
Find the number of values of x which satisfying, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$ , where [.] denotes greatest integer function.
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this question firstly we will find out he range of $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]$and $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]$. Then, we will find out the all possible cases for which leads to $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$. Then, we will solve all the cases and find out the all possible numbers of x satisfying $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Before we start the question, let us see what is the greatest integer function and what are its properties.
Function y = [ x ] is called greatest integer function which means the greatest integer less than or equals to x. also, if n belongs to set of integer, then y = [ x ] = n if $n\le xFor example if we put x = -3.1 in y = [ x ], then y = - 4 and if we put x = 0.2 in y = [ x ], then y = 0.
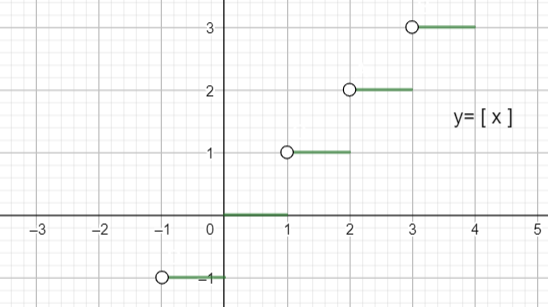
Graph of y = [ x ] is given as,
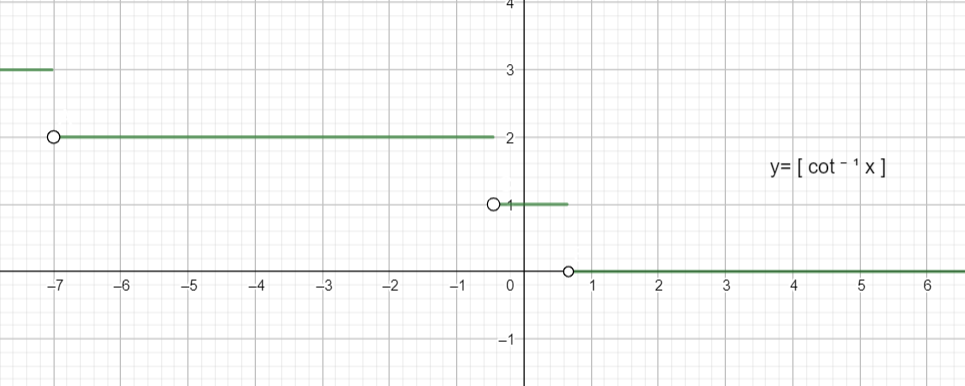
Graph of $y=[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ is given as,
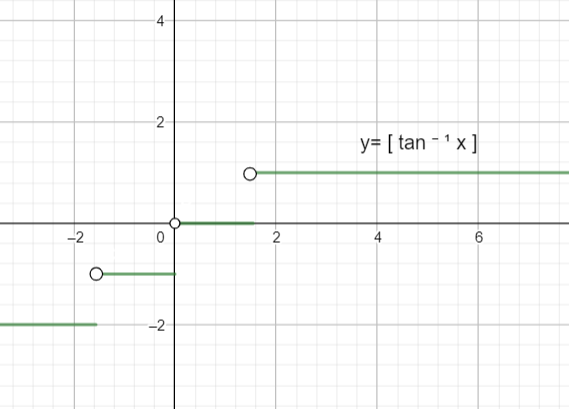
Graph of $y=[ta{{n}^{-1}}x]$ is given as
Now, in question it is asked to find the values of x such that, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$
Now, let us find the range of $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]$and $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]$
As we know that, $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}<{{\tan }^{-1}}x<\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
So, using definition of greatest integer function, we get
$\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=\{-2,-1,0,1\}$
Similarly, we know that $0<{{\cot }^{-1}}x<\pi $
So, using definition of greatest integer function, we get
$\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=\{0,1,2,3\}$
Now, we can see that to get a sum of a total of 2, we have three cases.
So, let see those cases on by one.
Case- 1
When, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=1$
We get, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=1$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$1\le {{\tan }^{-1}}x<\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Then, $x\in [\tan 1,\infty )$ …..( i ), as $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}=\infty $
For, $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=1$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$1\le {{\cot }^{-1}}x<2$
Then, $x\in (cot2,cot1]$……..( ii ) , as cot2 < cot1
So, from ( i ) and ( ii ), we get
$x\in \phi $ as cot 1 < tan 1
Hence, No solution
Case – 2
When, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=0,\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$
We get, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=0$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$0\le {{\tan }^{-1}}x<1$
Then, $x\in [\tan 0,tan1)$ …..( iii ), as $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}=\infty $
For, $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$2\le {{\cot }^{-1}}x<3$
Then, $x\in (cot3,cot2]$……..( iv ) , as cot3 < cot2
So, from ( iii ) and ( iv ), we get
$x\in \phi $, as cot 2 < tan 1
Hence, No solution
Case – 3
When, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=-1,\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=3$
We get, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=-1$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$-1\le {{\tan }^{-1}}x<0$
Then, $x\in [-\tan 1,tan0)$ …..( v ),
For, $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=3$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$3\le {{\cot }^{-1}}x<\infty $
Then, $x\in [cot3,\infty )$……..( vi ) , as $\cot 3<\infty $
So, from ( v ) and ( vi ), we get
$x\in \phi $, as cot 3 < -tan 1
Hence, No solution
So, for all three cases, we have no solution.
Then, there exist no x, such that $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$.
Hence, option ( a ) is true.
Note: Always remember that y = [ x ] = n if $n\le x< n+1$ that is $x\in [n,n+1)$. While solving the question, consider all the cases which can be solved further to get the answer according to the question. Try not to do any calculation mistake as this will change the final answer.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Before we start the question, let us see what is the greatest integer function and what are its properties.
Function y = [ x ] is called greatest integer function which means the greatest integer less than or equals to x. also, if n belongs to set of integer, then y = [ x ] = n if $n\le x
Graph of y = [ x ] is given as,

Graph of $y=[{{\cot }^{-1}}x]$ is given as,

Graph of $y=[ta{{n}^{-1}}x]$ is given as

Now, in question it is asked to find the values of x such that, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$
Now, let us find the range of $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]$and $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]$
As we know that, $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}<{{\tan }^{-1}}x<\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
So, using definition of greatest integer function, we get
$\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=\{-2,-1,0,1\}$
Similarly, we know that $0<{{\cot }^{-1}}x<\pi $
So, using definition of greatest integer function, we get
$\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=\{0,1,2,3\}$
Now, we can see that to get a sum of a total of 2, we have three cases.
So, let see those cases on by one.
Case- 1
When, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=1$
We get, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=1$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$1\le {{\tan }^{-1}}x<\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Then, $x\in [\tan 1,\infty )$ …..( i ), as $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}=\infty $
For, $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=1$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$1\le {{\cot }^{-1}}x<2$
Then, $x\in (cot2,cot1]$……..( ii ) , as cot2 < cot1
So, from ( i ) and ( ii ), we get
$x\in \phi $ as cot 1 < tan 1
Hence, No solution
Case – 2
When, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=0,\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$
We get, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=0$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$0\le {{\tan }^{-1}}x<1$
Then, $x\in [\tan 0,tan1)$ …..( iii ), as $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}=\infty $
For, $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$2\le {{\cot }^{-1}}x<3$
Then, $x\in (cot3,cot2]$……..( iv ) , as cot3 < cot2
So, from ( iii ) and ( iv ), we get
$x\in \phi $, as cot 2 < tan 1
Hence, No solution
Case – 3
When, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=-1,\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=3$
We get, $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]=-1$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$-1\le {{\tan }^{-1}}x<0$
Then, $x\in [-\tan 1,tan0)$ …..( v ),
For, $\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=3$
Using definition of greatest integer function we get
$3\le {{\cot }^{-1}}x<\infty $
Then, $x\in [cot3,\infty )$……..( vi ) , as $\cot 3<\infty $
So, from ( v ) and ( vi ), we get
$x\in \phi $, as cot 3 < -tan 1
Hence, No solution
So, for all three cases, we have no solution.
Then, there exist no x, such that $\left[ {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right]+\left[ {{\cot }^{-1}}x \right]=2$.
Hence, option ( a ) is true.
Note: Always remember that y = [ x ] = n if $n\le x< n+1$ that is $x\in [n,n+1)$. While solving the question, consider all the cases which can be solved further to get the answer according to the question. Try not to do any calculation mistake as this will change the final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




