
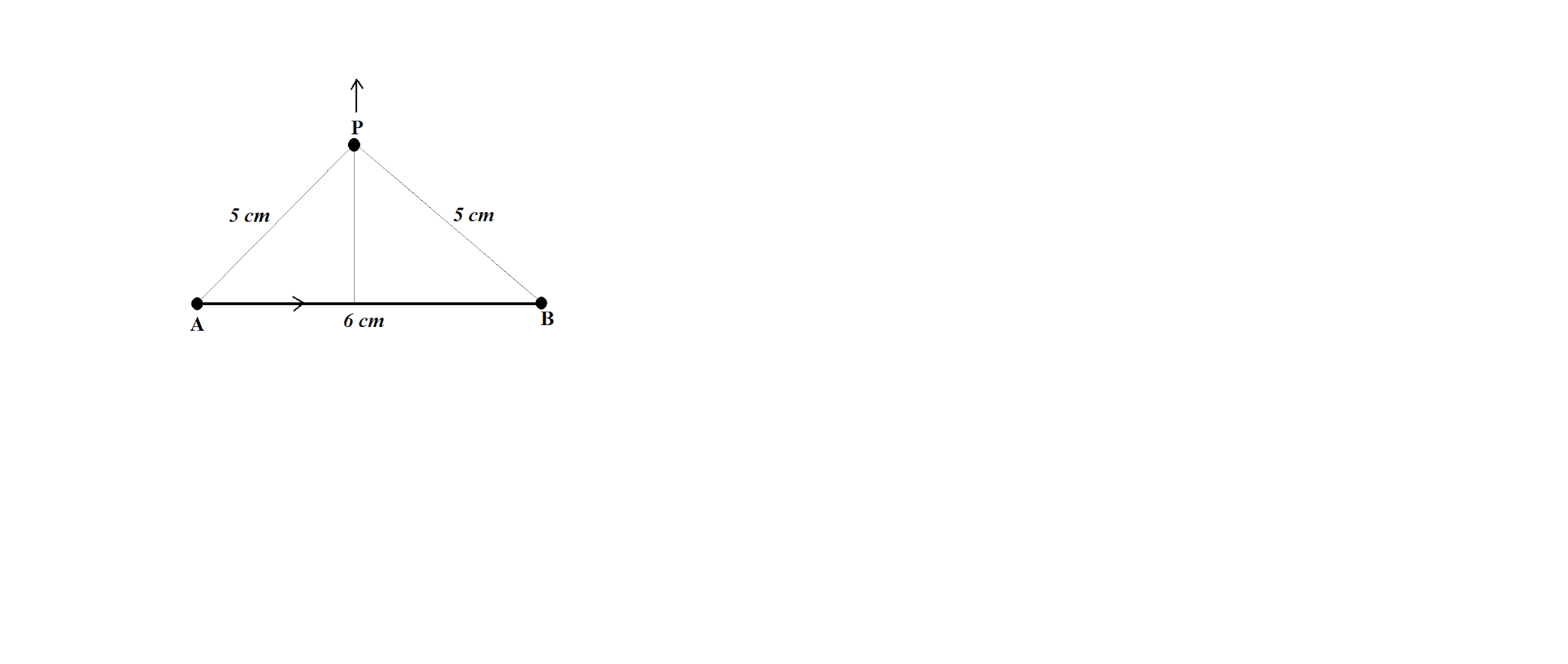
Find the magnetic field at point P due to a straight line segment $AB$ of length $6cm$ carrying a current of $5A$. (See figure)
$\left( {{\mu }_{o}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}N{{A}^{-2}} \right)$
$\text{A}\text{. }3.0\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
$\text{B}\text{. 2}\text{.5}\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
$\text{C}\text{. 2}.0\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
$\text{D}\text{. 1}.5\times {{10}^{-5}}T$

Answer
600k+ views
Hint: To find the value of magnetic field at point P, we will use the formula of magnetic field due to a straight current carrying wire segment at a point present on the equatorial axis of the segment.
Formula used:
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi r}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
Magnetic field is a vector field, or pseudo vector field, that describes the magnetic influence or impact of electric charges in relative motion with each other and effect of magnetized materials. A charge moving parallel to a current of other charges experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity. We can say that the magnetic field is the area around a magnet in which there is presence of magnetic force. Magnetic field is a type of field that passes through space and which makes a magnetic force move electric charges and magnetic dipoles.
Suppose MN is a straight conductor carrying a current $I$ and magnetic field intensity is to be determined at point X.
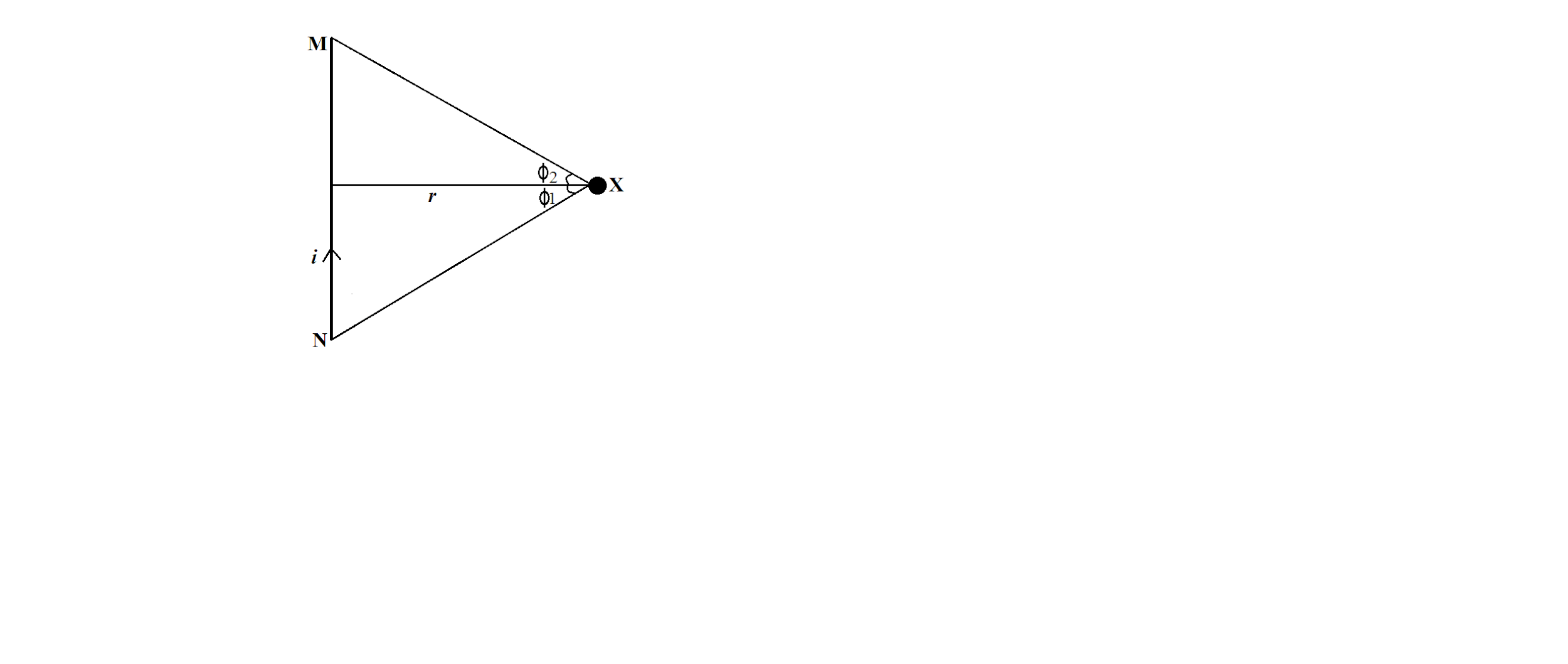
According to Biot-Savart law, magnetic field at point X is,
$\overrightarrow{dB}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I\overrightarrow{dl}\times \overrightarrow{r}}{{{r}^{3}}}$
Angle between $I\overrightarrow{dl}$ and $\overrightarrow{r}$ is \[\left( 180-\theta \right)\], so,
$dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{Idl\sin (180-\theta )}{{{r}^{2}}}$
$dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{Idl\sin \theta }{{{r}^{2}}}$
Now, $EG=EF\sin \theta =dl\sin \theta $
And, $EG=EP\sin d\phi =r\sin d\phi =rd\phi $
We get, $dl\sin \theta =rd\phi $
Therefore, $dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{Id\phi }{r}$
Also, $r=\dfrac{R}{\cos \phi }$
$dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I\cos \phi d\phi }{R}$
Total magnetic field at point X due to entire conductor is,
\[\begin{align}
& B=\int\limits_{-{{\phi }_{1}}}^{{{\phi }_{2}}}{\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{1}{R}\cos \phi d\phi } \\
& =\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I}{R}\mathop{\left[ \sin \phi \right]}_{-{{\phi }_{1}}}^{{{\phi }_{2}}}
\end{align}\]
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi r}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Magnetic field due to a finite current carrying wire is given by,
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi r}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
We are given a wire segment $AB$ of length $6cm$ carrying a current of $5A$ and we have to the find the value of magnetic field at point P
Magnetic field due to a finite current carrying wire is given by,
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi d}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Distance $d=4cm=4\times {{10}^{-2}}m$
Current $i=5A$
Angle ${{\theta }_{1}}={{\theta }_{2}}={{37}^{\circ }}$
$\sin {{\theta }_{1}}=\sin {{\theta }_{2}}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
${{\mu }_{o}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}$
Putting all the values, we get,
$B=\dfrac{5}{4\times {{10}^{-2}}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{3}{5} \right)\times {{10}^{-7}}$
$B=\dfrac{5}{4}\times 2\times \dfrac{3\times {{10}^{-7}}}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}}$
$B=1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
Value of Magnetic field at point P due to straight line segment $AB$ is $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: Students should note that the value of $d$ or $r$ in the formula of Magnetic field is the perpendicular distance from the wire to the point where we have to find the value of the Magnetic field.
Formula used:
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi r}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
Magnetic field is a vector field, or pseudo vector field, that describes the magnetic influence or impact of electric charges in relative motion with each other and effect of magnetized materials. A charge moving parallel to a current of other charges experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity. We can say that the magnetic field is the area around a magnet in which there is presence of magnetic force. Magnetic field is a type of field that passes through space and which makes a magnetic force move electric charges and magnetic dipoles.
Suppose MN is a straight conductor carrying a current $I$ and magnetic field intensity is to be determined at point X.

According to Biot-Savart law, magnetic field at point X is,
$\overrightarrow{dB}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I\overrightarrow{dl}\times \overrightarrow{r}}{{{r}^{3}}}$
Angle between $I\overrightarrow{dl}$ and $\overrightarrow{r}$ is \[\left( 180-\theta \right)\], so,
$dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{Idl\sin (180-\theta )}{{{r}^{2}}}$
$dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{Idl\sin \theta }{{{r}^{2}}}$
Now, $EG=EF\sin \theta =dl\sin \theta $
And, $EG=EP\sin d\phi =r\sin d\phi =rd\phi $
We get, $dl\sin \theta =rd\phi $
Therefore, $dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{Id\phi }{r}$
Also, $r=\dfrac{R}{\cos \phi }$
$dB=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I\cos \phi d\phi }{R}$
Total magnetic field at point X due to entire conductor is,
\[\begin{align}
& B=\int\limits_{-{{\phi }_{1}}}^{{{\phi }_{2}}}{\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{1}{R}\cos \phi d\phi } \\
& =\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{I}{R}\mathop{\left[ \sin \phi \right]}_{-{{\phi }_{1}}}^{{{\phi }_{2}}}
\end{align}\]
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi r}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Magnetic field due to a finite current carrying wire is given by,
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi r}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
We are given a wire segment $AB$ of length $6cm$ carrying a current of $5A$ and we have to the find the value of magnetic field at point P
Magnetic field due to a finite current carrying wire is given by,
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{o}}i}{4\pi d}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Distance $d=4cm=4\times {{10}^{-2}}m$
Current $i=5A$
Angle ${{\theta }_{1}}={{\theta }_{2}}={{37}^{\circ }}$
$\sin {{\theta }_{1}}=\sin {{\theta }_{2}}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
${{\mu }_{o}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}$
Putting all the values, we get,
$B=\dfrac{5}{4\times {{10}^{-2}}}\left( \dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{3}{5} \right)\times {{10}^{-7}}$
$B=\dfrac{5}{4}\times 2\times \dfrac{3\times {{10}^{-7}}}{5\times {{10}^{-2}}}$
$B=1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
Value of Magnetic field at point P due to straight line segment $AB$ is $1.5\times {{10}^{-5}}T$
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: Students should note that the value of $d$ or $r$ in the formula of Magnetic field is the perpendicular distance from the wire to the point where we have to find the value of the Magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




