
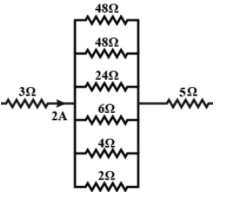
Find the potential difference across the $24\Omega $ .
A) $8$ volts
B) $4$ volts
C) $2$ volts
D) $1$ volt

Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint:You can solve this question by first finding out the net resistance of the parallel arrangement, then with its help, finding out the net resistance of the circuit and using the fact given that the current going through the circuit is $2A$, then, use this to find the potential drop across the parallel arrangement, which is the answer itself.
Complete step by step answer:
We will be proceeding with a solution exactly as told in the hint section.
Let us first find out the resultant resistance of the given parallel arrangement of resistors. For this, we need to use the following formula of resistors in parallel arrangement:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \sum {\dfrac{1}{{{R_i}}}} $
Substituting in the values that we have, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{1}{{48}} + \dfrac{1}{{48}} + \dfrac{1}{{24}} + \dfrac{1}{6} + \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{2}$
Taking LCM, we get:
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{{1 + 1 + 2 + 8 + 12 + 24}}{{48}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{{48}}{{48}} = 1\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}} \\
{R_p} = 1\,\Omega \\
$
Now, we have found out the value of the resultant resistance of the parallel arrangement of resistors.
We now need to find the value of the net resistance of the circuit using the formula:
${R_s} = \sum {{R_i}} $
Substituting in the values, we get:
${R_s} = 3 + 1 + 5 = 9\Omega $
It has been given to us that the current going through this circuit is $2A$, using this, we can find the value of applied potential difference across the given bit of the circuit as:
$V = IR$
We have been given the value of current and we found out the value of resistance ourselves, using them here, we get:
$V = 2 \times 9 = 18$ volts
Now, we know that the potential gets divided proportional to the resistances when resistors are placed in series arrangement. Hence, we can write:
${V_p} = V\left( {\dfrac{{{R_p}}}{{{R_s}}}} \right)$
Where, ${V_p}$ is the voltage across the parallel arrangement of the resistors.
Substituting the values that we found out:
${V_p} = 18\left( {\dfrac{1}{9}} \right) = 2$volts
Since all the resistors are in parallel arrangement, we know that the potential difference across each resistor in parallel arrangement is the same, and equal to the potential difference across the net parallel resistance, hence, potential difference across $24\Omega $ is $2$ volts.
Note:Many students divide the potential difference according to the resistances in parallel arrangement of resistors, which is a completely wrong thing to do. Also, you could faster the process of reaching the answer by simply multiplying the current in the circuit with the resultant parallel resistance to get the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
We will be proceeding with a solution exactly as told in the hint section.
Let us first find out the resultant resistance of the given parallel arrangement of resistors. For this, we need to use the following formula of resistors in parallel arrangement:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \sum {\dfrac{1}{{{R_i}}}} $
Substituting in the values that we have, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{1}{{48}} + \dfrac{1}{{48}} + \dfrac{1}{{24}} + \dfrac{1}{6} + \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{2}$
Taking LCM, we get:
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{{1 + 1 + 2 + 8 + 12 + 24}}{{48}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{{R_p}}} = \dfrac{{48}}{{48}} = 1\,{\Omega ^{ - 1}} \\
{R_p} = 1\,\Omega \\
$
Now, we have found out the value of the resultant resistance of the parallel arrangement of resistors.
We now need to find the value of the net resistance of the circuit using the formula:
${R_s} = \sum {{R_i}} $
Substituting in the values, we get:
${R_s} = 3 + 1 + 5 = 9\Omega $
It has been given to us that the current going through this circuit is $2A$, using this, we can find the value of applied potential difference across the given bit of the circuit as:
$V = IR$
We have been given the value of current and we found out the value of resistance ourselves, using them here, we get:
$V = 2 \times 9 = 18$ volts
Now, we know that the potential gets divided proportional to the resistances when resistors are placed in series arrangement. Hence, we can write:
${V_p} = V\left( {\dfrac{{{R_p}}}{{{R_s}}}} \right)$
Where, ${V_p}$ is the voltage across the parallel arrangement of the resistors.
Substituting the values that we found out:
${V_p} = 18\left( {\dfrac{1}{9}} \right) = 2$volts
Since all the resistors are in parallel arrangement, we know that the potential difference across each resistor in parallel arrangement is the same, and equal to the potential difference across the net parallel resistance, hence, potential difference across $24\Omega $ is $2$ volts.
Note:Many students divide the potential difference according to the resistances in parallel arrangement of resistors, which is a completely wrong thing to do. Also, you could faster the process of reaching the answer by simply multiplying the current in the circuit with the resultant parallel resistance to get the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




