
Find the product of:
$ C{H_2}C{H_2} - O - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - O - C{H_2} - {C_6}{H_5} + H{I_{(Excess)}} \to ? $
$ \left( A \right)OH - C{H_2}C{H_2}OH,{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2} - I,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - I \\
\left( B \right){C_6}{H_5}C{H_2} - OH,C{H_3}C{H_2} - I,C{H_3}C{H_2} - OH \\
\left( C \right)I - C{H_2}C{H_2} - I,{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2} - I,C{H_3}C{H_2} - OH \\
\left( D \right)HO - C{H_2}C{H_2} - OH,{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2} - I,C{H_3}C{H_2} - OH \\ $
Answer
535.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we are going to first see what mechanism does this reaction favors and which factors are causing the stability of the carbocation that will be formed in this case. Then after writing the reaction equation, for this reaction, we get the products that are obtained from this reaction.
Example of $ {S_N}1 $ type nucleophilic reaction.
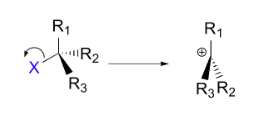
Here, in this example, the $ C - X $ bond breaks first, before the nucleophile approaches.
Complete step by step answer:
Presence of excess of $ HI $ favors the $ {S_N}1 $ mechanism.
Here, $ {S_N}1 $ follows a step by step process wherein first, the carbocation is formed from the removal of the leaving group. Then the carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile. Finally the deprotonation of the protonated nucleophile takes place to give the required product. The rate determining step of this reaction depends purely on the electrophilicity of the leaving group and is not impacted at all by the nucleophile.
So, formation of products is controlled by the stability of the carbocation resulting in the cleavage of $ C - O $ bond in protonated ether. Thus the product for given reaction are
$ {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}I,C{H_3}C{H_2}I,HOC{H_2} - C{H_2}OH $
Hence, option $ \left( A \right)OH - C{H_2}C{H_2}OH,{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2} - I,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - I $ is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to know that in order to know the products of this reaction, you must know how to differentiate between the $ {S_N}1 $ and the $ {S_N}2 $ mechanism. $ {S_N}1 $ Reactions are unimolecular proceeding through an intermediate carbocation and these reactions give racemization of stereochemistry at the reaction centre. The first step is slower in this case and therefore, determines the rate.
Example of $ {S_N}1 $ type nucleophilic reaction.

Here, in this example, the $ C - X $ bond breaks first, before the nucleophile approaches.
Complete step by step answer:
Presence of excess of $ HI $ favors the $ {S_N}1 $ mechanism.
Here, $ {S_N}1 $ follows a step by step process wherein first, the carbocation is formed from the removal of the leaving group. Then the carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile. Finally the deprotonation of the protonated nucleophile takes place to give the required product. The rate determining step of this reaction depends purely on the electrophilicity of the leaving group and is not impacted at all by the nucleophile.
So, formation of products is controlled by the stability of the carbocation resulting in the cleavage of $ C - O $ bond in protonated ether. Thus the product for given reaction are
$ {C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}I,C{H_3}C{H_2}I,HOC{H_2} - C{H_2}OH $
Hence, option $ \left( A \right)OH - C{H_2}C{H_2}OH,{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2} - I,C{H_3} - C{H_2} - I $ is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to know that in order to know the products of this reaction, you must know how to differentiate between the $ {S_N}1 $ and the $ {S_N}2 $ mechanism. $ {S_N}1 $ Reactions are unimolecular proceeding through an intermediate carbocation and these reactions give racemization of stereochemistry at the reaction centre. The first step is slower in this case and therefore, determines the rate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




