
Find the ratio in which the line $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ divides the line segment joining the points $ \left( {8, - 9} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,1} \right) $ . Also find the coordinates of the point of division.
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: In the given problem, we are asked to find the ratio and co-ordinates of the point of division such that the line $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ divides the line segment joining the points $ \left( {8, - 9} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,1} \right) $ . In order to find the ratio we will use a section formula.
Complete step by step solution:
In this given problem, the line of equation is $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ . Let $ A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {8, - 9} \right) $ and $ B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {2,1} \right) $ be the end points of line segment $ AB $ and $ P\left( {x,y} \right) $ be the point of division of line segment joining the $ AB $ .
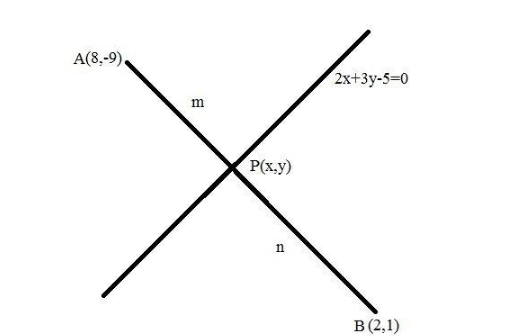
Let us assume that the ratio in which $ P $ divides $ AB $ is $ m:n = k:1 $ . Therefore, by using section formula coordinates of $ P $ is
$
P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) \;
$
We know that $ P $ lies on the line $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ . Hence it will satisfy the equation of line. Therefore, we can write
$
2\left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}}} \right) + 3\left( {\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) - 5 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}}} \right) + 3\left( {\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) = 5 \\
$
Now we take $ \dfrac{1}{{k + 1}} $ common in the left hand side of the equality sign and then multiplied both sides by $ k + 1 $ . Then, we get
$ 2\left( {2k + 8} \right) + 3\left( {k - 9} \right) = 5\left( {k + 1} \right) $
Let us simplify the above equation and find the value of $ k $ . Therefore, we can write
$
4k + 16 + 3k - 27 = 5k + 5 \\
\Rightarrow 4k + 3k - 5k = 5 + 27 - 16 \\
\Rightarrow 2k = 16 \\
\Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{16}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow k = 8 \;
$
Let us put $ k = 8 $ in $ P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) $ . Therefore, we get $ P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{24}}{9}, - \dfrac{1}{9}} \right) $
Therefore, we can say that the ratio in which the line $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ divided the line segment joining the point $ \left( {8, - 9} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,1} \right) $ is $ k:1 = 8:1 $ and coordinates of point $ P $ is given by $ \left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{24}}{9},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{9}} \right) $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ \left( {\dfrac{{24}}{9},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{9}} \right) $ .”
Note: According to the section formula, the coordinates of the point $ P\left( {x,y} \right) $ which divides the line segment joining the point $ A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) $ and $ B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) $ in the ratio $ {m_1}:{m_2} $ internally, is $ \left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_1} + {m_2}{x_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_1} + {m_2}{y_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right) $ . Then by using this ratio we will find the coordinates of the point of division. If the midpoint of a line segment divides the line segment in the ratio $ 1:1 $ then the coordinates of the mid-point $ P $ is $ \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right) $ .
Complete step by step solution:
In this given problem, the line of equation is $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ . Let $ A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {8, - 9} \right) $ and $ B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {2,1} \right) $ be the end points of line segment $ AB $ and $ P\left( {x,y} \right) $ be the point of division of line segment joining the $ AB $ .

Let us assume that the ratio in which $ P $ divides $ AB $ is $ m:n = k:1 $ . Therefore, by using section formula coordinates of $ P $ is
$
P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) \;
$
We know that $ P $ lies on the line $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ . Hence it will satisfy the equation of line. Therefore, we can write
$
2\left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}}} \right) + 3\left( {\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) - 5 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}}} \right) + 3\left( {\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) = 5 \\
$
Now we take $ \dfrac{1}{{k + 1}} $ common in the left hand side of the equality sign and then multiplied both sides by $ k + 1 $ . Then, we get
$ 2\left( {2k + 8} \right) + 3\left( {k - 9} \right) = 5\left( {k + 1} \right) $
Let us simplify the above equation and find the value of $ k $ . Therefore, we can write
$
4k + 16 + 3k - 27 = 5k + 5 \\
\Rightarrow 4k + 3k - 5k = 5 + 27 - 16 \\
\Rightarrow 2k = 16 \\
\Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{16}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow k = 8 \;
$
Let us put $ k = 8 $ in $ P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) $ . Therefore, we get $ P\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{24}}{9}, - \dfrac{1}{9}} \right) $
Therefore, we can say that the ratio in which the line $ 2x + 3y - 5 = 0 $ divided the line segment joining the point $ \left( {8, - 9} \right) $ and $ \left( {2,1} \right) $ is $ k:1 = 8:1 $ and coordinates of point $ P $ is given by $ \left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{2k + 8}}{{k + 1}},\dfrac{{k - 9}}{{k + 1}}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{24}}{9},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{9}} \right) $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ \left( {\dfrac{{24}}{9},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{9}} \right) $ .”
Note: According to the section formula, the coordinates of the point $ P\left( {x,y} \right) $ which divides the line segment joining the point $ A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) $ and $ B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) $ in the ratio $ {m_1}:{m_2} $ internally, is $ \left( {\dfrac{{{m_1}{x_1} + {m_2}{x_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}},\dfrac{{{m_1}{y_1} + {m_2}{y_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right) $ . Then by using this ratio we will find the coordinates of the point of division. If the midpoint of a line segment divides the line segment in the ratio $ 1:1 $ then the coordinates of the mid-point $ P $ is $ \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right) $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




