
How do you find the inverse of \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\] and graph both \[f\] and \[{{f}^{-1}}\]?
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Any function \[f\] can have its inverse function \[{{f}^{-1}}\] if and only if the function \[f\] is bijective. A bijective function is both one-one function and onto function. That is, each image of \[f\] has a distinct preimage and the co-domain of \[f\] is equal to the range of the function \[f\]. We find the inverse function \[{{f}^{-1}}\] by considering the function \[f\] to be y, expressing x in terms of y and then replacing y with x. One can verify the obtained inverse function \[{{f}^{-1}}\] by an important fact that the composition of functions \[f\] and \[{{f}^{-1}}\] which is \[f\circ {{f}^{-1}}(x)\] gives x itself.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, the function \[f\] is given as \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\]. Let \[f(x)\] be y that is,
\[f(x)=y=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\]
Taking \[\left( x\text{ }\text{ }-2 \right)\] to the left-hand side, we get
\[\Rightarrow y(x-2)=x+1\]
Then on expansion, we can write
\[\Rightarrow yx\text{ }\text{ }-2y\text{ }=\text{ }x+1\]
Rearranging the terms to simplify the equation by taking variable x as common, we get
\[\Rightarrow yx\text{ }\text{ }-x\text{ }=\text{ }2y\text{ }+\text{ }1\]
By taking x common, we get
\[\Rightarrow x\left( y\text{ }\text{ }-1 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }2y\text{ }+\text{ }1\]
Now, we write x in terms of y as
\[\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2y+1}{y-1}\]
Therefore, \[{{f}^{-1}}(x)=\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\]. (on replacing y with x)
Verification: -
\[f\left( {{f}^{-1}}(x) \right)=f\left( \dfrac{2x+1}{x-1} \right)=\dfrac{\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}+1}{\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}-2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{2x+1+x-1}{2x+1-2x+2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3\dfrac{x}{3}\Rightarrow x\]
Hence, verified.
By substituting different values of x in \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\], we get points lying on the given function. On tracing these points on the xy – plane and joining them gives an approximate graph of \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\]. It will same as shown in the figure below:
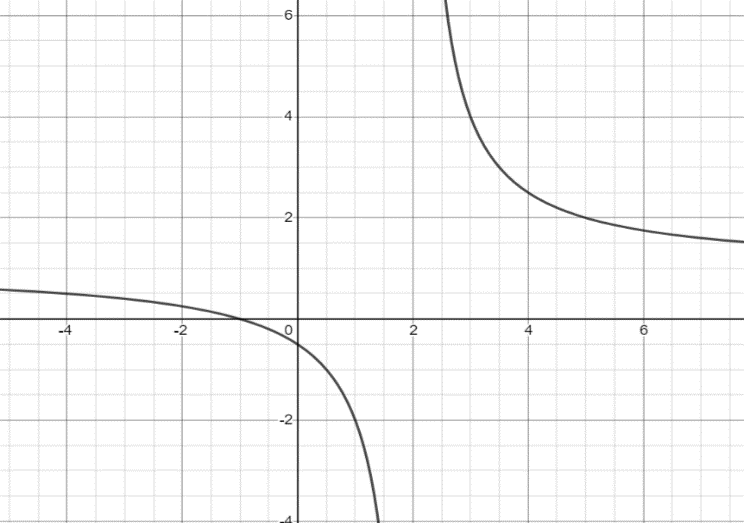
\[\Rightarrow \] undefined at x=2
Similarly, we get the graph of \[{{f}^{-1}}\] as shown below:
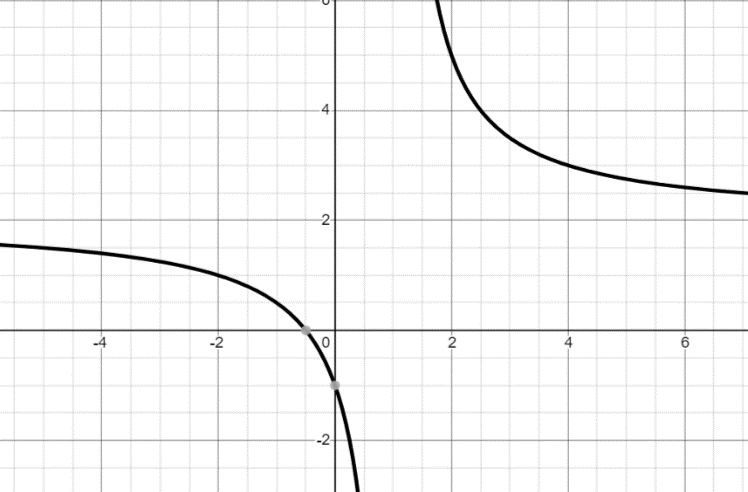
\[\Rightarrow \] undefined at y=2
Note: Common errors while composing functions: Students sometimes forget where each of the functions is defined before composing functions, which lead to non – existing results. They also sometimes forget that composition is not a commutative operation that is, \[f\circ g\ne g\circ f\]. Also, the graphs of \[f\] and \[{{f}^{-1}}\] are symmetric about the line \[y=x\].
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, the function \[f\] is given as \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\]. Let \[f(x)\] be y that is,
\[f(x)=y=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\]
Taking \[\left( x\text{ }\text{ }-2 \right)\] to the left-hand side, we get
\[\Rightarrow y(x-2)=x+1\]
Then on expansion, we can write
\[\Rightarrow yx\text{ }\text{ }-2y\text{ }=\text{ }x+1\]
Rearranging the terms to simplify the equation by taking variable x as common, we get
\[\Rightarrow yx\text{ }\text{ }-x\text{ }=\text{ }2y\text{ }+\text{ }1\]
By taking x common, we get
\[\Rightarrow x\left( y\text{ }\text{ }-1 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }2y\text{ }+\text{ }1\]
Now, we write x in terms of y as
\[\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2y+1}{y-1}\]
Therefore, \[{{f}^{-1}}(x)=\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\]. (on replacing y with x)
Verification: -
\[f\left( {{f}^{-1}}(x) \right)=f\left( \dfrac{2x+1}{x-1} \right)=\dfrac{\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}+1}{\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}-2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{2x+1+x-1}{2x+1-2x+2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3\dfrac{x}{3}\Rightarrow x\]
Hence, verified.
By substituting different values of x in \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\], we get points lying on the given function. On tracing these points on the xy – plane and joining them gives an approximate graph of \[f(x)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\]. It will same as shown in the figure below:

\[\Rightarrow \] undefined at x=2
Similarly, we get the graph of \[{{f}^{-1}}\] as shown below:

\[\Rightarrow \] undefined at y=2
Note: Common errors while composing functions: Students sometimes forget where each of the functions is defined before composing functions, which lead to non – existing results. They also sometimes forget that composition is not a commutative operation that is, \[f\circ g\ne g\circ f\]. Also, the graphs of \[f\] and \[{{f}^{-1}}\] are symmetric about the line \[y=x\].
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




