
Find the point of intersection of normals at $P\left( {{t}_{1}} \right)$ and $Q\left( {{t}_{2}} \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ .
Answer
610.5k+ views
Hint: The given problem is related to the equation of normal to parabola in parametric form. The general equation of the normal to the parabola at a point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] is given by \[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\] , where \[t\] is a parameter.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the equation of the parabola as \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] .
Now, we will consider two points on the parabola given by \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] and \[Q\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] , where \[{{t}_{1}}\] , and \[{{t}_{2}}\] are parameters.
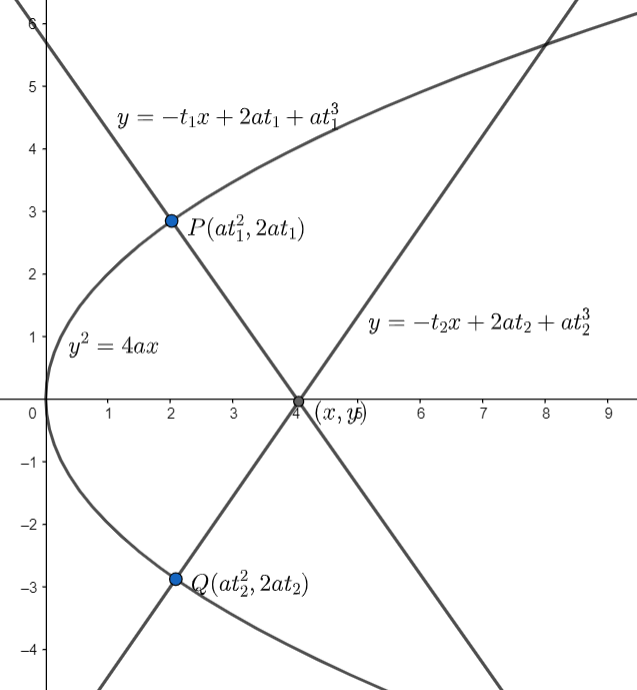
Now, we need to find the equation of normal at \[P\] and \[Q\] .
We know, the general equation of the normal to the parabola at a point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] is given by \[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\] , where \[t\] is a parameter.
So, the normal to the parabola at the point \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] will be given is given by substituting \[{{t}_{1}}\] in place of \[t\] in the general equation of the normal.
On substituting \[{{t}_{1}}\] in place of \[t\] in the general equation of the normal, we get \[y=-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}....\left( i \right)\] .
And the normal to the parabola at the point \[Q\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] is given as \[y=-{{t}_{2}}x+2a{{t}_{2}}+at_{2}^{3}....\left( ii \right)\] .
Now, to find the point of intersection of \[\left( i \right)\] and \[\left( ii \right)\] , we substitute the value of \[y\] from equation \[\left( i \right)\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\] .
On substituting the value of \[y\] from equation \[\left( i \right)\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\] , we get \[-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}=-{{t}_{2}}x+2a{{t}_{2}}+at_{2}^{3}\] .
\[\Rightarrow \left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)x=2a\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)+a\left( t_{2}^{3}-t_{1}^{3} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)x=2a\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)+a\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow x=2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
Now, we will substitute \[x=2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\] in equation \[\left( i \right)\] .
On substituting \[x=2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\] in equation \[\left( i \right)\] , we get \[y=-{{t}_{1}}\left( 2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right) \right)+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}\] .
\[=-2a{{t}_{1}}-at_{1}^{3}-at_{2}^{2}{{t}_{1}}-at_{1}^{2}{{t}_{2}}+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow y=-a{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\left( {{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
So, the point of intersection of the normal is \[\left( 2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right),-a{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\left( {{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}} \right) \right)\] .
Note: While simplifying the equations, please make sure that sign mistakes do not occur. These mistakes are very common and can confuse while solving. Ultimately the answer becomes wrong. So, sign conventions should be carefully taken.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the equation of the parabola as \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] .
Now, we will consider two points on the parabola given by \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] and \[Q\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] , where \[{{t}_{1}}\] , and \[{{t}_{2}}\] are parameters.

Now, we need to find the equation of normal at \[P\] and \[Q\] .
We know, the general equation of the normal to the parabola at a point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] is given by \[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\] , where \[t\] is a parameter.
So, the normal to the parabola at the point \[P\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] will be given is given by substituting \[{{t}_{1}}\] in place of \[t\] in the general equation of the normal.
On substituting \[{{t}_{1}}\] in place of \[t\] in the general equation of the normal, we get \[y=-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}....\left( i \right)\] .
And the normal to the parabola at the point \[Q\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\] is given as \[y=-{{t}_{2}}x+2a{{t}_{2}}+at_{2}^{3}....\left( ii \right)\] .
Now, to find the point of intersection of \[\left( i \right)\] and \[\left( ii \right)\] , we substitute the value of \[y\] from equation \[\left( i \right)\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\] .
On substituting the value of \[y\] from equation \[\left( i \right)\] in equation \[\left( ii \right)\] , we get \[-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}=-{{t}_{2}}x+2a{{t}_{2}}+at_{2}^{3}\] .
\[\Rightarrow \left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)x=2a\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)+a\left( t_{2}^{3}-t_{1}^{3} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)x=2a\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)+a\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow x=2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
Now, we will substitute \[x=2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\] in equation \[\left( i \right)\] .
On substituting \[x=2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right)\] in equation \[\left( i \right)\] , we get \[y=-{{t}_{1}}\left( 2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right) \right)+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}\] .
\[=-2a{{t}_{1}}-at_{1}^{3}-at_{2}^{2}{{t}_{1}}-at_{1}^{2}{{t}_{2}}+2a{{t}_{1}}+at_{1}^{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow y=-a{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\left( {{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
So, the point of intersection of the normal is \[\left( 2a+a\left( t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}+{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}} \right),-a{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\left( {{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}} \right) \right)\] .
Note: While simplifying the equations, please make sure that sign mistakes do not occur. These mistakes are very common and can confuse while solving. Ultimately the answer becomes wrong. So, sign conventions should be carefully taken.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




