
Find the perimeter and the area of a square, the length of whose diagonal is equal to $10\sqrt{2}$ units.
Answer
616.5k+ views
Hint: Let the side of the square be of length a unit. Draw a figure of the square with a diagonal to understand the situation. Then use the Pythagoras theorem in one of the right angled triangles to find the value of a. Use this value of a to find the area and the perimeter of the square.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given a square whose diagonal has a length equal to $10\sqrt{2}$ units.
We need to find the area and the perimeter of this square.
Let the length of a side of this square be a unit.
We already know that all the sides of a square are of equal length.
So, the length of all the sides is equal to a unit.
Let us make a figure of this square to understand the situation better.
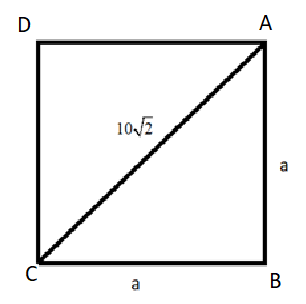
Now, we also know that all the internal angles of a square are right angles.
So, the angle B in the above figure is a right angle.
So, the triangle ABC in the above figure is a right angled triangle.
So, we will apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC.
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right angle triangle. It states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
i.e. ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$, where c is the hypotenuse and a and b are the other sides.
In triangle ABC, side AC is the hypotenuse of length $10\sqrt{2}$ units and AB and BC are the sides of length a units.
Applying the Pythagoras theorem on triangle ABC, we will get the following:${{\left( 10\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}$
$2{{a}^{2}}=200$
${{a}^{2}}=100$
\[a=10\] units.
So, the side length of the square is 10 units.
Now, area of the square = \[{{\left( side \right)}^{2}}\] = \[{{\left( 10 \right)}^{2}}=100\] sq. units
Perimeter of the square = \[4\times side=4\times 10=40\] units.
So, the area of the square is 100 sq. units and its perimeter is 40 units.
Note: In this question, it is very important to know about the Pythagoras theorem and how to apply it according to our need. Note that the fact that diagonal is $\sqrt{2}$ times the side of the square can be used directly for other questions instead of using Pythagoras theorem every time.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given a square whose diagonal has a length equal to $10\sqrt{2}$ units.
We need to find the area and the perimeter of this square.
Let the length of a side of this square be a unit.
We already know that all the sides of a square are of equal length.
So, the length of all the sides is equal to a unit.
Let us make a figure of this square to understand the situation better.

Now, we also know that all the internal angles of a square are right angles.
So, the angle B in the above figure is a right angle.
So, the triangle ABC in the above figure is a right angled triangle.
So, we will apply the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ABC.
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right angle triangle. It states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
i.e. ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$, where c is the hypotenuse and a and b are the other sides.
In triangle ABC, side AC is the hypotenuse of length $10\sqrt{2}$ units and AB and BC are the sides of length a units.
Applying the Pythagoras theorem on triangle ABC, we will get the following:${{\left( 10\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}$
$2{{a}^{2}}=200$
${{a}^{2}}=100$
\[a=10\] units.
So, the side length of the square is 10 units.
Now, area of the square = \[{{\left( side \right)}^{2}}\] = \[{{\left( 10 \right)}^{2}}=100\] sq. units
Perimeter of the square = \[4\times side=4\times 10=40\] units.
So, the area of the square is 100 sq. units and its perimeter is 40 units.
Note: In this question, it is very important to know about the Pythagoras theorem and how to apply it according to our need. Note that the fact that diagonal is $\sqrt{2}$ times the side of the square can be used directly for other questions instead of using Pythagoras theorem every time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





