
How do you find the missing sides and angles in the right triangle, where \[a\] is the side across from angle \[A\], \[b\] across from \[B\], and \[c\] across from the right angle, given \[a = 28\], \[c = 42\]?
Answer
557.4k+ views
Hint: We will first find the missing side by using the Pythagoras theorem. Then, we will use the law of sines and equate the unknown ratios to the known ratio. Solving the sine ratios will give us the angles of the right triangle.
The formula used:
We will use the following formulas:
Pythagoras theorem: \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}\], where \[a,b\] are the legs of a right-triangle and \[c\] is the hypotenuse.
Law of sines: \[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}}\], where \[a,b,c\] are the sides of a $\vartriangle ABC$.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that in a
$\vartriangle ABC$, \[a\] is the side across from angle \[A\], \[b\] across from \[B\], and \[c\] across from the right angle. This is illustrated in the adjoining figure:
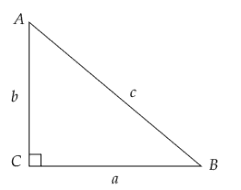
It is also given that \[a = 28\] and \[c = 42\]. We can find the side \[b\] using the Pythagoras theorem. So,
\[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {c^2} - {a^2}\]
Substituting the known values, we have
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {(42)^2} - {(28)^2}\]
Applying the exponent on the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = 1764 - 784\]
Subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = 980\]
Now, to find \[b\], we have to find the square root of \[980\]. To do this, let us prime factorize \[980\]. We have
\[980 = 2 \times 2 \times 5 \times 7 \times 7\]
When we take square root, we get
\[b = \sqrt {980} = 14\sqrt 5 \].
We have found all the sides of the triangle. We must now find the angles. Here, \[\angle C = 90^\circ \]. We have to find \[\angle A\] and \[\angle B\]. We can do this by using the Law of sines which is
\[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}}\]
Let us substitute all the known values. We have,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{28}}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{{42}}{{\sin 90^\circ }}\]
We know that \[\sin 90^\circ = 1\].
So the third ratio becomes equal to \[\dfrac{{42}}{1} = 42\].
We can equate the first and the second ratios separately to the third ratio.
Equating the first ratio to \[42\], we have
\[\dfrac{{28}}{{\sin A}} = 42\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{{28}}{{42}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) = 41.81^\circ \]
Now, let us equate the second ratio to \[42\].
\[\dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{\sin B}} = 42\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin B = \dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{42}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}} \right) = 48.19^\circ \]
Note: In the above problem, we have found the missing angles using the Law of Sines. An alternate way to find the missing angles is by simply using the ratio \[\sin \]. For example, to find \[\angle A\], we have
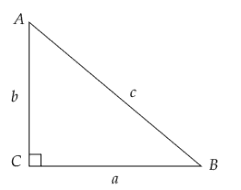
\[\sin A = \dfrac{{{\rm{opp}}{\rm{. side}}}}{{{\rm{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{a}{c}\]
Substituting the values of \[a\] and \[c\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{{28}}{{42}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) = 41.81^\circ \]
Similarly, \[\sin B = \dfrac{{{\rm{opp}}{\rm{. side}}}}{{{\rm{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{b}{c}\]
Substituting the values of \[b\] and \[c\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin B = \dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{42}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}} \right) = 48.19^\circ \].
The formula used:
We will use the following formulas:
Pythagoras theorem: \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}\], where \[a,b\] are the legs of a right-triangle and \[c\] is the hypotenuse.
Law of sines: \[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}}\], where \[a,b,c\] are the sides of a $\vartriangle ABC$.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that in a
$\vartriangle ABC$, \[a\] is the side across from angle \[A\], \[b\] across from \[B\], and \[c\] across from the right angle. This is illustrated in the adjoining figure:

It is also given that \[a = 28\] and \[c = 42\]. We can find the side \[b\] using the Pythagoras theorem. So,
\[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {c^2} - {a^2}\]
Substituting the known values, we have
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {(42)^2} - {(28)^2}\]
Applying the exponent on the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = 1764 - 784\]
Subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = 980\]
Now, to find \[b\], we have to find the square root of \[980\]. To do this, let us prime factorize \[980\]. We have
\[980 = 2 \times 2 \times 5 \times 7 \times 7\]
When we take square root, we get
\[b = \sqrt {980} = 14\sqrt 5 \].
We have found all the sides of the triangle. We must now find the angles. Here, \[\angle C = 90^\circ \]. We have to find \[\angle A\] and \[\angle B\]. We can do this by using the Law of sines which is
\[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}}\]
Let us substitute all the known values. We have,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{28}}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{{42}}{{\sin 90^\circ }}\]
We know that \[\sin 90^\circ = 1\].
So the third ratio becomes equal to \[\dfrac{{42}}{1} = 42\].
We can equate the first and the second ratios separately to the third ratio.
Equating the first ratio to \[42\], we have
\[\dfrac{{28}}{{\sin A}} = 42\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{{28}}{{42}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) = 41.81^\circ \]
Now, let us equate the second ratio to \[42\].
\[\dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{\sin B}} = 42\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin B = \dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{42}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}} \right) = 48.19^\circ \]
Note: In the above problem, we have found the missing angles using the Law of Sines. An alternate way to find the missing angles is by simply using the ratio \[\sin \]. For example, to find \[\angle A\], we have

\[\sin A = \dfrac{{{\rm{opp}}{\rm{. side}}}}{{{\rm{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{a}{c}\]
Substituting the values of \[a\] and \[c\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{{28}}{{42}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) = 41.81^\circ \]
Similarly, \[\sin B = \dfrac{{{\rm{opp}}{\rm{. side}}}}{{{\rm{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{b}{c}\]
Substituting the values of \[b\] and \[c\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin B = \dfrac{{14\sqrt 5 }}{{42}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}\]
Taking sine inverse on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}} \right) = 48.19^\circ \].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




