
Find the quadrant, where the point of intersection of the lines \[2x - 3y = - 3, - 12 = - 4x + y\] lies.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: First we have to find the point of intersection of the given 2 lines. Next we must check the Quadrant in which the point lies.
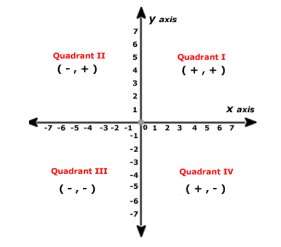
Coordinate axes divide the Cartesian plane in 4 quadrants.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: Two equations of line
\[2x - 3y = - 3\] ........ (I)
\[ - 4x + y = - 12\] ........ (II)
Now, by substitution method we solving these equations to get value of \[x,y\]
From equation (II) \[y = - 12 + 4x\] ……. (III)
Put this value in equation (I)
\[2x - 3( - 12 + 4x) = - 3\]
\[2x + 36 - 12x = - 3\]
\[36 - 10x = - 3\]
\[ - 10x = - 3 - 36\]
\[ - 10x = - 39\]
\[x = 3.9\]
Which is positive so, lies in quadrant 1
Now for find the value of by using \[x = 3.9\] in equation (III)
\[y = - 12 + 4(3.90)\]
\[y = - 12 + 15.6\]
\[y = 3.6\]
Which are positive lies in Ist quadrant
Hence, \[x = + 3.9\] & \[y = + 3.6\]
\[(x,y) = ( + 3.9, + 3.6)\] [point of intersection]
Quadrant 1 \[( + , + )\] is the correct answer.
Note: Quadrant: When the axis of two dimensional cartesian systems divide the plane into four infinite regions, then that is called quadrants, each bounded by two half axes. The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants by horizontal number of lines (the axis) and a vertical line (the axis) that intersect at a point called the origin. When Two or more lines cross each other in a plane they are called intersecting lines. The intersecting lines share a common point, which exists on all the intersecting lines and is called the point of intersection.
There are four quadrant I, II, III, IV for every quadrant sign are fixed which are for 1st it is \[( + , + )\] for 2nd \[( - , + )\], 3rd \[( - , - )\], 4th \[( + , - )\].

Coordinate axes divide the Cartesian plane in 4 quadrants.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: Two equations of line
\[2x - 3y = - 3\] ........ (I)
\[ - 4x + y = - 12\] ........ (II)
Now, by substitution method we solving these equations to get value of \[x,y\]
From equation (II) \[y = - 12 + 4x\] ……. (III)
Put this value in equation (I)
\[2x - 3( - 12 + 4x) = - 3\]
\[2x + 36 - 12x = - 3\]
\[36 - 10x = - 3\]
\[ - 10x = - 3 - 36\]
\[ - 10x = - 39\]
\[x = 3.9\]
Which is positive so, lies in quadrant 1
Now for find the value of by using \[x = 3.9\] in equation (III)
\[y = - 12 + 4(3.90)\]
\[y = - 12 + 15.6\]
\[y = 3.6\]
Which are positive lies in Ist quadrant
Hence, \[x = + 3.9\] & \[y = + 3.6\]
\[(x,y) = ( + 3.9, + 3.6)\] [point of intersection]
Quadrant 1 \[( + , + )\] is the correct answer.
Note: Quadrant: When the axis of two dimensional cartesian systems divide the plane into four infinite regions, then that is called quadrants, each bounded by two half axes. The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants by horizontal number of lines (the axis) and a vertical line (the axis) that intersect at a point called the origin. When Two or more lines cross each other in a plane they are called intersecting lines. The intersecting lines share a common point, which exists on all the intersecting lines and is called the point of intersection.
There are four quadrant I, II, III, IV for every quadrant sign are fixed which are for 1st it is \[( + , + )\] for 2nd \[( - , + )\], 3rd \[( - , - )\], 4th \[( + , - )\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




