
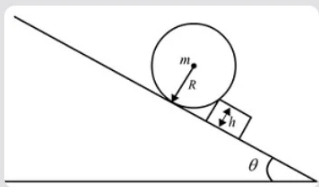
Find the minimum height of the obstacle so that the sphere can stay in equilibrium.
A. $\dfrac{R}{{1 + \cos \theta }}$
B. $\dfrac{R}{{1 + \sin \theta }}$
C. $R(1 - \sin \theta )$
D. $R(1 - \cos \theta )$

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:The sphere is on an inclined plane obstructed by an obstacle. The weight of the sphere acts downwards. The force due to weight is given as, $W = mg$. The normal force provided by the surface acts upwards and perpendicular to the sphere. The normal force is equal and opposite to the gravitational force acting on the sphere. This normal force is the force applied by the surface which prevents the sphere from falling. The normal force makes an angle with the inclined surface.
Complete step by step solution:
Given,
The mass of the sphere is $m$.
The radius of the sphere is $R$.
The height of the obstacle is $h$.
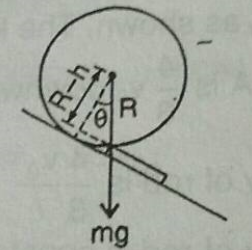
The distance from the center of sphere to the obstacle edge is $R - h$.
The angle subtended by the normal force with the obstacle is $\theta $.
The equilibrium is because of the action of weight and the normal reaction provided by the surface of the inclined plane.
The minimum height can be calculated by taking cosine of the angle as,
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{{R - h}}{R}$ …… (1)
Simplifying the equation (1) we get,
$\begin{array}{l}\cos \theta = \dfrac{{R - h}}{R}\\ \Rightarrow R\cos \theta = R - h\\ \Rightarrow h = R - R\cos \theta \\ \Rightarrow h = R(1 - \cos \theta )\end{array}$
Hence the correct answer is (D).
Note:The students have to apply the concept of normal reaction when a body is on an inclined plane or surface. In this case, the obstacle prevents the sphere from falling. The equilibrium is because of the line of action of weight and the normal reaction provided by the surface. The normal force applied by the surface prevents the sphere from falling.
Complete step by step solution:

Given,
The mass of the sphere is $m$.
The radius of the sphere is $R$.
The height of the obstacle is $h$.
The distance from the center of sphere to the obstacle edge is $R - h$.
The angle subtended by the normal force with the obstacle is $\theta $.
The equilibrium is because of the action of weight and the normal reaction provided by the surface of the inclined plane.
The minimum height can be calculated by taking cosine of the angle as,
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{{R - h}}{R}$ …… (1)
Simplifying the equation (1) we get,
$\begin{array}{l}\cos \theta = \dfrac{{R - h}}{R}\\ \Rightarrow R\cos \theta = R - h\\ \Rightarrow h = R - R\cos \theta \\ \Rightarrow h = R(1 - \cos \theta )\end{array}$
Hence the correct answer is (D).
Note:The students have to apply the concept of normal reaction when a body is on an inclined plane or surface. In this case, the obstacle prevents the sphere from falling. The equilibrium is because of the line of action of weight and the normal reaction provided by the surface. The normal force applied by the surface prevents the sphere from falling.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




