
How do you find the measure of each of the angles of a triangle given the measurements of the sides are 7, 24, 25?
Answer
546k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, we have to find the angle of each side of the triangle by using the given measurements. While observing we can easily say that the given triangle is right angle triangle on the basis of the equation of the Pythagoras' theorem later using any one of the trigonometric ratios we can find the required angles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
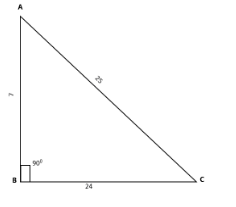
Consider the triangle given the measurements of the sides 7, 24, 25
By the Pythagoras’ theorem, on observing the measurements of triangle we can easily say that the given triangle is a right angled triangle because Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. The theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. i.e.,
\[{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}\]
Here, by the given measurements take
a=7, b=24 and c=25
\[ \Rightarrow {7^2} + {24^2} = {25^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 49 + 576 = 625\]
\[ \Rightarrow 625 = 625\]
Now consider the right angle triangle with angle B is \[{90^0}\] i.e., \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. = {90^0} = {\dfrac{\pi }{2}^c}\]
Now use the any one of the trigonometric ratio for find the remaining two angles \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \] and \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. \]
Consider the definition of sine ratio i.e.,
\[\sin A = \dfrac{{opp}}{{hyp}}\]
The length of opposite side is 7 and hypotenuse side is 25, on by substituting we get
\[ \Rightarrow \,\sin A = \dfrac{7}{{25}}\]
Taking inverse sine function on both side, then
\[ \Rightarrow \,A = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{25}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,A = {0.2838^c}\] or \[{16.26^0}\]
Now we have the two angle \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. \] and \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \] by using this we can easily find the remaining angle \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. \].
As we know the sum of the all angles of the triangle is equal to the \[{180^0}\] or \[{\pi ^c}\].
Consider the \[\Delta \,ABC\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = \pi \]
Isolate the \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = \pi - \left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. - \left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \]
Substitute the values of \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \] and \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. \], then
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = \pi - \dfrac{\pi }{2} - 0.2838\]
On simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = {1.287^c}\] or \[{73.74^0}\]
Verification
The sum of all the angles of triangle is equal to the \[{180^0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = {180^0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {16.26^0} + {90^0} + {73.74^0} = {180^0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {180^0} = {180^0}\]
Note: The sides of the triangles are different therefore the angles of the triangle will be different. The one of the triangles is \[{90^ \circ }\], hence by using the Pythagoras' theorem and the trigonometry ratios definition we solve the given problem. The theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. i.e., \[{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the triangle given the measurements of the sides 7, 24, 25
By the Pythagoras’ theorem, on observing the measurements of triangle we can easily say that the given triangle is a right angled triangle because Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. The theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. i.e.,
\[{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}\]
Here, by the given measurements take
a=7, b=24 and c=25
\[ \Rightarrow {7^2} + {24^2} = {25^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 49 + 576 = 625\]
\[ \Rightarrow 625 = 625\]
Now consider the right angle triangle with angle B is \[{90^0}\] i.e., \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. = {90^0} = {\dfrac{\pi }{2}^c}\]
Now use the any one of the trigonometric ratio for find the remaining two angles \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \] and \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. \]
Consider the definition of sine ratio i.e.,
\[\sin A = \dfrac{{opp}}{{hyp}}\]
The length of opposite side is 7 and hypotenuse side is 25, on by substituting we get
\[ \Rightarrow \,\sin A = \dfrac{7}{{25}}\]
Taking inverse sine function on both side, then
\[ \Rightarrow \,A = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{7}{{25}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,A = {0.2838^c}\] or \[{16.26^0}\]
Now we have the two angle \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. \] and \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \] by using this we can easily find the remaining angle \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. \].
As we know the sum of the all angles of the triangle is equal to the \[{180^0}\] or \[{\pi ^c}\].
Consider the \[\Delta \,ABC\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = \pi \]
Isolate the \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = \pi - \left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. - \left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \]
Substitute the values of \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. \] and \[\left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. \], then
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = \pi - \dfrac{\pi }{2} - 0.2838\]
On simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = {1.287^c}\] or \[{73.74^0}\]
Verification
The sum of all the angles of triangle is equal to the \[{180^0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \!{\underline {\,
A \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
B \,}} \right. + \left| \!{\underline {\,
C \,}} \right. = {180^0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {16.26^0} + {90^0} + {73.74^0} = {180^0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {180^0} = {180^0}\]
Note: The sides of the triangles are different therefore the angles of the triangle will be different. The one of the triangles is \[{90^ \circ }\], hence by using the Pythagoras' theorem and the trigonometry ratios definition we solve the given problem. The theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. i.e., \[{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




