
Find the range of $f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1$.
A. $\left( 0,\infty \right)$
B. $\left( 1,\infty \right)$
C. $\left( 2,\infty \right)$
D. $\left( 3,\infty \right)$
Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: We first try to find the general term for the individual exponential forms. We try to find the minimum values for the exponential form when the base is positive. So, for any $a,a > 0$ we try to find the value of ${{a}^{x}} > 0,\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$. After getting the minimum part we try to understand the maximum value possible for the same function. We get the value the exponential terms tend to get. This way we find the range of the function.
Complete step by step answer:
We have a given function of exponential form $f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1$.
There are sum of two exponentials of positive numbers 2 and 4.
We know that for any $a,a>0$ we have ${{a}^{x}}>0,\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$.
We try to find the graphical representation of ${{a}^{x}}>0,\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$.
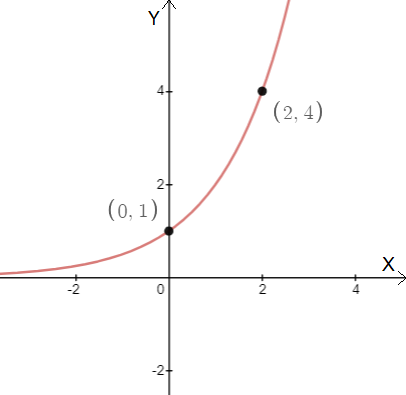
We see that the graph never goes under the X-axis for values of $a,a>0$.
So, replacing the value of a with both 2 and 4 we get ${{2}^{x}}>0$ and ${{4}^{x}}>0$.
Now, we place the minimum values of the terms in the function to find the minimum value of the whole function.
$f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1>0+0+1>1$.
The lower limiting value of the function is 1.
Now we need to find the maximum value. Again, the terms of ${{2}^{x}}$ and ${{4}^{x}}$ defines the maximum value of the function. The function is an increasing function.
If we take $g\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}}$ and the differentiation of the function $g\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}}$, we get
\[\begin{align}
& g\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{g}^{'}}\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}}\log a \\
\end{align}\]
The slope of the function is always positive as both \[{{a}^{x}}\] and \[\log a\] are positive.
The value of \[{{a}^{x}}\] keeps increasing towards $\infty $ as long we keep increasing the value of x.
This way we can say there is no maximum value of ${{2}^{x}}$ and ${{4}^{x}}$ as it tends to infinity.
Again, we place the maximum values of the terms in the function to find the minimum value of the whole function.
$f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1\to \infty +\infty +1\to \infty $.
The limiting value of the function is 1.
So, the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1$ is $\left( 1,\infty \right)$.
The correct option is B.
Note:
We need to place a point to get the idea how the exponential terms work. We mainly were trying to find the extremum values for its domain. The limit of the function is non-existent. This is not a converging sequence. The minimum value of the exponential is independent of x. it can never attain negative value. As x goes in negative for $x=-m,m>0$, we can say that ${{a}^{x}}={{a}^{-m}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{m}}}$. The value still remains positive.
Complete step by step answer:
We have a given function of exponential form $f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1$.
There are sum of two exponentials of positive numbers 2 and 4.
We know that for any $a,a>0$ we have ${{a}^{x}}>0,\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$.
We try to find the graphical representation of ${{a}^{x}}>0,\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$.

We see that the graph never goes under the X-axis for values of $a,a>0$.
So, replacing the value of a with both 2 and 4 we get ${{2}^{x}}>0$ and ${{4}^{x}}>0$.
Now, we place the minimum values of the terms in the function to find the minimum value of the whole function.
$f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1>0+0+1>1$.
The lower limiting value of the function is 1.
Now we need to find the maximum value. Again, the terms of ${{2}^{x}}$ and ${{4}^{x}}$ defines the maximum value of the function. The function is an increasing function.
If we take $g\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}}$ and the differentiation of the function $g\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}}$, we get
\[\begin{align}
& g\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{g}^{'}}\left( x \right)={{a}^{x}}\log a \\
\end{align}\]
The slope of the function is always positive as both \[{{a}^{x}}\] and \[\log a\] are positive.
The value of \[{{a}^{x}}\] keeps increasing towards $\infty $ as long we keep increasing the value of x.
This way we can say there is no maximum value of ${{2}^{x}}$ and ${{4}^{x}}$ as it tends to infinity.
Again, we place the maximum values of the terms in the function to find the minimum value of the whole function.
$f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1\to \infty +\infty +1\to \infty $.
The limiting value of the function is 1.
So, the range of the function $f\left( x \right)={{4}^{x}}+{{2}^{x}}+1$ is $\left( 1,\infty \right)$.
The correct option is B.
Note:
We need to place a point to get the idea how the exponential terms work. We mainly were trying to find the extremum values for its domain. The limit of the function is non-existent. This is not a converging sequence. The minimum value of the exponential is independent of x. it can never attain negative value. As x goes in negative for $x=-m,m>0$, we can say that ${{a}^{x}}={{a}^{-m}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{m}}}$. The value still remains positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




