Let the temperature at the junction be $T$.
${Q_1} + {Q_2} = {Q_3}$ (Here, Q is the heat energy in each branch)
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2kA}}{l}(80 - t) + \dfrac{{3kA}}{l}(60 - T) = \dfrac{{kA}}{l}(T - 20)$
$\Rightarrow 160 - 2T + 180 - 3T = T - 2 \\
\Rightarrow 6T = 360 \\
\therefore T = {60^0}C \\ $
Hence, the final temperature of the junction is 60 degrees.
Note: According to Energy Education, heat is energy transmitted between substances or systems due to a temperature differential between them. Heat is a kind of energy that can't be made or destroyed, hence it can't be made or destroyed. However, it can be moved from one location to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




