
Find the ratio in which point P (k, 7) divides the segment joining A (8, 9) and B (1, 2). Also find k.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Use the internal section formula\[P(x,y) \equiv (\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}})\]and substitute the given values to obtain the equations for the coordinates of point P.
Convert the ratio $m:n$into $r:1$by dividing the numerator and denominator of the fractions in the RHS of the equations of the coordinates by n; and then replace \[\dfrac{m}{n}\]by r.
Find the value of r by using the equation of the y-coordinate of P to get the value of \[\dfrac{m}{n}\]. Substitute the values of m and n in the equation for k to find its value.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given three points P (k, 7), A (8, 9) and B (1, 2) such that the point P divides the segment joining the points A and B in some ratio.
We are asked to find this ratio.
Also, we can see that the x-coordinate of the point P is denoted by k.
This means that the value of k is unknown. So, we are also asked to find the value of k.
We will solve this question using the section formula.
Now, there are two types of section formula available to solve such questions based on whether the point divides the segment internally or externally.
But as we can see, in this case, it is not explicitly mentioned that the division is internal or external.
In such scenarios, we use the internal section formula which is as follows:
If a point$P \equiv (x,y)$divides the segment formed by joining the points$A \equiv ({x_1},{y_1})$and$B \equiv ({x_2},{y_2})$ in the ratio say$m:n$internally, then the coordinates of P are given by
\[P(x,y) \equiv (\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}})\]
The pictorial representation of the internal division is as follows:
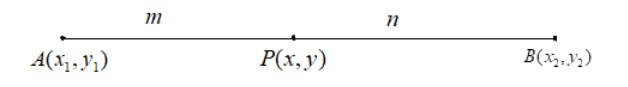
Using this section formula and substituting for the given coordinates of the points P, A, and B, we have:
\[P(k,7) \equiv (\dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}})\]
On comparing the coordinates, we get
$k = \dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}}........(1)$
$7 = \dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}}.......(2)$
But the ratio is not known, so what we can do is divide the numerator and denominator of the RHS of both the equations (1) and (2) by n
Thus, we get
$k = \dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{m}{n} + 8}}{{\dfrac{m}{n} + 1}}$
\[7 = \dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{2m}}{n} + 9}}{{\dfrac{m}{n} + 1}}\]
Now denote \[\dfrac{m}{n}\]by r.
Then the ratio becomes$r:1$
Then we get
$k = \dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{r + 8}}{{r + 1}}$
\[7 = \dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{2r + 9}}{{r + 1}}\]
Now,
\[
7 = \dfrac{{2r + 9}}{{r + 1}} \\
\Rightarrow 7(r + 1) = 2r + 9 \\
\Rightarrow 7r + 7 = 2r + 9 \\
\Rightarrow 7r - 2r = 9 - 7 = 2 \\
\Rightarrow 5r = 2 \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{2}{5} \\
\]
Therefore, we get\[\dfrac{m}{n} = \dfrac{2}{5}\]
Hence the required ratio is$2:5$.
This implies that m = 2 and n = 5.
Using these values in equation (1), we get
$k = \dfrac{{2 + 8(5)}}{{2 + 5}} = \dfrac{{2 + 40}}{{2 + 5}} = \dfrac{{42}}{7} = 6$
Hence the value of k is 6.
Note: Dividing by \[\dfrac{m}{n}\] is necessary to reduce the number of variables for easier solving of equations.
Not converting the ratio of $m:n$ in the form of $r:1$ is the key to solving such problems where the ratio and the coordinates are not known to us.
Convert the ratio $m:n$into $r:1$by dividing the numerator and denominator of the fractions in the RHS of the equations of the coordinates by n; and then replace \[\dfrac{m}{n}\]by r.
Find the value of r by using the equation of the y-coordinate of P to get the value of \[\dfrac{m}{n}\]. Substitute the values of m and n in the equation for k to find its value.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given three points P (k, 7), A (8, 9) and B (1, 2) such that the point P divides the segment joining the points A and B in some ratio.
We are asked to find this ratio.
Also, we can see that the x-coordinate of the point P is denoted by k.
This means that the value of k is unknown. So, we are also asked to find the value of k.
We will solve this question using the section formula.
Now, there are two types of section formula available to solve such questions based on whether the point divides the segment internally or externally.
But as we can see, in this case, it is not explicitly mentioned that the division is internal or external.
In such scenarios, we use the internal section formula which is as follows:
If a point$P \equiv (x,y)$divides the segment formed by joining the points$A \equiv ({x_1},{y_1})$and$B \equiv ({x_2},{y_2})$ in the ratio say$m:n$internally, then the coordinates of P are given by
\[P(x,y) \equiv (\dfrac{{m{x_2} + n{x_1}}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{m{y_2} + n{y_1}}}{{m + n}})\]
The pictorial representation of the internal division is as follows:
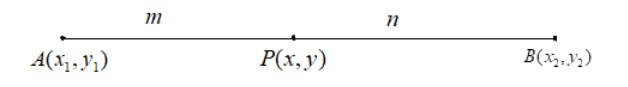
Using this section formula and substituting for the given coordinates of the points P, A, and B, we have:
\[P(k,7) \equiv (\dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}},\dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}})\]
On comparing the coordinates, we get
$k = \dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}}........(1)$
$7 = \dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}}.......(2)$
But the ratio is not known, so what we can do is divide the numerator and denominator of the RHS of both the equations (1) and (2) by n
Thus, we get
$k = \dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{m}{n} + 8}}{{\dfrac{m}{n} + 1}}$
\[7 = \dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{2m}}{n} + 9}}{{\dfrac{m}{n} + 1}}\]
Now denote \[\dfrac{m}{n}\]by r.
Then the ratio becomes$r:1$
Then we get
$k = \dfrac{{m + 8n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{r + 8}}{{r + 1}}$
\[7 = \dfrac{{2m + 9n}}{{m + n}} = \dfrac{{2r + 9}}{{r + 1}}\]
Now,
\[
7 = \dfrac{{2r + 9}}{{r + 1}} \\
\Rightarrow 7(r + 1) = 2r + 9 \\
\Rightarrow 7r + 7 = 2r + 9 \\
\Rightarrow 7r - 2r = 9 - 7 = 2 \\
\Rightarrow 5r = 2 \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{2}{5} \\
\]
Therefore, we get\[\dfrac{m}{n} = \dfrac{2}{5}\]
Hence the required ratio is$2:5$.
This implies that m = 2 and n = 5.
Using these values in equation (1), we get
$k = \dfrac{{2 + 8(5)}}{{2 + 5}} = \dfrac{{2 + 40}}{{2 + 5}} = \dfrac{{42}}{7} = 6$
Hence the value of k is 6.
Note: Dividing by \[\dfrac{m}{n}\] is necessary to reduce the number of variables for easier solving of equations.
Not converting the ratio of $m:n$ in the form of $r:1$ is the key to solving such problems where the ratio and the coordinates are not known to us.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




