
How do you find the remaining trigonometric function \[\theta \] of given \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{24}}{{25}}\] and \[\theta \] terminates in QIV \[?\]
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: In the given question we have to find the remaining different trigonometric function like sin, cos, tan, cot, sec, csc for \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{24}}{{25}}\] and \[\theta \] terminates in QIV.
Here \[\theta \] terminates in QIV means that \[\theta \] terminates in quadrant IV where the abscissa x axis is \[ + \] and ordinate y axis is \[ - \] .
Now you should know that \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{r}\] , and \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{y}{r}\] , where \[x,y,r\] are two side and hypotenuse of a right angle triangle. From this you can find value of \[\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\sec \theta ,\csc \theta \] in terms of \[x,y,r\] using identity i.e.
\[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\]
Because \[x,y,r\] are sides of right angled triangle, now solving for \[y\] , we get
\[y = \pm \sqrt {{r^2} - {x^2}} \]
Now you can find the value of all trigonometric functions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given question we have been asked to find the remaining trigonometric functions using \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{24}}{{25}}\] and also \[\theta \] terminates in QIV.
Let the point \[P(x,y)\] be on a circle of radius r centered at the origin and \[P\] is on the terminal ray of \[\theta \] . Now let suppose the angle \[\theta \] be the non reflex angle from the positive x axis that is coterminal with the angle \[\theta \] .
The line segments from \[(0,0)\] to \[(x,0)\] and to \[(0,y)\] form a right angled triangle with hypotenuse \[r\] and angle \[\theta \] between \[x\] and \[r\] .
So \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{r}\] and \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{y}{r}\] .
\[x,y,r\] are the lengths of the two sides and the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle respectively.
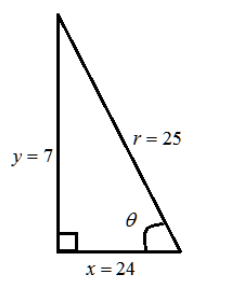
Therefore,
\[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\]
Now solving for \[y\] , we get
\[y = \pm \sqrt {{r^2} - {x^2}} \]
Now We know the values of \[x\] and \[r\] , so we can find that value of \[y\] using formula i.e.
\[
y = \pm \sqrt {{r^2} - {x^2}} \\
\Rightarrow y = \pm \sqrt {{{25}^2} - {{24}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow y = \pm 7 \;
\]
Now we know that \[y\] is negative so \[y = - 7\] .
So the value of trigonometric functions will be:
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{y}{r} = \dfrac{{ - 7}}{{25}} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{x} = \dfrac{{ - 7}}{{24}} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{{24}}{{ - 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 24}}{7} \\
\sec \theta = \dfrac{1}{x} = \dfrac{25}{{24}} \\
\csc \theta = \dfrac{1}{y} = \dfrac{25}{{ - 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 25}}{7} \;
\]
Hence this is the required answer.
Note: Here you should know that what a right angled triangle is, you should also study the proof of the formula \[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\] which was used in this entire questions. Also the basic trigonometric formula like \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\csc \theta }},\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sec \theta }},\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }},\cot \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\tan \theta }}\] .Using these formula you can easily find the solution of these kind of questions.
Here \[\theta \] terminates in QIV means that \[\theta \] terminates in quadrant IV where the abscissa x axis is \[ + \] and ordinate y axis is \[ - \] .
Now you should know that \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{r}\] , and \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{y}{r}\] , where \[x,y,r\] are two side and hypotenuse of a right angle triangle. From this you can find value of \[\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\sec \theta ,\csc \theta \] in terms of \[x,y,r\] using identity i.e.
\[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\]
Because \[x,y,r\] are sides of right angled triangle, now solving for \[y\] , we get
\[y = \pm \sqrt {{r^2} - {x^2}} \]
Now you can find the value of all trigonometric functions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given question we have been asked to find the remaining trigonometric functions using \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{24}}{{25}}\] and also \[\theta \] terminates in QIV.
Let the point \[P(x,y)\] be on a circle of radius r centered at the origin and \[P\] is on the terminal ray of \[\theta \] . Now let suppose the angle \[\theta \] be the non reflex angle from the positive x axis that is coterminal with the angle \[\theta \] .
The line segments from \[(0,0)\] to \[(x,0)\] and to \[(0,y)\] form a right angled triangle with hypotenuse \[r\] and angle \[\theta \] between \[x\] and \[r\] .
So \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{x}{r}\] and \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{y}{r}\] .
\[x,y,r\] are the lengths of the two sides and the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle respectively.

Therefore,
\[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\]
Now solving for \[y\] , we get
\[y = \pm \sqrt {{r^2} - {x^2}} \]
Now We know the values of \[x\] and \[r\] , so we can find that value of \[y\] using formula i.e.
\[
y = \pm \sqrt {{r^2} - {x^2}} \\
\Rightarrow y = \pm \sqrt {{{25}^2} - {{24}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow y = \pm 7 \;
\]
Now we know that \[y\] is negative so \[y = - 7\] .
So the value of trigonometric functions will be:
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{y}{r} = \dfrac{{ - 7}}{{25}} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{x} = \dfrac{{ - 7}}{{24}} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{{24}}{{ - 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 24}}{7} \\
\sec \theta = \dfrac{1}{x} = \dfrac{25}{{24}} \\
\csc \theta = \dfrac{1}{y} = \dfrac{25}{{ - 7}} = \dfrac{{ - 25}}{7} \;
\]
Hence this is the required answer.
Note: Here you should know that what a right angled triangle is, you should also study the proof of the formula \[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\] which was used in this entire questions. Also the basic trigonometric formula like \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\csc \theta }},\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sec \theta }},\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }},\cot \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\tan \theta }}\] .Using these formula you can easily find the solution of these kind of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




