
Find the length of direct common tangent
A. $ \sqrt {98} $
B. $ \sqrt {99} $
C.10
D. $ \sqrt {101} $

Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: This question can be easily answered by constructing a tangent which makes a right angle with the radius of the both circles and using this given information you will get a better approach to solution to the given problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
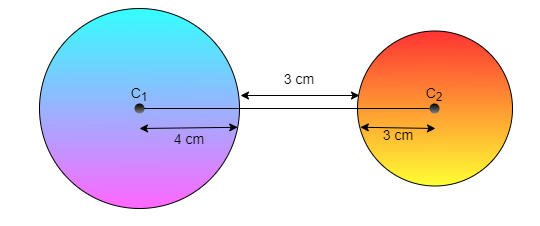
To find the solution of the given question first construct and common tangent to both the circles with center $ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ respectively and name the points that are unknown in the given diagram
So after observing the above diagram we have $ {C_1}C $ is equal to 4 cm, $ {C_2}D $ is equal to 3 cm and CD is equal to 3 cm
Since after observing the above diagram we know that the line $ {C_1}C $ and $ {C_2}D $ are also perpendicular to the radius of the circles
Constructing a line EB equal to the length of $ {C_1}{C_2} $ where E is the point on line $ A{C_1} $
So to find the length of AB we have to find the length of EB and AE
So since we know that $ EB = {C_1}{C_2} $
So EB = $ {C_1}C $ + CD + $ {C_2}D $ (equation 1)
After substituting the given values in equation 1 we get
EB = 4 + 3 + 3
$ \Rightarrow $ EB = 10 cm
And since $ A{C_1} $ is equal to AE + $ E{C_1} $ here $ E{C_1} $ is equal to $ B{C_2} $ so $ E{C_1} $ = 3 cm
Now substituting the values in the equation $ A{C_1} $ = AE + $ E{C_1} $
4 = AE + 3
$ \Rightarrow $ AE = 4 – 3
AE = 1cm
In triangle AEB by Pythagoras theorem
$ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {AE} \right)^2} + {\left( {EB} \right)^2} $
Substituting the given values in the above formula
$ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( 1 \right)^2} + {\left( {10} \right)^2} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = 1 + 100 $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ AB = \sqrt {101} $ cm
So the length of the common tangent is $ \sqrt {101} $ cm
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The concept of tangent played a main role to solve the above problem which can be explained as the line which intersect circle at one point that lie on the circumference of the circle here at the point where tangent intersect the circle, radius of the circle becomes perpendicular to the tangent. There are some basic properties that are shown by the tangent such as: the line of tangent never passes through the circle and the tangent drawn from the external points of the circle are equal to each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To find the solution of the given question first construct and common tangent to both the circles with center $ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ respectively and name the points that are unknown in the given diagram
So after observing the above diagram we have $ {C_1}C $ is equal to 4 cm, $ {C_2}D $ is equal to 3 cm and CD is equal to 3 cm
Since after observing the above diagram we know that the line $ {C_1}C $ and $ {C_2}D $ are also perpendicular to the radius of the circles
Constructing a line EB equal to the length of $ {C_1}{C_2} $ where E is the point on line $ A{C_1} $
So to find the length of AB we have to find the length of EB and AE
So since we know that $ EB = {C_1}{C_2} $
So EB = $ {C_1}C $ + CD + $ {C_2}D $ (equation 1)
After substituting the given values in equation 1 we get
EB = 4 + 3 + 3
$ \Rightarrow $ EB = 10 cm
And since $ A{C_1} $ is equal to AE + $ E{C_1} $ here $ E{C_1} $ is equal to $ B{C_2} $ so $ E{C_1} $ = 3 cm
Now substituting the values in the equation $ A{C_1} $ = AE + $ E{C_1} $
4 = AE + 3
$ \Rightarrow $ AE = 4 – 3
AE = 1cm
In triangle AEB by Pythagoras theorem
$ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {AE} \right)^2} + {\left( {EB} \right)^2} $
Substituting the given values in the above formula
$ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( 1 \right)^2} + {\left( {10} \right)^2} $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = 1 + 100 $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ AB = \sqrt {101} $ cm
So the length of the common tangent is $ \sqrt {101} $ cm
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The concept of tangent played a main role to solve the above problem which can be explained as the line which intersect circle at one point that lie on the circumference of the circle here at the point where tangent intersect the circle, radius of the circle becomes perpendicular to the tangent. There are some basic properties that are shown by the tangent such as: the line of tangent never passes through the circle and the tangent drawn from the external points of the circle are equal to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





