
How do you find the length of $a$ and $b$ of a right triangle using angles of $A$ and $B$ and the distance from $c$ to $C$? The angles of $A$ and $B$ are ${{45}^{\circ }}$ with $C$ being ${{90}^{\circ }}$ and the distance from $C$ to the hypotenuse $c$ is 22. \[\]
Answer
562.5k+ views
Hint: We see that triangle ABC is isosceles right angled triangle and the perpendicular dropped from apex C will bisect the angle C. We denote the foot of the perpendicular as D. We use sine law in triangle BCD to find $a$ and equality of sides opposite equal angles to find $b$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
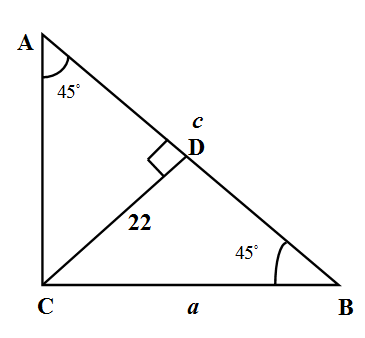
We know from sine law triangles that the ratios of sides of triangles with sine of the opposite angles are equal. If $a,b,c$ be the lengths of the sides and $A,B,C$ are measures of the angles opposite to them respectively then we have
$\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$\[\]
We are given the right angled triangle ABC whose measure of angles are given to us as $A={{45}^{\circ }},B={{45}^{\circ }},C={{90}^{\circ }}$. We are also given the lengths of the sides opposite to them respectively as $a,b,c$. We are given the distance between the vertex C and the hypotenuse $c$ as 22 units. We have denoted the foot of the perpendicular from $C$ to $c$ as D.
We know that in a triangle lengths of sides opposite to equal angles are equal. So in triangle ABC sides opposite to equal angles $A=B={{45}^{\circ }}$ are
\[a=b.......\left( 1 \right)\]
So the triangle is ABC isosceles whose apex is C. We know that in an isosceles triangle the perpendicular dropped from the apex opposite side bisects the angle the apex. So in triangle ABC the perpendicular CD will bisect C. So we have
\[\angle ACD=\angle BCD=\dfrac{{{90}^{\circ }}}{2}={{45}^{\circ }}\]
We use sine law in triangle BCD to have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{BC}{\sin \left( \angle BCD \right)}=\dfrac{CD}{\sin \left( \angle CBD \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{\sin {{90}^{\circ }}}=\dfrac{22}{\sin {{45}^{\circ }}} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{22}{\sin {{45}^{\circ }}}\times \sin {{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{22}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}\times 1=22\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}\]
So we have from (1) required length as
\[a=b=22\sqrt{2}\]
Note: We can also use sine law in triangle ACD to first find $b=22\sqrt{2}$. We should remember that in the isosceles triangle the vertex which shares sides of equal length is called apex and the median and altitude drawn from apex to opposite side are the same. We can find the length of hypotenuse $c$ using Pythagoras theorem $c=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=44$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:

We know from sine law triangles that the ratios of sides of triangles with sine of the opposite angles are equal. If $a,b,c$ be the lengths of the sides and $A,B,C$ are measures of the angles opposite to them respectively then we have
$\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}$\[\]
We are given the right angled triangle ABC whose measure of angles are given to us as $A={{45}^{\circ }},B={{45}^{\circ }},C={{90}^{\circ }}$. We are also given the lengths of the sides opposite to them respectively as $a,b,c$. We are given the distance between the vertex C and the hypotenuse $c$ as 22 units. We have denoted the foot of the perpendicular from $C$ to $c$ as D.
We know that in a triangle lengths of sides opposite to equal angles are equal. So in triangle ABC sides opposite to equal angles $A=B={{45}^{\circ }}$ are
\[a=b.......\left( 1 \right)\]
So the triangle is ABC isosceles whose apex is C. We know that in an isosceles triangle the perpendicular dropped from the apex opposite side bisects the angle the apex. So in triangle ABC the perpendicular CD will bisect C. So we have
\[\angle ACD=\angle BCD=\dfrac{{{90}^{\circ }}}{2}={{45}^{\circ }}\]
We use sine law in triangle BCD to have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{BC}{\sin \left( \angle BCD \right)}=\dfrac{CD}{\sin \left( \angle CBD \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{\sin {{90}^{\circ }}}=\dfrac{22}{\sin {{45}^{\circ }}} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{22}{\sin {{45}^{\circ }}}\times \sin {{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{22}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}\times 1=22\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}\]
So we have from (1) required length as
\[a=b=22\sqrt{2}\]
Note: We can also use sine law in triangle ACD to first find $b=22\sqrt{2}$. We should remember that in the isosceles triangle the vertex which shares sides of equal length is called apex and the median and altitude drawn from apex to opposite side are the same. We can find the length of hypotenuse $c$ using Pythagoras theorem $c=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}=44$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




