
How do you find the slope and intercept of $x-2y=0$ ?
Answer
549k+ views
Hint: We are given an equation of line as $x-2y=0$ . We are asked to find the slope of it, we will first learn what is slope then we focus on various methods to find slope. We learn what slope is, find using $\tan \theta $ and also by $m=\dfrac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}}$ . We will learn about slope intercept form, we convert our problem to slope intercept form then we will find the slope and intercept.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given an equation as $x-2y=0$ .
We are asked to find the slope of the given equation and also to find the y-intercept.
We will first understand what the slope means then we will focus on the ways to find the slope of any given equation.
Now, the slope of any line is the angle made by the line with the positive x-axis.
We generally find the slope by finding the ratio of rise and run.
Rise means movement of the function along the y-axis while run refers to the movement along x-axis.
So, one way in slope $=\dfrac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}}$ .
Another way is to find the term of the angle made by the line with x-axis.
So, slope $=\tan \theta $ .
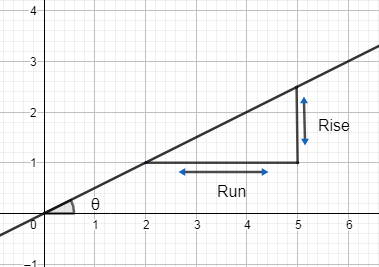
Slope is denoted as ‘m’, so –
$m=\tan \theta $ or $m=\dfrac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}}$
Other ways to find the slope is to use the equation given to us.
Generally the equation of line in standard form is given as $ax+bx+c=0$ .
We can convert this equation to slope intercept from given as –
$y=mx+c$ .
Where ‘m’ is a slope, ‘c’ is the y-intercept .
So, we can find slope and intercept from here.
Now, we have $x-2y=0$ , so we will transform this into slope intercept form. We will use algebraic tools $\left( +,-,\times ,\div \right)$ to change into the required slope intercept form .
Now, as we have $x-2y=0$
We subtract ‘x’ on both sides.
$x-2y-x=-x+0$
So, $-2y=-x+0$
Now, we divide by -2, on both sides.
So, $\dfrac{-2y}{-2}=\dfrac{-x}{-2}+\dfrac{0}{-2}$
By simplifying, we get –
$y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+0$
By comparing it with $y=mx+c$ .
We get slope as $m=\dfrac{1}{2}$ and intercept as $c=0$.
Note: In our equation $x-2y=0$ .
We have $a=1,b=-2$
So, slope $m=\dfrac{-a}{b}$ , will be –
$m=\dfrac{-\left( 1 \right)}{-2}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
And the direct way to find an intercept is to put $x=0$ in our equation, the value of ‘y’ that will come will be y-intercept.
So, putting $x=0$ in $x-2y=0$ we get –
$y=0$
So, y-intercept is 0.
Similarly, we get $x=0$ when we put $y=0$ in the given equation.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given an equation as $x-2y=0$ .
We are asked to find the slope of the given equation and also to find the y-intercept.
We will first understand what the slope means then we will focus on the ways to find the slope of any given equation.
Now, the slope of any line is the angle made by the line with the positive x-axis.
We generally find the slope by finding the ratio of rise and run.
Rise means movement of the function along the y-axis while run refers to the movement along x-axis.
So, one way in slope $=\dfrac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}}$ .
Another way is to find the term of the angle made by the line with x-axis.
So, slope $=\tan \theta $ .

Slope is denoted as ‘m’, so –
$m=\tan \theta $ or $m=\dfrac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}}$
Other ways to find the slope is to use the equation given to us.
Generally the equation of line in standard form is given as $ax+bx+c=0$ .
We can convert this equation to slope intercept from given as –
$y=mx+c$ .
Where ‘m’ is a slope, ‘c’ is the y-intercept .
So, we can find slope and intercept from here.
Now, we have $x-2y=0$ , so we will transform this into slope intercept form. We will use algebraic tools $\left( +,-,\times ,\div \right)$ to change into the required slope intercept form .
Now, as we have $x-2y=0$
We subtract ‘x’ on both sides.
$x-2y-x=-x+0$
So, $-2y=-x+0$
Now, we divide by -2, on both sides.
So, $\dfrac{-2y}{-2}=\dfrac{-x}{-2}+\dfrac{0}{-2}$
By simplifying, we get –
$y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+0$
By comparing it with $y=mx+c$ .
We get slope as $m=\dfrac{1}{2}$ and intercept as $c=0$.
Note: In our equation $x-2y=0$ .
We have $a=1,b=-2$
So, slope $m=\dfrac{-a}{b}$ , will be –
$m=\dfrac{-\left( 1 \right)}{-2}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
And the direct way to find an intercept is to put $x=0$ in our equation, the value of ‘y’ that will come will be y-intercept.
So, putting $x=0$ in $x-2y=0$ we get –
$y=0$
So, y-intercept is 0.
Similarly, we get $x=0$ when we put $y=0$ in the given equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




