
Find the slope of the line joining the points$( - 4,1)$and$( - 5,2)$
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Let$M({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 4,1)$and$N({x_2},{y_2}) = ( - 5,2)$Verify that ${x_1} \ne {x_2}$
Then use the formula $m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$to determine the required slope.
Complete step by step solution:
In this problem, we are given two points but not the equation of the line joining them.
Determining the slope of a line from its equation is an easy task.
However, it is not difficult to determine the slope in this case either.
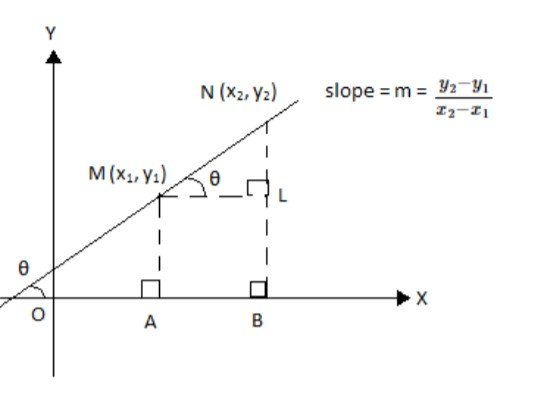
Let$M({x_1},{y_1})$and$N({x_2},{y_2})$be two points on a plane. The slope of a line joining the two
points M and N is denoted by m and is given by the formula: slope$ = m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} -
{x_1}}}$where the x-coordinates ${x_1} \ne {x_2}$
We can see that if${x_1} = {x_2}$, then the denominator in the formula would be equal to zero and the
slope would be not defined.
A graphical representation of the slope of a line joining the points M and N would be as given below:
We are given two points $( - 4,1)$and$( - 5,2)$
We need to find the slope of the line joining these two points.
From the above discussion, it is clear that we need to check if the slope is defined in order to apply the
formula for calculating the slope.
Let$M({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 4,1)$and$N({x_2},{y_2}) = ( - 5,2)$
Therefore, the x-coordinates of M and N are -4 and -5 which are clearly different from each other.
This implies that we can use the formula of slope given above.
So, let us substitute the values in the formula.
Therefore, we have slope\[ = m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{2 - 1}}{{ - 5 - ( - 4)}} =
\dfrac{1}{{ - 5 + 4}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 1}} = - 1\]
Hence the slope of the line joining the points $( - 4,1)$and$( - 5,2)$is -1.
Note: Slope of a line is constant throughout the way.
That is, for any two points on a given line, the value of m remains constant.
Then use the formula $m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$to determine the required slope.
Complete step by step solution:
In this problem, we are given two points but not the equation of the line joining them.
Determining the slope of a line from its equation is an easy task.
However, it is not difficult to determine the slope in this case either.
Let$M({x_1},{y_1})$and$N({x_2},{y_2})$be two points on a plane. The slope of a line joining the two
points M and N is denoted by m and is given by the formula: slope$ = m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} -
{x_1}}}$where the x-coordinates ${x_1} \ne {x_2}$
We can see that if${x_1} = {x_2}$, then the denominator in the formula would be equal to zero and the
slope would be not defined.
A graphical representation of the slope of a line joining the points M and N would be as given below:

We are given two points $( - 4,1)$and$( - 5,2)$
We need to find the slope of the line joining these two points.
From the above discussion, it is clear that we need to check if the slope is defined in order to apply the
formula for calculating the slope.
Let$M({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 4,1)$and$N({x_2},{y_2}) = ( - 5,2)$
Therefore, the x-coordinates of M and N are -4 and -5 which are clearly different from each other.
This implies that we can use the formula of slope given above.
So, let us substitute the values in the formula.
Therefore, we have slope\[ = m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{2 - 1}}{{ - 5 - ( - 4)}} =
\dfrac{1}{{ - 5 + 4}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 1}} = - 1\]
Hence the slope of the line joining the points $( - 4,1)$and$( - 5,2)$is -1.
Note: Slope of a line is constant throughout the way.
That is, for any two points on a given line, the value of m remains constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




