
Find the orthocentre of the triangle with sides\[x + y = 6\], \[2x + y = 4\] and \[x + 2y = 5\].
A. \[\left( { - 12, - 10} \right)\]
B. \[\left( { - 11, - 10} \right)\]
C. \[\left( { - 1, - 10} \right)\]
D. \[\left( {1,10} \right)\]
Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we are required to find the orthocentre of the triangle formed by the equations of the lines. Orthocentre of a triangle is a point where the altitudes to all the sides of the triangle meet. Here, we have to first find the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines. Then, we will find the equations of perpendicular drawn from the vertices to the opposite sides.
Complete step by step solution:
Let triangles formed have vertices A, B and C.
Let \[x + y = 6\] be equation \[1\], \[2x + y = 4\] be equation \[2\] and \[x + 2y = 5\] be equation \[3\].
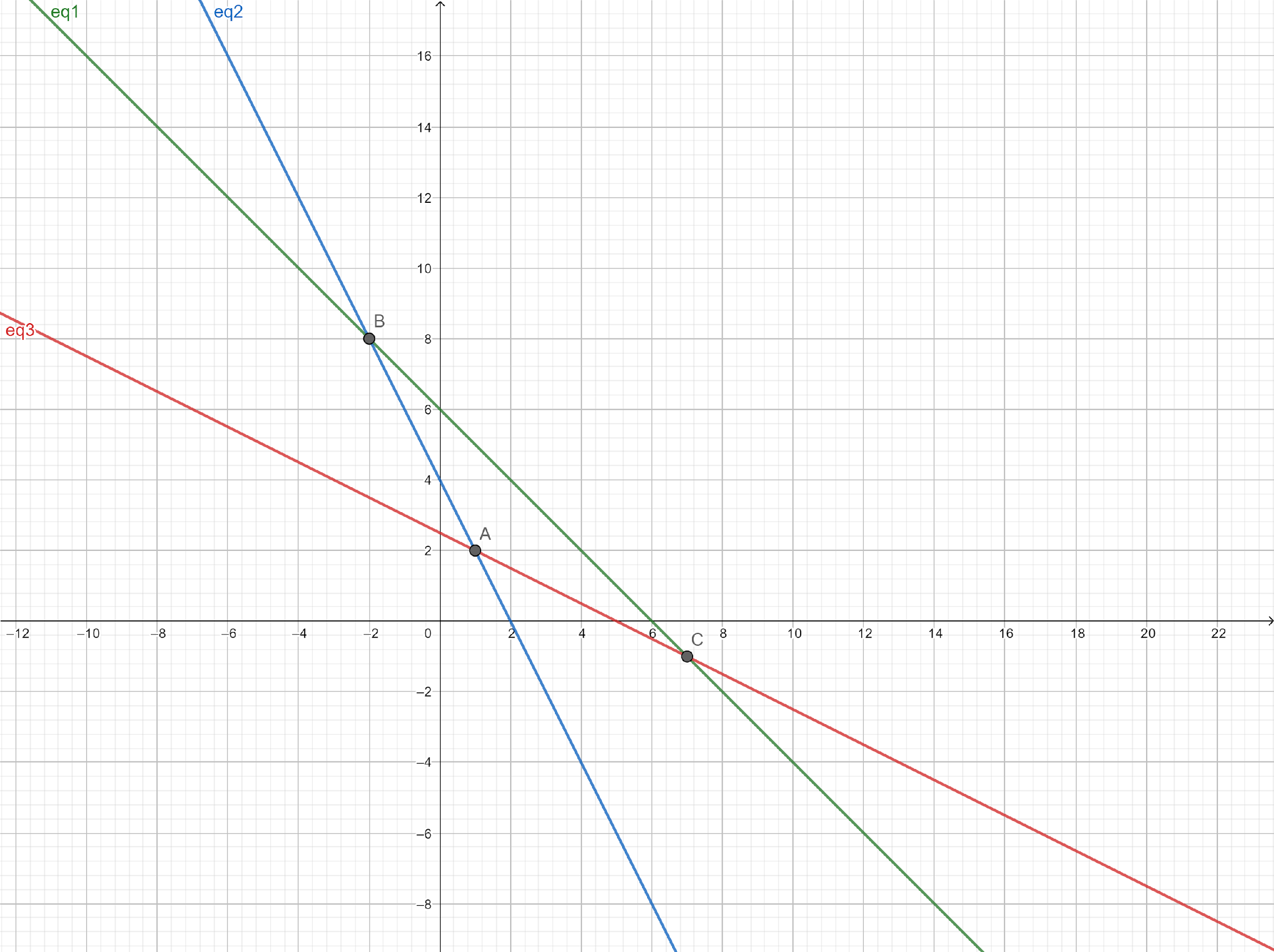
Plotting the straight lines on a graph, we can see the triangle made by the lines.
So, to find the vertices of the triangle, we need to solve the equations in pairs of two.
So, solving equation \[1\] and equation \[2\],
\[x + y = 6\] and \[2x + y = 4\]
So, subtracting equation \[1\] from \[2\],
We get, $x = - 2$.
Putting $x = - 2$ in equation \[1\], we get,
$y = 8$
So, the coordinates of B are $\left( { - 2,8} \right)$.
So, solving equation \[3\] and equation\[2\],
\[x + 2y = 5\] and \[2x + y = 4\]
So, substituting value of x from equation \[2\] into equation \[3\],
\[2\left( {5 - 2y} \right) + y = 4\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10 - 4y + y = 4\]
Rearranging the terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 3y = 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 2\]
Putting $y = 2$ in equation \[1\], we get,
$x = 5 - 2\left( 2 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = 1$
So, the coordinates of A are $\left( {1,2} \right)$.
So, solving equation \[1\] and equation\[3\],
\[x + y = 6\] and \[x + 2y = 5\]
So, subtracting equation \[1\] from \[2\],
We get, $y = - 1$.
Putting $y = - 1$ in equation \[1\], we get,
$x = 7$
So, the coordinates of C are $\left( {7, - 1} \right)$.
Now, slope of AB $ = \dfrac{{8 - \left( 2 \right)}}{{ - 2 - 1}} = \left( { - 2} \right)$
Slope of AC $ = \dfrac{{ - 1 - 2}}{{7 - 1}} = \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
So, slope of perpendicular from B $ = 2$
Slope of perpendicular from C $ = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So, the equation of altitude from C is $y = \dfrac{1}{2}x + c$. This line would pass through C. So, putting the coordinates of C so as to find the constant c.
Hence, $y = \dfrac{1}{2}x + c$
$ \Rightarrow - 1 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 7 + c$
$ \Rightarrow c = - 1 - \dfrac{7}{2} = \dfrac{{ - 9}}{2}$
So, the equation of perpendicular from C is $2y = x - 9$.
Similarly, the equation of altitude from B is $y = 2x + c$. This line would pass through A. So, putting the coordinates of B so as to find the constant c.
$ \Rightarrow 8 = 2 \times \left( { - 2} \right) + c$
$ \Rightarrow c = 12$
So, the equation of perpendicular from B is $y = 2x + 12$.
So, the orthocentre of the triangle is the intersection of the lines $2y = x - 9$ and $y = 2x + 12$. Substituting the value of y from $y = 2x + 12$ into $2y = x - 9$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( {2x + 12} \right) = x - 9$
$ \Rightarrow 4x + 24 = x - 9$
$ \Rightarrow 3x = - 33$
$ \Rightarrow x = - 11$
Putting the value of x in $2y = x - 9$, we get the value of y as $ - 10$.
Therefore, orthocentre of the triangle is (−11, −10).
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Orthocentre of a triangle is a point where all the perpendiculars from vertices of a triangle intersect. We must know how to find the vertices of a triangle when given the equation of its side so as to be able to solve the given problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Let triangles formed have vertices A, B and C.
Let \[x + y = 6\] be equation \[1\], \[2x + y = 4\] be equation \[2\] and \[x + 2y = 5\] be equation \[3\].

Plotting the straight lines on a graph, we can see the triangle made by the lines.
So, to find the vertices of the triangle, we need to solve the equations in pairs of two.
So, solving equation \[1\] and equation \[2\],
\[x + y = 6\] and \[2x + y = 4\]
So, subtracting equation \[1\] from \[2\],
We get, $x = - 2$.
Putting $x = - 2$ in equation \[1\], we get,
$y = 8$
So, the coordinates of B are $\left( { - 2,8} \right)$.
So, solving equation \[3\] and equation\[2\],
\[x + 2y = 5\] and \[2x + y = 4\]
So, substituting value of x from equation \[2\] into equation \[3\],
\[2\left( {5 - 2y} \right) + y = 4\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10 - 4y + y = 4\]
Rearranging the terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 3y = 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 2\]
Putting $y = 2$ in equation \[1\], we get,
$x = 5 - 2\left( 2 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x = 1$
So, the coordinates of A are $\left( {1,2} \right)$.
So, solving equation \[1\] and equation\[3\],
\[x + y = 6\] and \[x + 2y = 5\]
So, subtracting equation \[1\] from \[2\],
We get, $y = - 1$.
Putting $y = - 1$ in equation \[1\], we get,
$x = 7$
So, the coordinates of C are $\left( {7, - 1} \right)$.
Now, slope of AB $ = \dfrac{{8 - \left( 2 \right)}}{{ - 2 - 1}} = \left( { - 2} \right)$
Slope of AC $ = \dfrac{{ - 1 - 2}}{{7 - 1}} = \left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)$
So, slope of perpendicular from B $ = 2$
Slope of perpendicular from C $ = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So, the equation of altitude from C is $y = \dfrac{1}{2}x + c$. This line would pass through C. So, putting the coordinates of C so as to find the constant c.
Hence, $y = \dfrac{1}{2}x + c$
$ \Rightarrow - 1 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 7 + c$
$ \Rightarrow c = - 1 - \dfrac{7}{2} = \dfrac{{ - 9}}{2}$
So, the equation of perpendicular from C is $2y = x - 9$.
Similarly, the equation of altitude from B is $y = 2x + c$. This line would pass through A. So, putting the coordinates of B so as to find the constant c.
$ \Rightarrow 8 = 2 \times \left( { - 2} \right) + c$
$ \Rightarrow c = 12$
So, the equation of perpendicular from B is $y = 2x + 12$.
So, the orthocentre of the triangle is the intersection of the lines $2y = x - 9$ and $y = 2x + 12$. Substituting the value of y from $y = 2x + 12$ into $2y = x - 9$, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( {2x + 12} \right) = x - 9$
$ \Rightarrow 4x + 24 = x - 9$
$ \Rightarrow 3x = - 33$
$ \Rightarrow x = - 11$
Putting the value of x in $2y = x - 9$, we get the value of y as $ - 10$.
Therefore, orthocentre of the triangle is (−11, −10).
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Orthocentre of a triangle is a point where all the perpendiculars from vertices of a triangle intersect. We must know how to find the vertices of a triangle when given the equation of its side so as to be able to solve the given problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




