
How do you find the tangent lines of parametric curves?
Show that the curve with parametric equations$x = \sin t$, $y = \sin \left( {t + \sin t} \right)$ has two tangent lines at the origin and find their equations. Illustrate by graphing the curve and its tangents.
Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: In this question we have to find the tangents of the given parametric equations, first we will derive the two equations then we will find $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$, now we will get two values for $t$ by substituting the origin in the two equations as the two equations passes through the origin, now substitute the two values in $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ to get the slopes of the required tangents, now by using slope intercept form i.e., $y = mx + b$, we will get the required tangent lines.
Complete step by step solution:
Given parametric equations are $x = \sin t$, $y = \sin \left( {t + \sin t} \right)$,
Now we will derive the first equation i.e.,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\sin t$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = \cos t$,
Now we will derive the second equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{dt}}y = \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\sin \left( {t + \sin t} \right)$,
Now simplifying by applying derivatives we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {\dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {t + \sin t} \right)} \right)$,
Further simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {1 + \cos t} \right)$,
Now we divide both the equations we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}}}}{{\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {1 + \cos t} \right)}}{{\cos t}}\],
Now simplifying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {1 + \cos t} \right)}}{{\cos t}}\],
Now we have to find the tangent at the origin i.e., $\left( {0,0} \right)$, so here substitute $x = 0$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 0 = \sin t$,
Now by trigonometric ratios we get,
$ \Rightarrow t = 0$or $t = \pi $,
Now substitute these values of $t$ into $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ to find the equation of tangent line,
First substitute $t = 0$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = 0}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {0 + \sin 0} \right)\left( {1 + \cos 0} \right)}}{{\cos 0}}$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = 0}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( 0 \right)\left( {1 + \cos 0} \right)}}{{\cos 0}}$,
Further simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = 0}} = \dfrac{{1\left( {1 + 1} \right)}}{1} = \dfrac{2}{1} = 2$,
Next substitute $t = \pi $, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {\pi + \sin \pi } \right)\left( {1 + \cos \pi } \right)}}{{\cos \pi }}$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {\pi + 0} \right)\left( {1 + \cos \pi } \right)}}{{\cos \pi }}$,
Further simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( \pi \right)\left( {1 + \cos \pi } \right)}}{{\cos \pi }}$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\left( { - 1} \right)\left( {1 - 1} \right)}}{{ - 1}} = 0$,
So we have the gradients to our two tangent lines and they are ${m_{\tan 0}} = 2$ and ${m_{\tan 1}} = 0$, and we know that the tangent passes through the origin i.e.,$\left( {0,0} \right)$,
So, for the equation of a straight line $y = mx + b$ which passes through the origin, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = mx + 0$.
Now substituting the two value of $m$in the slope intercept form, then our two tangents will be:
First tangent is when $m = 2$, by substituting we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y_1} = \left( 2 \right)x + 0 = 2x$,
Now second tangent is when $m = 0$, by substituting value we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y_2} = \left( 0 \right)x + 0 = 0$,
So, the two tangents will be $y = 0$ and $y = 2x$, now we will graph all the tangents, and the given curves then the graph will be
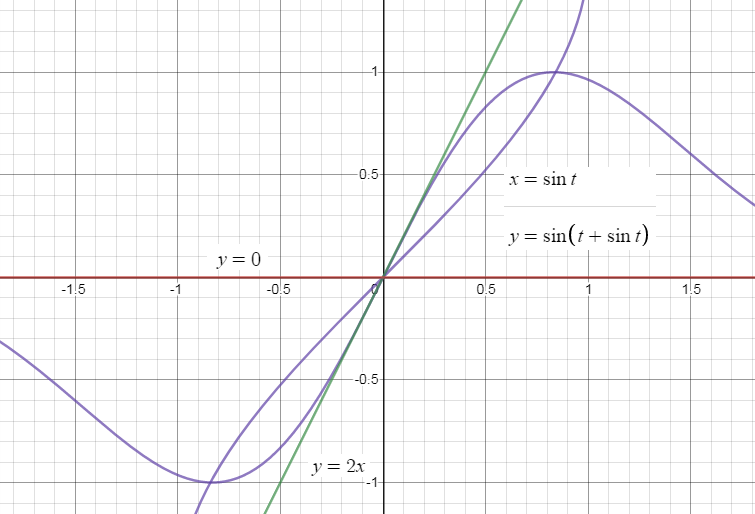
Note: Parametric equation, a type of equation that employs an independent variable called a parameter often denoted by $t$ and in which dependent variables are defined as continuous functions of the parameter and are not dependent on another existing variable.
Complete step by step solution:
Given parametric equations are $x = \sin t$, $y = \sin \left( {t + \sin t} \right)$,
Now we will derive the first equation i.e.,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\sin t$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = \cos t$,
Now we will derive the second equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{dt}}y = \dfrac{d}{{dt}}\sin \left( {t + \sin t} \right)$,
Now simplifying by applying derivatives we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {\dfrac{d}{{dt}}\left( {t + \sin t} \right)} \right)$,
Further simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = \cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {1 + \cos t} \right)$,
Now we divide both the equations we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}}}}{{\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {1 + \cos t} \right)}}{{\cos t}}\],
Now simplifying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {t + \sin t} \right)\left( {1 + \cos t} \right)}}{{\cos t}}\],
Now we have to find the tangent at the origin i.e., $\left( {0,0} \right)$, so here substitute $x = 0$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 0 = \sin t$,
Now by trigonometric ratios we get,
$ \Rightarrow t = 0$or $t = \pi $,
Now substitute these values of $t$ into $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ to find the equation of tangent line,
First substitute $t = 0$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = 0}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {0 + \sin 0} \right)\left( {1 + \cos 0} \right)}}{{\cos 0}}$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = 0}} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( 0 \right)\left( {1 + \cos 0} \right)}}{{\cos 0}}$,
Further simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = 0}} = \dfrac{{1\left( {1 + 1} \right)}}{1} = \dfrac{2}{1} = 2$,
Next substitute $t = \pi $, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {\pi + \sin \pi } \right)\left( {1 + \cos \pi } \right)}}{{\cos \pi }}$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( {\pi + 0} \right)\left( {1 + \cos \pi } \right)}}{{\cos \pi }}$,
Further simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\cos \left( \pi \right)\left( {1 + \cos \pi } \right)}}{{\cos \pi }}$,
Now simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}_{t = \pi }} = \dfrac{{\left( { - 1} \right)\left( {1 - 1} \right)}}{{ - 1}} = 0$,
So we have the gradients to our two tangent lines and they are ${m_{\tan 0}} = 2$ and ${m_{\tan 1}} = 0$, and we know that the tangent passes through the origin i.e.,$\left( {0,0} \right)$,
So, for the equation of a straight line $y = mx + b$ which passes through the origin, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = mx + 0$.
Now substituting the two value of $m$in the slope intercept form, then our two tangents will be:
First tangent is when $m = 2$, by substituting we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y_1} = \left( 2 \right)x + 0 = 2x$,
Now second tangent is when $m = 0$, by substituting value we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y_2} = \left( 0 \right)x + 0 = 0$,
So, the two tangents will be $y = 0$ and $y = 2x$, now we will graph all the tangents, and the given curves then the graph will be

Note: Parametric equation, a type of equation that employs an independent variable called a parameter often denoted by $t$ and in which dependent variables are defined as continuous functions of the parameter and are not dependent on another existing variable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




