
how do you find the slope of the secant lines of \[f(x) = 6x - 1{x^2}\] through the points \[(2,f(2))\] and \[(2 + h,f(2 + h))\]?
Answer
540.3k+ views
Hint: First, we will use the formula of the gradient to find slope. We will put the points in the formula and try to simplify it. After that we will put the value of f(x) in that solving part and try to solve them, this will give us our answer.
Formula used: \[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Slope also means gradient here.
According to this question, we have to find the slope by using the two points. Here, we will use the gradient formula to find the slope or gradient. The formula is:
\[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
In this formula, \[({x_1},{y_1})\,\,and\,\,({x_2},{y_2})\] are the points. So, according to the question, we get:
\[({x_1},{y_1}) = (2,f(2))\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (2 + h,f(2 + h))\]
Now, we will put the values or points in the formula, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{f(2 + h) - f(2)}}{{2 + h - 2}}\]
Now, we will substitute the values \[6x - {x^2}\] in the solving part, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{(6 - (2 + h))(2 + h) - (6 \times 2 - {2^2})}}{{2 + h - 2}}\]
Now, we will simplify the denominator, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{(6 - (2 + h))(2 + h) - (6 \times 2 - {2^2})}}{h}\]
Now, we will simplify the numerator, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{(4 - h)(2 + h) - (12 - 4)}}{h}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{4(2 + h) - h(2 + h) - 8}}{h}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{8 + 4h - 2h - {h^2} - 8}}{h}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{2h - {h^2}}}{h}\]
Now, we will take \[h\]common here, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{h(2 - h)}}{h}\]
Now, the common terms from the numerator and denominator get cancelled. Here, \[h\] gets cancelled from both numerator and denominator, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = (2 - h)\]
Therefore, we get the slope as \[(2 - h)\].
If we calculate by taking limit, then \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \,m(h) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \,2 - h\]. We get our answer as \[2\]. This is the coefficient of the tangent line to \[f(x)\] at the point \[2\].
Note: While plotting a graph, when we draw a line on that graph of curve, if the line intersects that curve at two or more than two points, then that line is a secant line, as we can see in the following graph, the blue line is a secant to the curve because it is intersecting the curve twice at “A” and “B”
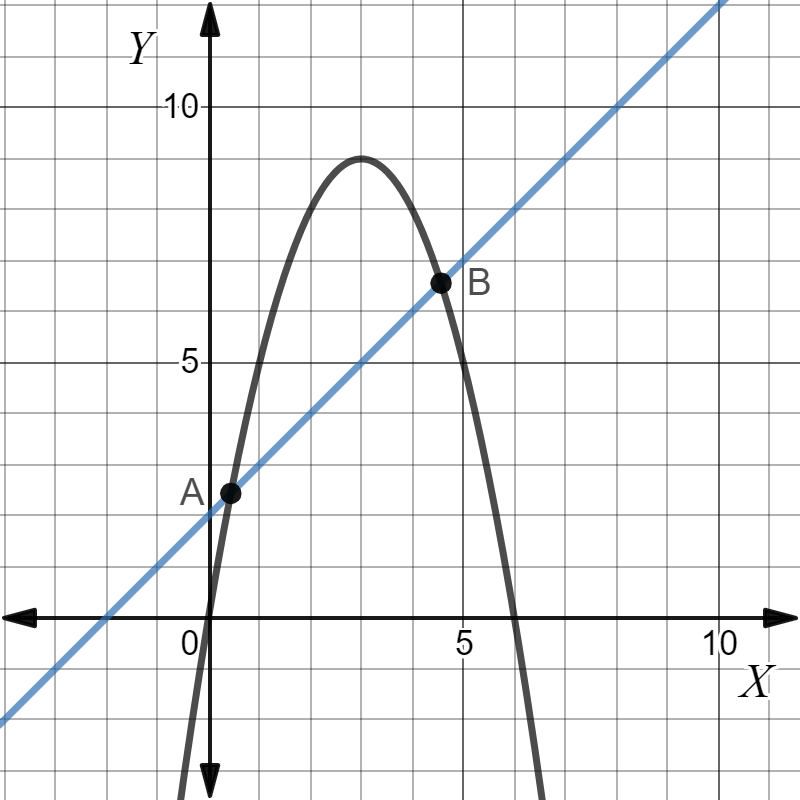
Formula used: \[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Slope also means gradient here.
According to this question, we have to find the slope by using the two points. Here, we will use the gradient formula to find the slope or gradient. The formula is:
\[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\]
In this formula, \[({x_1},{y_1})\,\,and\,\,({x_2},{y_2})\] are the points. So, according to the question, we get:
\[({x_1},{y_1}) = (2,f(2))\] and \[({x_2},{y_2}) = (2 + h,f(2 + h))\]
Now, we will put the values or points in the formula, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{f(2 + h) - f(2)}}{{2 + h - 2}}\]
Now, we will substitute the values \[6x - {x^2}\] in the solving part, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{(6 - (2 + h))(2 + h) - (6 \times 2 - {2^2})}}{{2 + h - 2}}\]
Now, we will simplify the denominator, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{(6 - (2 + h))(2 + h) - (6 \times 2 - {2^2})}}{h}\]
Now, we will simplify the numerator, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{(4 - h)(2 + h) - (12 - 4)}}{h}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{4(2 + h) - h(2 + h) - 8}}{h}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{8 + 4h - 2h - {h^2} - 8}}{h}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{2h - {h^2}}}{h}\]
Now, we will take \[h\]common here, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = \dfrac{{h(2 - h)}}{h}\]
Now, the common terms from the numerator and denominator get cancelled. Here, \[h\] gets cancelled from both numerator and denominator, and we get:
\[ \Rightarrow m(h) = (2 - h)\]
Therefore, we get the slope as \[(2 - h)\].
If we calculate by taking limit, then \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \,m(h) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} \,2 - h\]. We get our answer as \[2\]. This is the coefficient of the tangent line to \[f(x)\] at the point \[2\].
Note: While plotting a graph, when we draw a line on that graph of curve, if the line intersects that curve at two or more than two points, then that line is a secant line, as we can see in the following graph, the blue line is a secant to the curve because it is intersecting the curve twice at “A” and “B”

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




